Check Docker Installation Details Part - 3
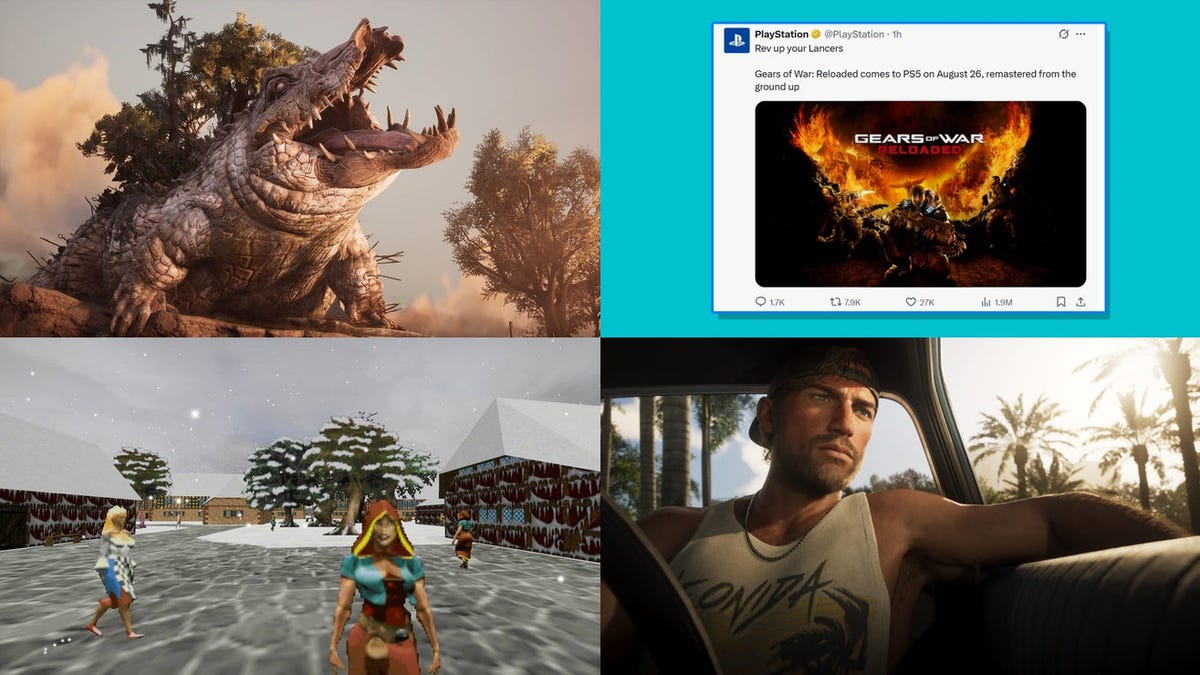
Exploring Basic Docker Commands Now that we've verified our Docker installation works correctly (Part-2), let's explore some basic Docker commands that will help you manage containers and images. Running an Interactive Container Unlike the hello-world container that runs and exits immediately, we can run containers interactively. 1.Let's run an Ubuntu container and interact with its shell: docker run -it ubuntu bash This command: • -i keeps STDIN open • -t allocates a pseudo-TTY (terminal) • ubuntu is the image name. • bash is the command to run inside the container. Once the container starts, you'll be at a bash prompt inside the container. The prompt shows you're logged in as root in the container. The alphanumeric string is the container ID. 2.Try running some Linux commands inside the container: cat /etc/os-release This will display information about the Ubuntu version running in the container: 3.When you're done exploring, exit the container by typing: exit This will return you to your host terminal. Container Lifecycle Management 4.Let's explore how to manage the lifecycle of a container. First, we'll start a container in detached mode: docker run -d --name web nginx This command: • -d runs the container in detached mode (in the background) • --name web assigns the name "web" to the container • nginx is the image to use. You'll see a long container ID printed on the screen. 5.Now, let's check that the container is running: docker ps You should see the nginx container running. 6.To stop the container: docker stop web 7.Verify it's stopped: docker ps 8.The container should no longer appear in the list of running containers. To see all containers including stopped ones: docker ps -a You should the nginx containers in the stopped state. 9.To start the container again and check container status: docker start web docker ps 10.to remove a container when you no longer need it: docker rm web 11.Error response from daemon: cannot remove container "/web": container is running stop the container before removing. First stop the running container then remove and check: docker stop web docker rm web Command: docker ps -a You should see the web container not available. Managing Docker Images Let's explore how to manage Docker images. To list all images: 12.Let’s check the docker images available of your system. docker images You should see at least the hello-world and nginx images. 13.To remove an image when you no longer need it: docker rmi hello-world Error response from daemon: conflict: unable to remove repository reference "hello-world" (must force) - container be8b92819418 is using its referenced image 74cc54e27dc4. Note that you can't remove images that are being used by containers (even stopped ones). You'll need to remove those containers first. 14.Let’s remove the hello-world container then remove hello-world image: Command:docker ps -a Command: docker rmi hello-world Command: docker images You should see the hello-world image not available in the images list. Docker System Information To check disk space used by Docker (containers, images, volumes): 15.Let’s check disk space used by docker: docker system df This will show a summary of disk usage. 16.To get more detailed information: docker system df -v This will show a breakdown of each image and container and their sizes. LinkedIn: https://linkedin.com/in/kamrul-dev GitHub: https://github.com/kamrul-dev Related Keywords: How to verify Docker installation on your system, Checking Docker version and system info via CLI, Confirming Docker is properly installed on Linux/Mac/Windows, Commands to check Docker installation status, Troubleshooting Docker setup issues, Kamrul Hasan DevOps Engineer, DevOps tips by Kamrul Hasan, Kamrul Hasan Docker tutorials, Learn DevOps with Kamrul Hasan, Kamrul Hasan automation expert, Kamrul Hasan cloud and containers, CI/CD pipelines by Kamrul Hasan, Kamrul Hasan Kubernetes & Docker,

