How to Create Fully Styled Forms in Tailwind CSS (Including Validation)
Forms are an essential part of web development, allowing users to interact with your application by submitting data. Whether it's a login form, a registration form, or a contact form, styling and validating these forms is crucial for a good user experience. In this blog post, we'll explore how to create fully styled forms using Tailwind CSS, a utility-first CSS framework, and how to add validation to ensure the data submitted is correct. Why Tailwind CSS? Tailwind CSS is a highly customizable, low-level CSS framework that provides utility classes to build designs directly in your markup. It allows you to create responsive, modern, and fully styled components without writing custom CSS. Tailwind's utility-first approach makes it easy to style forms quickly and consistently. Setting Up Tailwind CSS Before we dive into creating forms, let's ensure you have Tailwind CSS set up in your project. 1. Install Tailwind CSS If you haven't already installed Tailwind CSS, you can do so using npm or yarn: npm install tailwindcss 2. Configure Tailwind Generate a tailwind.config.js file: npx tailwindcss init 3. Include Tailwind in Your CSS Create a CSS file (e.g., styles.css) and include Tailwind's base, components, and utilities: @tailwind base; @tailwind components; @tailwind utilities; 4. Build Your CSS Use a build tool like PostCSS to process your CSS file: npx tailwindcss -i ./src/styles.css -o ./dist/output.css --watch Now you're ready to start building forms with Tailwind CSS! Creating a Basic Form Let's start by creating a simple contact form with fields for name, email, and message. Name Email Message Submit Explanation: Container Styling: The form is wrapped in a div with max-w-md, mx-auto, and p-6 to center it and add padding. Input Fields: Each input field is styled with Tailwind's utility classes for width, padding, borders, and focus states. Submit Button: The button is styled with a background color, hover effect, and focus ring. Adding Validation Validation is crucial to ensure users submit correct data. We'll use HTML5 validation attributes and Tailwind CSS to style validation states. 1. HTML5 Validation Attributes Add required and type attributes to enforce validation: 2. Styling Invalid Fields Tailwind doesn't provide built-in classes for invalid states, but you can use the :invalid pseudo-class in your CSS: input:invalid, textarea:invalid { border-color: #f87171; /* Red border for invalid fields */ } Alternatively, you can use JavaScript to dynamically add classes for invalid fields. 3. Displaying Validation Messages Use JavaScript to display custom validation messages: Email Please enter a valid email address. Add JavaScript to handle validation: document.querySelector('form').addEventListener('submit', (e) => { const emailInput = document.getElementById('email'); const emailError = document.getElementById('email-error'); if (!emailInput.checkValidity()) { e.preventDefault(); emailError.classList.remove('hidden'); } else { emailError.classList.add('hidden'); } }); Enhancing the Form with Tailwind Plugins Tailwind CSS can be extended with plugins to add additional functionality. For example, you can use the @tailwindcss/forms plugin to style form elements consistently. 1. Install the Plugin npm install @tailwindcss/forms 2. Add the Plugin to tailwind.config.js module.exports = { plugins: [ require('@tailwindcss/forms'), ], }; 3. Use the Plugin The plugin provides default styles for form elements, making it easier to style inputs, checkboxes, and radio buttons. Final Example: A Fully Styled and Validated Form Here's the complete code for a fully styled and validated form: Name Please enter your name. Email Please enter a valid email address. Message Please enter a message. Submit document.querySelector('form').addEventListener('submit', (e) => { const nameInput = document.getElementById('name'); const emailInput = document.getElementById('email'); const messageInput = document.getElementById('message'); const nameError = document.getElementById('name-error'); const emailError = document.getElementById('email-error'); const messageError = document.getElementById('message-error'); if (!nameInput.checkValidity()) { e.preventDefault(); nameError.classList.remove('hidden'); } else { nameError.classList.add('hidden'); } if (!emailInput.checkValidity()) { e.preventDefault(); emailError.classList.remove('hidden'); } else { emailError.

Forms are an essential part of web development, allowing users to interact with your application by submitting data. Whether it's a login form, a registration form, or a contact form, styling and validating these forms is crucial for a good user experience. In this blog post, we'll explore how to create fully styled forms using Tailwind CSS, a utility-first CSS framework, and how to add validation to ensure the data submitted is correct.
Why Tailwind CSS?
Tailwind CSS is a highly customizable, low-level CSS framework that provides utility classes to build designs directly in your markup. It allows you to create responsive, modern, and fully styled components without writing custom CSS. Tailwind's utility-first approach makes it easy to style forms quickly and consistently.
Setting Up Tailwind CSS
Before we dive into creating forms, let's ensure you have Tailwind CSS set up in your project.
1. Install Tailwind CSS
If you haven't already installed Tailwind CSS, you can do so using npm or yarn:
npm install tailwindcss
2. Configure Tailwind
Generate a tailwind.config.js file:
npx tailwindcss init
3. Include Tailwind in Your CSS
Create a CSS file (e.g., styles.css) and include Tailwind's base, components, and utilities:
@tailwind base;
@tailwind components;
@tailwind utilities;
4. Build Your CSS
Use a build tool like PostCSS to process your CSS file:
npx tailwindcss -i ./src/styles.css -o ./dist/output.css --watch
Now you're ready to start building forms with Tailwind CSS!
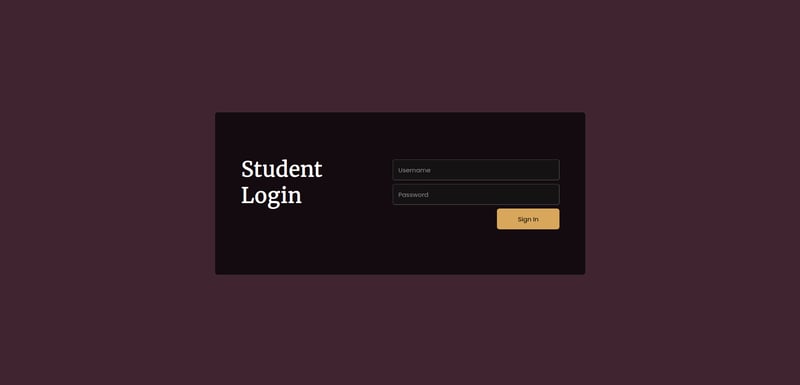
Creating a Basic Form
Let's start by creating a simple contact form with fields for name, email, and message.
class="max-w-md mx-auto p-6 bg-white shadow-md rounded-lg">
class="mb-4">
for="name" class="block text-gray-700 text-sm font-bold mb-2">Name
type="text"
id="name"
name="name"
class="w-full px-3 py-2 border border-gray-300 rounded-md focus:outline-none focus:ring-2 focus:ring-blue-500"
placeholder="Enter your name"
/>































































![iFixit Tears Down New M4 MacBook Air [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96717/96717/96717-640.jpg)

![Apple Officially Announces Return of 'Ted Lasso' for Fourth Season [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96710/96710/96710-640.jpg)













![[Update: Fix] Chromecast (2nd gen) and Audio can’t Cast in ‘Untrusted’ outage](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2019/08/chromecast_audio_1.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)





















































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 139]: The Government Knows AGI Is Coming, Superintelligence Strategy, OpenAI’s $20,000 Per Month Agents & Top 100 Gen AI Apps](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20139%20cover-2.png)


![[The AI Show Episode 138]: Introducing GPT-4.5, Claude 3.7 Sonnet, Alexa+, Deep Research Now in ChatGPT Plus & How AI Is Disrupting Writing](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20138%20cover.png)





































































































































.jpg?#)