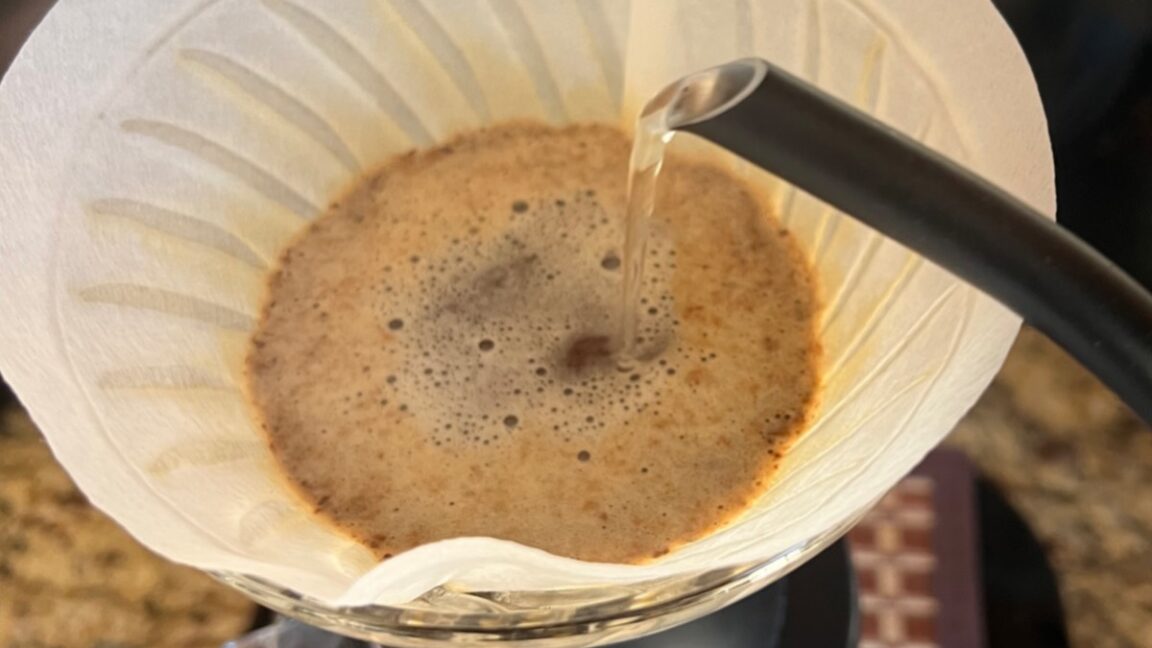
Fewer beans = great coffee if you get the pour height right
Pour-over coffee is made by flowing a strong, laminar water jet through a bed of ground coffee beans.

Coffee is one of the most popular beverages in the world, counting many scientists among its fans. Naturally those scientists are sometimes drawn to study their beloved beverage from various angles with an eye toward achieving the perfect cup.
While espresso has received the lion's share of such attention, physicists at the University of Pennsylvania have investigated the physics behind brewing so-called "pour-over" coffee, in which hot water is poured over coffee grounds in a filter within a funnel-shaped cone and allowed to percolate and drip into a cup below. The trick is to pour the water from as high as possible without letting the jet of water break up upon impact with the grounds, according to their new paper published in the journal Physics of Fluids.
In 2020, we reported on a mathematical model for brewing the perfect cup of espresso with minimal waste. Many variables can affect the quality of a steaming cup of espresso, including so-called "channeling" during the brewing process, in which the water doesn't seep uniformly through the grounds but branches off in various preferential paths instead. This significantly reduces the extraction yield (EY)—the fraction of coffee that dissolves into the final beverage—and thus the quality of the final brew. That, in turn, depends on controlling water flow and pressure as the liquid percolates through the coffee grounds.


































































![Apple M4 13-inch iPad Pro On Sale for $200 Off [Deal]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97056/97056/97056-640.jpg)

![Apple Shares New 'Mac Does That' Ads for MacBook Pro [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97055/97055/97055-640.jpg)
![Apple Releases tvOS 18.4.1 for Apple TV [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97047/97047/97047-640.jpg)




























































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 144]: ChatGPT’s New Memory, Shopify CEO’s Leaked “AI First” Memo, Google Cloud Next Releases, o3 and o4-mini Coming Soon & Llama 4’s Rocky Launch](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20144%20cover.png)