New RSV vaccine, treatment linked to dramatic fall in baby hospitalizations
CDC study finds big declines in hospitalizations—and they may be underestimates.
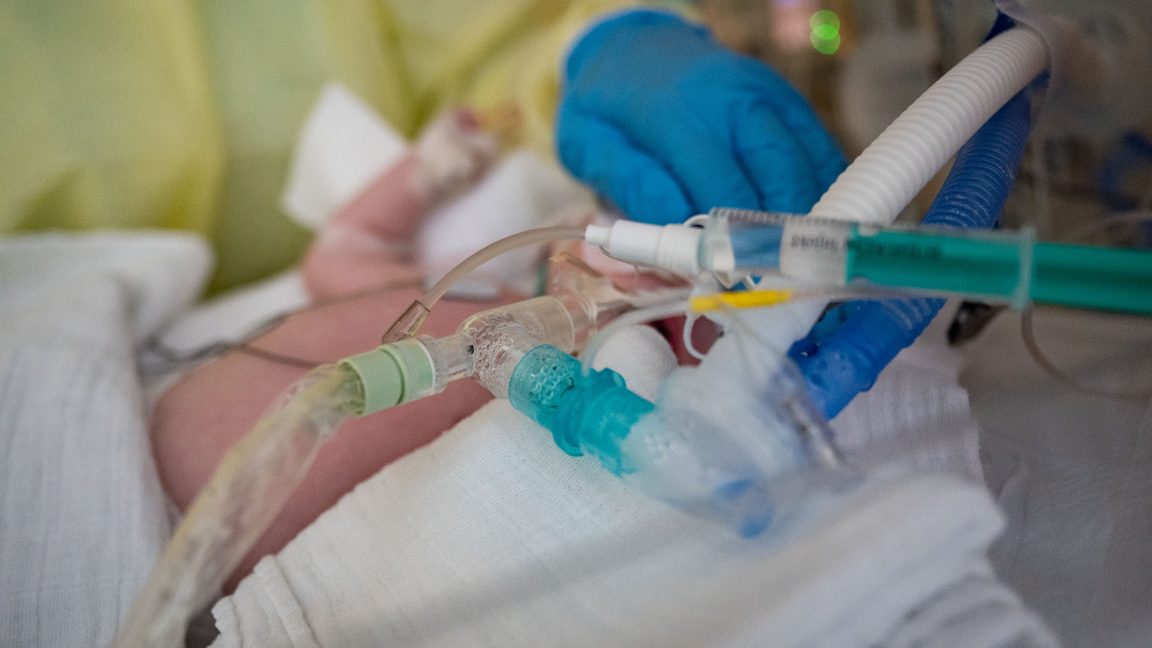
Far fewer babies went to the hospital struggling to breathe from RSV, a severe respiratory infection, after the debut of a new vaccine and treatment this season, according to an analysis published today by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
RSV, or respiratory syncytial (sin-SISH-uhl) virus, is the leading cause of hospitalization for infants in the US. An estimated 58,000–80,000 children younger than 5 years old are hospitalized each year. Newborns—babies between 0 and 2 months—are the most at risk of being hospitalized with RSV. The virus circulates seasonally, typically rising in the fall and peaking in the winter, like many other respiratory infections.
But the 2024–2025 season was different—there were two new ways to protect against the infection. One is a maternal vaccine, Pfizer's Abrysvo, which is given to pregnant people when their third trimester aligns with RSV season (generally September through January). Maternal antibodies generated from the vaccination pass to the fetus in the uterus and can protect a newborn in the first few months of life. The other new protection against RSV is a long-acting monoclonal antibody treatment, nirsevimab, which is given to babies under 8 months old as they enter or are born into their first RSV season and may not be protected by maternal antibodies.









































































![Apple Foldable iPhone to Feature New Display Tech, 19% Thinner Panel [Rumor]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97271/97271/97271-640.jpg)
![Apple Shares New Mother's Day Ad: 'A Gift for Mom' [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97267/97267/97267-640.jpg)
![Apple Developing New Chips for Smart Glasses, Macs, AI Servers [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97269/97269/97269-640.jpg)
![Apple Shares Official Trailer for 'Stick' Starring Owen Wilson [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97264/97264/97264-640.jpg)










































































































 Evolved as a Predominant Framework for Ransomware Attacks.webp?#)


_Aleksey_Funtap_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)
_Sergey_Tarasov_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)























































































































![[The AI Show Episode 146]: Rise of “AI-First” Companies, AI Job Disruption, GPT-4o Update Gets Rolled Back, How Big Consulting Firms Use AI, and Meta AI App](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20146%20cover.png)



































































































































































![[DEALS] The Premium Python Programming PCEP Certification Prep Bundle (67% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)





























-Mafia-The-Old-Country---The-Initiation-Trailer-00-00-54.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)



































































