Non-planar Slicing is for the Birds
When we say non-planar slicing is for the birds, we mean [Joshua Bird], who demonstrates the versatility of his new non-planar S4-Slicer by printing a Benchy upside down with the …read more

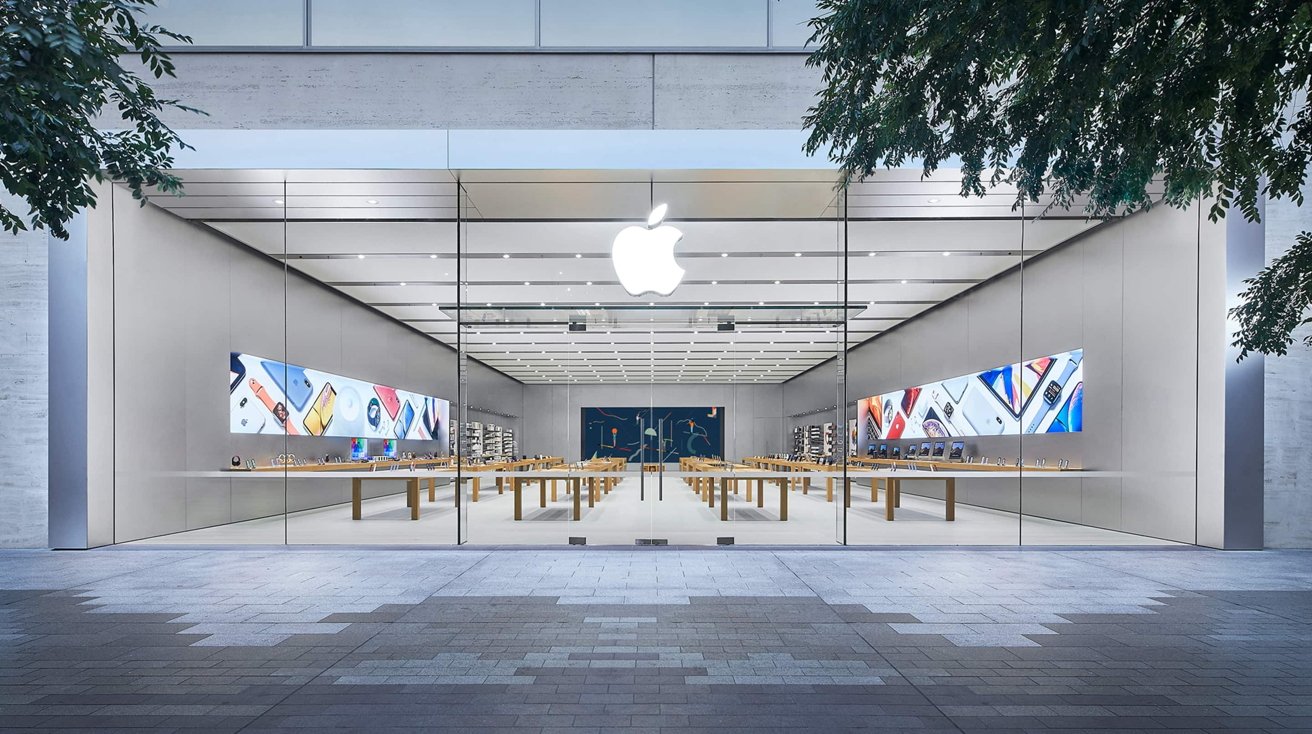
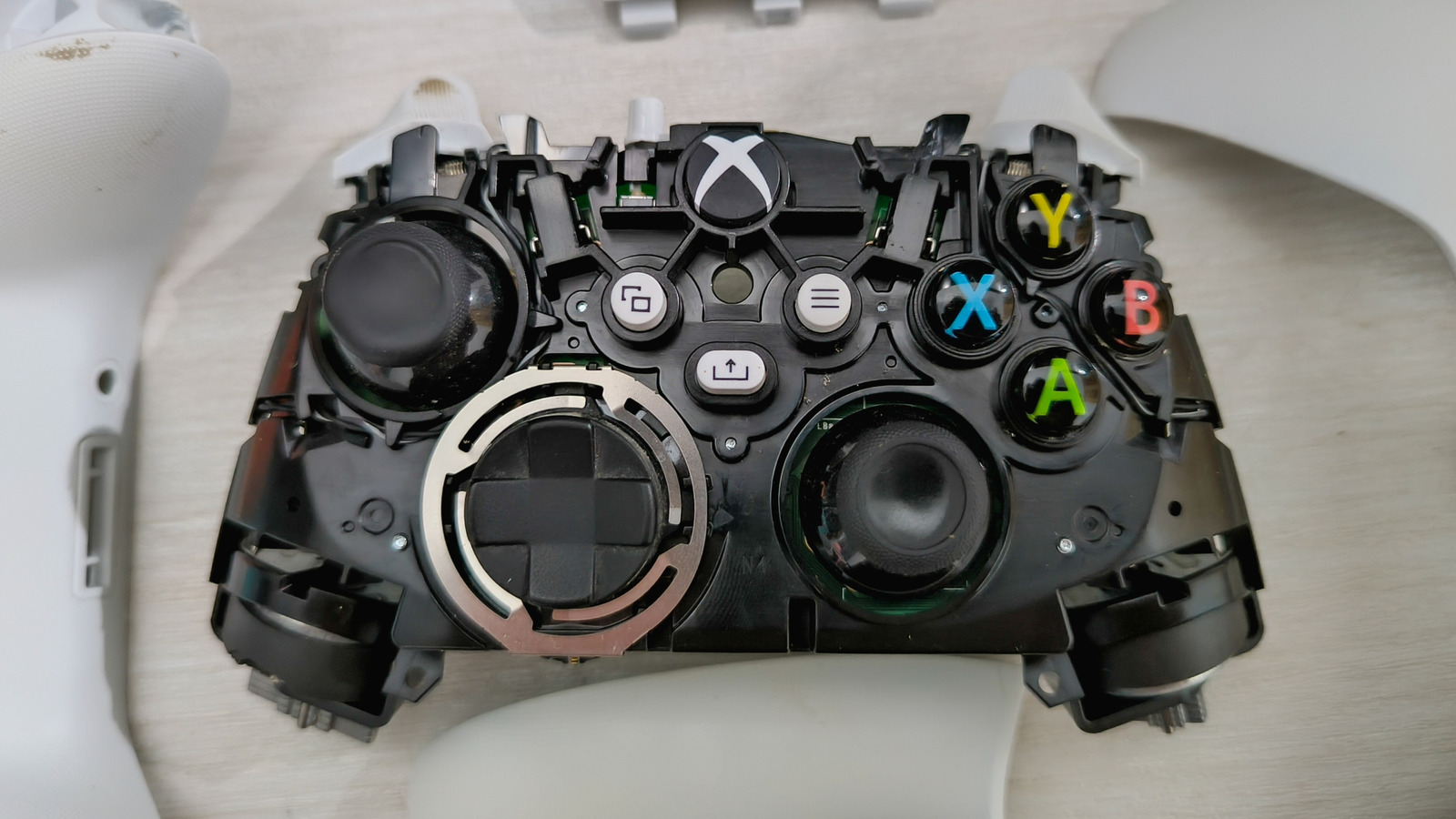
![Benchy, printed upside down on [Josh's] Core R-Theta printer.](https://hackaday.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/upside-down-benchy-nonplaner-e1745086286623.jpg?w=800)
When we say non-planar slicing is for the birds, we mean [Joshua Bird], who demonstrates the versatility of his new non-planar S4-Slicer by printing a Benchy upside down with the “Core R-Theta” printer we have featured here before.