Exploring Basic Docker Commands
Now that we've verified our Docker installation works correctly (Part-2), let's explore some basic Docker commands that will help you manage containers and images.
Running an Interactive Container
Unlike the hello-world container that runs and exits immediately, we can run containers interactively.
1.Let's run an Ubuntu container and interact with its shell:
docker run -it ubuntu bash
This command:
• -i keeps STDIN open
• -t allocates a pseudo-TTY (terminal)
• ubuntu is the image name.
• bash is the command to run inside the container.
Once the container starts, you'll be at a bash prompt inside the container. The prompt shows you're logged in as root in the container. The alphanumeric string is the container ID.
2.Try running some Linux commands inside the container:
cat /etc/os-release
This will display information about the Ubuntu version running in the container:
3.When you're done exploring, exit the container by typing:
exit
This will return you to your host terminal.
Container Lifecycle Management
4.Let's explore how to manage the lifecycle of a container. First, we'll start a container in detached mode:
docker run -d --name web nginx
This command:
• -d runs the container in detached mode (in the background)
• --name web assigns the name "web" to the container
• nginx is the image to use.
You'll see a long container ID printed on the screen.
5.Now, let's check that the container is running:
docker ps

You should see the nginx container running.
6.To stop the container:
docker stop web
7.Verify it's stopped:
docker ps
8.The container should no longer appear in the list of running containers. To see all containers including stopped ones:
docker ps -a

You should the nginx containers in the stopped state.
9.To start the container again and check container status:
docker start web
docker ps
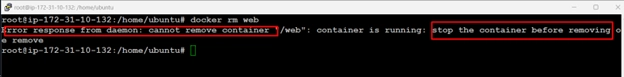
10.to remove a container when you no longer need it:
docker rm web
11.Error response from daemon: cannot remove container "/web": container is running stop the container before removing. First stop the running container then remove and check:
docker stop web
docker rm web
Command: docker ps -a
You should see the web container not available.
Managing Docker Images
Let's explore how to manage Docker images. To list all images:
12.Let’s check the docker images available of your system.
docker images

You should see at least the hello-world and nginx images.
13.To remove an image when you no longer need it:
docker rmi hello-world
Error response from daemon: conflict: unable to remove repository reference "hello-world" (must force) - container be8b92819418 is using its referenced image 74cc54e27dc4.
Note that you can't remove images that are being used by containers (even stopped ones). You'll need to remove those containers first.
14.Let’s remove the hello-world container then remove hello-world image:
Command:docker ps -a
Command: docker rmi hello-world
Command: docker images

You should see the hello-world image not available in the images list.
Docker System Information
To check disk space used by Docker (containers, images, volumes):
15.Let’s check disk space used by docker:
docker system df

This will show a summary of disk usage.
16.To get more detailed information:
docker system df -v
This will show a breakdown of each image and container and their sizes.
LinkedIn: https://linkedin.com/in/kamrul-dev
GitHub: https://github.com/kamrul-dev
Related Keywords:
How to verify Docker installation on your system,
Checking Docker version and system info via CLI,
Confirming Docker is properly installed on Linux/Mac/Windows,
Commands to check Docker installation status,
Troubleshooting Docker setup issues,
Kamrul Hasan DevOps Engineer,
DevOps tips by Kamrul Hasan,
Kamrul Hasan Docker tutorials,
Learn DevOps with Kamrul Hasan,
Kamrul Hasan automation expert,
Kamrul Hasan cloud and containers,
CI/CD pipelines by Kamrul Hasan,
Kamrul Hasan Kubernetes & Docker,























![[Exclusive] Infinix GT DynaVue: a Prototype that could change everything!](https://www.gizchina.com/wp-content/uploads/images/2025/05/Screen-Shot-2025-05-10-at-16.07.40-PM-copy.png)














































![Apple M4 iMac Drops to New All-Time Low Price of $1059 [Deal]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97281/97281/97281-640.jpg)
![Beats Studio Buds + On Sale for $99.95 [Lowest Price Ever]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96983/96983/96983-640.jpg)

![New iPad 11 (A16) On Sale for Just $277.78! [Lowest Price Ever]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97273/97273/97273-640.jpg)











![As Galaxy Watch prepares a major change, which smartwatch design to you prefer? [Poll]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2024/07/Galaxy-Watch-Ultra-and-Apple-Watch-Ultra-1.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)














-xl.jpg)















































































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 146]: Rise of “AI-First” Companies, AI Job Disruption, GPT-4o Update Gets Rolled Back, How Big Consulting Firms Use AI, and Meta AI App](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20146%20cover.png)



























































































































































![Ditching a Microsoft Job to Enter Startup Purgatory with Lonewolf Engineer Sam Crombie [Podcast #171]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1746753508177/0cd57f66-fdb0-4972-b285-1443a7db39fc.png?#)


![[FREE EBOOKS] Offensive Security Using Python, Learn Computer Forensics — 2nd edition & Four More Best Selling Titles](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)