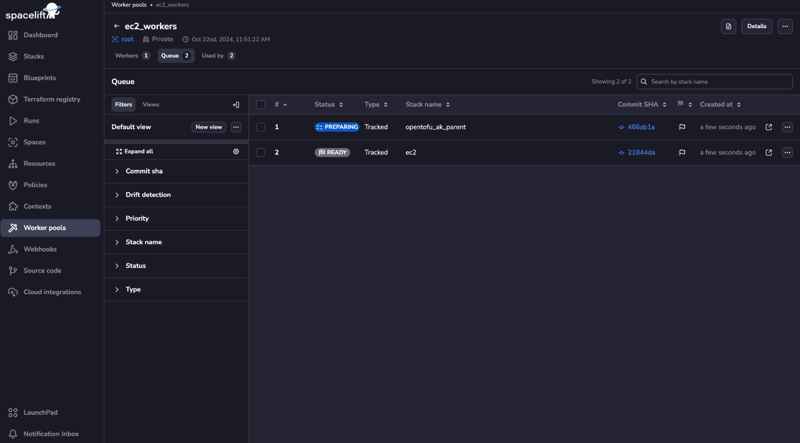
Spacelift Private Workers vs. Public Workers
If you are working with orchestration platforms, CI/CD pipelines, and infrastructure in general, one question that comes to mind is how you handle your workflows. While this is a pretty generic question and can cover anything from the integration to how you actually do the deployments, there is one important thing that doesn’t get talked about enough: the underlying infrastructure used by your workflows. In this post, we will explore what public and private workers, their benefits, and how Spacelift features are leveraging them. What is a worker? When you are building a workflow, you need computing power behind the scenes to handle the different tasks you require. This is where workers or runners come into play, as they will be the ones that handle all the tasks your workflows go through. In Spacelift, a worker is an entity that processes a single run at a time, meaning that the number of workers you can use will be equal to the number of the maximum concurrency that you can obtain. What is the difference between public and private workers? In SaaS, public workers are managed by your SaaS provider, while private workers are managed by the customer. By default, Spacelift uses a public worker pool, which is hosted and operated by Spacelift. The main benefits of using public workers are: Zero maintenance -- everything will be handled by Spacelift (patching, updates, etc.) No setup is required; you can use them out of the box Predictable performance Built-in security measures This makes the process very convenient, but to adhere to all of your security requirements, you can leverage private workers that are hosted in your environments. This doesn't mean, however, that Spacelift's public worker pool is not secure, but private workers are meant to offer you the flexibility you need. What are the benefits of using private workers? Private workers offer you complete control over where your workflow runs, and based on how you configure them, they can give you direct access to private networks, enhanced security and isolation, compliance with strict policies, support for the air-gapped environment, and more. From a network perspective, private workers excel at providing better isolation and security. You can implement precise network configurations, establish custom firewall rules, and define specific security groups and network access control lists that align with your organization's security requirements. They are key for environments where compliance is a top priority. For industries such as finance, health, and government, where operating in air-gapped environments is a must, taking advantage of private workers ensures there are no external threats and vulnerabilities are limited. If you are thinking about performance, private workers are also a great option because you can allocate how much computing power and memory you want. In this way, you ensure that you can handle intensive tasks better than in a shared environment. At the same time, with private workers, you can ensure that high-priority operations can execute reliably without any performance bottlenecks. Spacelift allows you to set priorities inside your running queue, ensuring that critical tasks receive immediate attention while less urgent ones are queued. With private workers, you can enable better debugging and troubleshooting capabilities because you have full access to the worker environment. This allows you to pinpoint issues, monitor different metrics, and optimize configurations accordingly. One of the best aspects of leveraging private workers is related to scalability. You can dynamically adjust the number of workers on demand, spinning up additional workers to handle your high-load periods and spinning down the workers when the load is low. By leveraging this elasticity, you ensure that you're not overprovisioning while maintaining the ability to handle peak workloads. What are the limitations of using private workers? Private workers will require internal maintenance, meaning that patching, updates and all the security responsibilities fall on your team. This can also introduce operational overhead, but the good news is that their creation can be easily automated, simplifying at the same time, all the maintenance operations.
If you are working with orchestration platforms, CI/CD pipelines, and infrastructure in general, one question that comes to mind is how you handle your workflows. While this is a pretty generic question and can cover anything from the integration to how you actually do the deployments, there is one important thing that doesn’t get talked about enough: the underlying infrastructure used by your workflows.
In this post, we will explore what public and private workers, their benefits, and how Spacelift features are leveraging them.