This non-planar slicer is built into a Jupyter notebook, which follows a relatively simple algorithm to automatically generate non-planar toolpaths for any model. It does this by first generating a tetrahedral mesh of the model and then calculating the shortest possible path through the model from any given tetrahedron to the print bed. Even with non-planar printing, you need to print from the print-bed up (or out).
Quite a lot of math is done to use these paths to calculate a deformation mesh, and we’ll leave that to [Joshua] to explain in his video below. After applying the deformation, he slices the resulting mesh in Cura, before the G-code goes back to Jupyter to be re-transformed, restoring the shape of the original mesh.

So yes, it is G-code bending as others have demonstrated before, but in a reproducible, streamlined, and straightforward workflow. Indeed, [Josh] credits much of the work to earlier work on the S^3-Slicer, which inspired much of the logic and the name behind his S4 slicer. (Not S4 as in “more than S^3” but S4 as a contraction of “Simplified S^3”). Once again, open source allows for incremental innovation.
It is admittedly a computationally intensive process, and [Joshua] uses a simplified model of Benchy for this demo. This seems exactly the sort of thing we’d like to burn compute power on, though.
This sort of non-planar 3D printing is an exciting frontier, one which we have covered before. We’ve seen techniques for non-planar infill, or even to print overhangs on unmodified Cartesian printers, but this is probably the first time we’ve seen Benchy given the non-planar treatment. You can try S4 slicer for yourself via GitHub, or just watch the non-planar magic in action after the break.




































































![Apple Shares Official Trailer for 'Long Way Home' Starring Ewan McGregor and Charley Boorman [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97069/97069/97069-640.jpg)
![Apple Watch Series 10 Back On Sale for $299! [Lowest Price Ever]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96657/96657/96657-640.jpg)
![Apple Slips to Fifth in China's Smartphone Market with 9% Decline [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97065/97065/97065-640.jpg)














![What features do you get with Gemini Advanced? [April 2025]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2024/02/gemini-advanced-cover.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)




























































































_Andreas_Prott_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)






















































































![[The AI Show Episode 144]: ChatGPT’s New Memory, Shopify CEO’s Leaked “AI First” Memo, Google Cloud Next Releases, o3 and o4-mini Coming Soon & Llama 4’s Rocky Launch](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20144%20cover.png)



























































































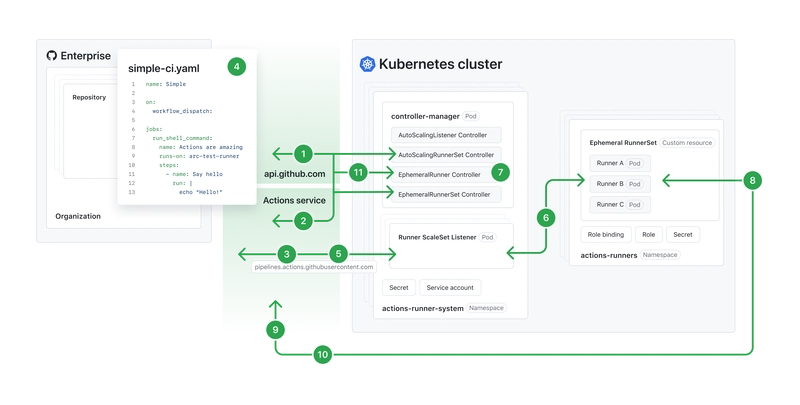
























![Is this too much for a modular monolith system? [closed]](https://i.sstatic.net/pYL1nsfg.png)




















![[DEALS] The All-in-One Microsoft Office Pro 2019 for Windows: Lifetime License + Windows 11 Pro Bundle (89% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)






























































































