Iron Nitride Permanent Magnets Made With DIY Ball Mill
Creating strong permanent magnets without using so-called rare earth elements is an ongoing topic of research. An interesting contestant here are iron nitride magnets (α”-Fe16N2), which have the potential to …read more


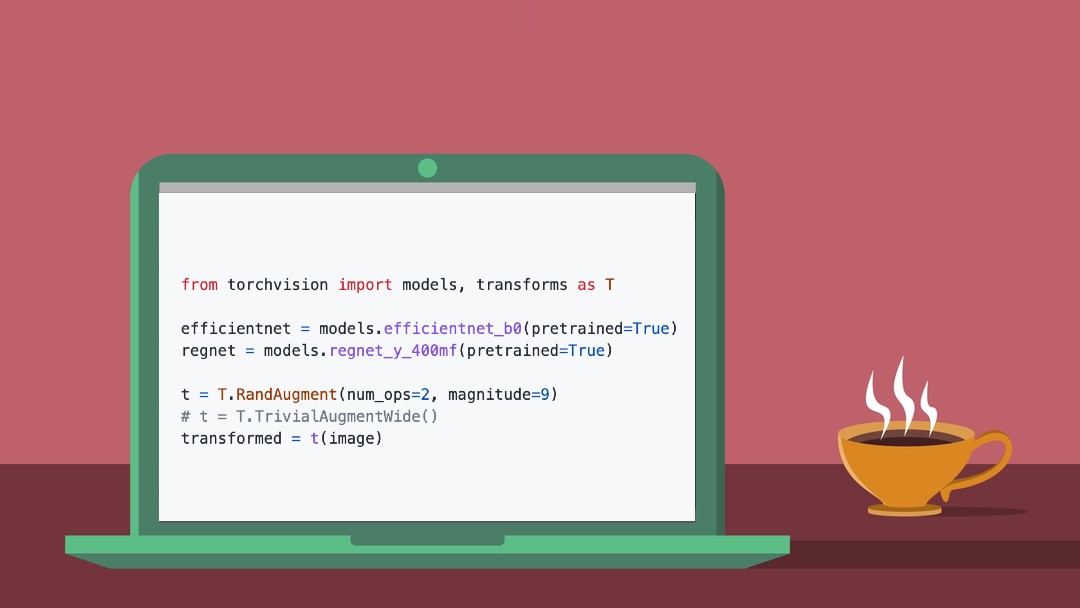
Creating strong permanent magnets without using so-called rare earth elements is an ongoing topic of research. An interesting contestant here are iron nitride magnets (α”-Fe16N2), which have the potential to create permanents magnets on-par with with neodymium (Nd2Fe14B) magnets. The challenging aspect with Fe-N magnets is their manufacturing, with recently [Ben Krasnow] giving it a shot over at the [Applied Science] YouTube channel following the method in a 2016 scientific paper by [Yanfeng Jiang] et al. in Advanced Engineering Materials.
This approach uses a ball mill (like [Ben]’s planetary version) with ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3) as the nitrogen source along with iron. After many hours of milling a significant part of the material is expected to have taken on the α”-Fe16N2 phase, after which shock compaction is applied to create a bulk magnet. After the ball mill grinding, [Ben] used a kiln at 200°C for a day to fix the desired phase. Instead of shock compaction, casting in epoxy was used as alternative.
We have covered Fe-N magnets before, along with the promises they hold. As one can see in [Ben]’s video, oxidation is a big problem, with the typical sintering as with other magnet types not possible either. Ultimately this led to the resulting magnet being fairly weak, with a DIY magnetometer used to determine the strength of the created magnet.
Interestingly, there’s a much newer paper by [Tetsuji Saito] et al. from 2024 in Metals that does use sintering, specifically spark plasma sintering with dynamic compression (SPS-DC). SPS-DC can be done at fairly low temperatures (373 – 573 K, or 99.85 – 299.85 °C), producing much stronger magnets than [Ben] accomplished.
Although Fe-N magnets hold a lot of promise, they have lower coercivity. This means that they demagnetize easier, which is another aspect that weighs against them. For now it would seem that we aren’t quite ready to say farewell to Nd-Fe-B magnets.







































































![Apple's F1 Camera Rig Revealed [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97651/97651/97651-640.jpg)

![Apple Shares New Apple Arcade Ad: 'Hold That Train!' [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97653/97653/97653-640.jpg)
![Apple Shares New Shot on iPhone Film: 'Big Man' [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97654/97654/97654-640.jpg)














































































































_Brain_light_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)

















































































































![[The AI Show Episode 153]: OpenAI Releases o3-Pro, Disney Sues Midjourney, Altman: “Gentle Singularity” Is Here, AI and Jobs & News Sites Getting Crushed by AI Search](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20153%20cover.png)


























































































































































![[DEALS] Internxt Cloud Storage Lifetime Subscription (20TB) (89% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)























.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)

































































