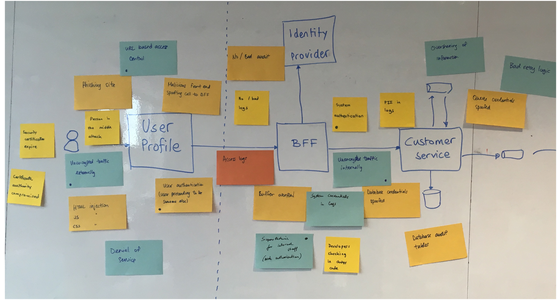
Microsoft Reveals Techniques To Defending Against Advancing AiTM Attacks
Microsoft’s latest security research has unveiled sophisticated defense strategies against the rapidly evolving threat landscape of Adversary-in-the-Middle (AiTM) attacks, marking a critical development in enterprise cybersecurity. The emergence of AiTM attacks represents a fundamental shift in how threat actors approach credential theft, particularly as organizations increasingly adopt multifactor authentication (MFA) and other advanced security measures […] The post Microsoft Reveals Techniques To Defending Against Advancing AiTM Attacks appeared first on Cyber Security News.

Microsoft’s latest security research has unveiled sophisticated defense strategies against the rapidly evolving threat landscape of Adversary-in-the-Middle (AiTM) attacks, marking a critical development in enterprise cybersecurity.
The emergence of AiTM attacks represents a fundamental shift in how threat actors approach credential theft, particularly as organizations increasingly adopt multifactor authentication (MFA) and other advanced security measures that have traditionally thwarted conventional phishing attempts.
The attack methodology involves deploying proxy servers between target users and legitimate websites, effectively intercepting authentication flows in real-time.
This technique has gained unprecedented traction through phishing-as-a-service (PhaaS) platforms, with frameworks like Evilginx becoming increasingly accessible to cybercriminals of varying skill levels.
The sophistication of these attacks has attracted high-profile threat actors, including the prolific phishing operator Storm-0485 and the Russian espionage group Star Blizzard, both of whom have weaponized AiTM capabilities for large-scale credential harvesting operations.
Microsoft analysts identified that modern AiTM attacks specifically target cloud-based enterprise environments, where stolen session tokens can provide persistent access to corporate resources.
The impact extends beyond simple credential theft, as successful AiTM campaigns enable threat actors to bypass traditional security controls and maintain prolonged access to sensitive organizational data.
Recent intelligence indicates that these attacks have evolved to incorporate artificial intelligence for crafting more convincing social engineering lures, making detection significantly more challenging for both automated systems and end users.
The technical analysis reveals that AiTM operators frequently utilize evasion tactics to circumvent security detection systems.
Storm-0485, for instance, consistently employs obfuscated Google Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) URLs to mask malicious links, making initial threat identification more complex for security teams.
.webp)
The threat actor’s campaigns typically feature carefully crafted lures with themes such as payment remittance notifications, shared document alerts, and fraudulent LinkedIn account verification requests, all designed to prompt immediate user response.
Advanced Persistence and Lateral Movement Mechanisms
The most concerning aspect of contemporary AiTM attacks lies in their post-compromise activities, where threat actors leverage initially compromised identities to orchestrate internal phishing campaigns.
Storm-0539, which specifically targets the retail industry for gift card fraud, demonstrates this technique by utilizing legitimate company resources to craft convincing internal phishing emails.
The group extracts authentic help desk tickets and organizational communications to serve as templates, creating AiTM phishing pages that precisely mimic the federated identity service providers of compromised organizations.
.webp)
This internal propagation method proves particularly effective because the phishing emails originate from legitimate internal accounts and closely resemble genuine organizational communications.
The technique enables significant lateral movement within corporate networks, as threat actors systematically seek identities with elevated privileges and access to critical cloud resources.
Microsoft’s analysis indicates that these follow-on attacks often incorporate device code authentication phishing, with payloads that remain active for only 15-minute windows, forcing attackers to conduct multiple coordinated waves of internal phishing to maximize credential acquisition success rates.
Celebrate 9 years of ANY.RUN! Unlock the full power of TI Lookup plan (100/300/600/1,000+ search requests), and your request quota will double.
The post Microsoft Reveals Techniques To Defending Against Advancing AiTM Attacks appeared first on Cyber Security News.



































































![Sonos Father's Day Sale: Save Up to 26% on Arc Ultra, Ace, Move 2, and More [Deal]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97469/97469/97469-640.jpg)












































































































.webp?#)


_Delphotos_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)


















































































































![[The AI Show Episode 150]: AI Answers: AI Roadmaps, Which Tools to Use, Making the Case for AI, Training, and Building GPTs](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20150%20cover.png)
![[The AI Show Episode 149]: Google I/O, Claude 4, White Collar Jobs Automated in 5 Years, Jony Ive Joins OpenAI, and AI’s Impact on the Environment](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20149%20cover.png)












































































































![[FREE EBOOKS] Solutions Architect’s Handbook, The Embedded Linux Security Handbook & Four More Best Selling Titles](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)











































![How to Survive in Tech When Everything's Changing w/ 21-year Veteran Dev Joe Attardi [Podcast #174]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1748483423794/0848ad8d-1381-474f-94ea-a196ad4723a4.png?#)