What is a worker?
When you are building a workflow, you need computing power behind the scenes to handle the different tasks you require. This is where workers or runners come into play, as they will be the ones that handle all the tasks your workflows go through.
In Spacelift, a worker is an entity that processes a single run at a time, meaning that the number of workers you can use will be equal to the number of the maximum concurrency that you can obtain.
What is the difference between public and private workers?
In SaaS, public workers are managed by your SaaS provider, while private workers are managed by the customer. By default, Spacelift uses a public worker pool, which is hosted and operated by Spacelift.
The main benefits of using public workers are:
- Zero maintenance -- everything will be handled by Spacelift (patching, updates, etc.)
- No setup is required; you can use them out of the box
- Predictable performance
- Built-in security measures
This makes the process very convenient, but to adhere to all of your security requirements, you can leverage private workers that are hosted in your environments.
This doesn't mean, however, that Spacelift's public worker pool is not secure, but private workers are meant to offer you the flexibility you need.
What are the benefits of using private workers?
Private workers offer you complete control over where your workflow runs, and based on how you configure them, they can give you direct access to private networks, enhanced security and isolation, compliance with strict policies, support for the air-gapped environment, and more.
From a network perspective, private workers excel at providing better isolation and security. You can implement precise network configurations, establish custom firewall rules, and define specific security groups and network access control lists that align with your organization's security requirements.
They are key for environments where compliance is a top priority. For industries such as finance, health, and government, where operating in air-gapped environments is a must, taking advantage of private workers ensures there are no external threats and vulnerabilities are limited.
If you are thinking about performance, private workers are also a great option because you can allocate how much computing power and memory you want. In this way, you ensure that you can handle intensive tasks better than in a shared environment. At the same time, with private workers, you can ensure that high-priority operations can execute reliably without any performance bottlenecks.
Spacelift allows you to set priorities inside your running queue, ensuring that critical tasks receive immediate attention while less urgent ones are queued.
With private workers, you can enable better debugging and troubleshooting capabilities because you have full access to the worker environment. This allows you to pinpoint issues, monitor different metrics, and optimize configurations accordingly.
One of the best aspects of leveraging private workers is related to scalability. You can dynamically adjust the number of workers on demand, spinning up additional workers to handle your high-load periods and spinning down the workers when the load is low. By leveraging this elasticity, you ensure that you're not overprovisioning while maintaining the ability to handle peak workloads.
What are the limitations of using private workers?
Private workers will require internal maintenance, meaning that patching, updates and all the security responsibilities fall on your team. This can also introduce operational overhead, but the good news is that their creation can be easily automated, simplifying at the same time, all the maintenance operations.
_JIRAROJ_PRADITCHAROENKUL_Alamy.jpg?#)

































































![Sonos Abandons Streaming Device That Aimed to Rival Apple TV [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96703/96703/96703-640.jpg)
![HomePod With Display Delayed to Sync With iOS 19 Redesign [Kuo]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96702/96702/96702-640.jpg)
![iPhone 17 Air to Measure 9.5mm Thick Including Camera Bar [Rumor]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96699/96699/96699-640.jpg)



































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 139]: The Government Knows AGI Is Coming, Superintelligence Strategy, OpenAI’s $20,000 Per Month Agents & Top 100 Gen AI Apps](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20139%20cover-2.png)


![[The AI Show Episode 138]: Introducing GPT-4.5, Claude 3.7 Sonnet, Alexa+, Deep Research Now in ChatGPT Plus & How AI Is Disrupting Writing](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20138%20cover.png)