Setting Up an S3 Bucket with Terraform
Setting Up an S3 Bucket with Terraform In this blog post, I'll walk you through the process of setting up an S3 bucket using Terraform. Terraform is an open-source infrastructure as code software tool that provides a consistent CLI workflow to manage hundreds of cloud services. Prerequisites Before we begin, make sure you have the following: An AWS account. Terraform installed on your machine. AWS CLI configured with your credentials. Step 1: Define the S3 Bucket First, we'll define an S3 bucket in our Terraform configuration. This bucket will be used to host a static website. resource "aws_s3_bucket" "portfolibucket" { bucket = "portfolio-17-03-2025-bucket" website { index_document = "bucket1.html" } tags = { Name = "portfolio-17-03-2025-bucket" Environment = "Dev" } } resource "aws_s3_bucket_object" "index" { bucket = aws_s3_bucket.portfolibucket.id key = "bucket1.html" source = "bucket1.html" content_type = "text/html" } In this configuration, we define an S3 bucket named portfolio-17-03-2025-bucket and specify that it will host a static website with bucket1.html as the index document. We also add some tags for better organization. Step 2: Set Up Public Access Block Next, we'll set up a public access block to control the public access settings for the bucket. resource "aws_s3_bucket_public_access_block" "public_access" { bucket = aws_s3_bucket.portfolibucket.id block_public_acls = false block_public_policy = false ignore_public_acls = false restrict_public_buckets = false depends_on = [ aws_s3_bucket.portfolibucket ] } This configuration ensures that the bucket's public access settings are managed according to our requirements. Step 3: Define the Bucket Policy We'll also define a bucket policy to allow public read access to the objects in the bucket. resource "aws_s3_bucket_policy" "allow_access_from_another_account" { bucket = aws_s3_bucket.portfolibucket.id policy =
Setting Up an S3 Bucket with Terraform
In this blog post, I'll walk you through the process of setting up an S3 bucket using Terraform. Terraform is an open-source infrastructure as code software tool that provides a consistent CLI workflow to manage hundreds of cloud services.
Prerequisites
Before we begin, make sure you have the following:
- An AWS account.
- Terraform installed on your machine.
- AWS CLI configured with your credentials.
Step 1: Define the S3 Bucket
First, we'll define an S3 bucket in our Terraform configuration. This bucket will be used to host a static website.
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "portfolibucket" {
bucket = "portfolio-17-03-2025-bucket"
website {
index_document = "bucket1.html"
}
tags = {
Name = "portfolio-17-03-2025-bucket"
Environment = "Dev"
}
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket_object" "index" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.portfolibucket.id
key = "bucket1.html"
source = "bucket1.html"
content_type = "text/html"
}
In this configuration, we define an S3 bucket named portfolio-17-03-2025-bucket and specify that it will host a static website with bucket1.html as the index document. We also add some tags for better organization.
Step 2: Set Up Public Access Block
Next, we'll set up a public access block to control the public access settings for the bucket.
resource "aws_s3_bucket_public_access_block" "public_access" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.portfolibucket.id
block_public_acls = false
block_public_policy = false
ignore_public_acls = false
restrict_public_buckets = false
depends_on = [ aws_s3_bucket.portfolibucket ]
}
This configuration ensures that the bucket's public access settings are managed according to our requirements.
Step 3: Define the Bucket Policy
We'll also define a bucket policy to allow public read access to the objects in the bucket.
resource "aws_s3_bucket_policy" "allow_access_from_another_account" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.portfolibucket.id
policy = <<EOF
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": "*",
"Action": "s3:GetObject",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::${aws_s3_bucket.portfolibucket.id}/*"
}
]
}
EOF
depends_on = [ aws_s3_bucket_public_access_block.public_access ]
}
This policy allows anyone to read the objects in the bucket, which is necessary for hosting a public website.
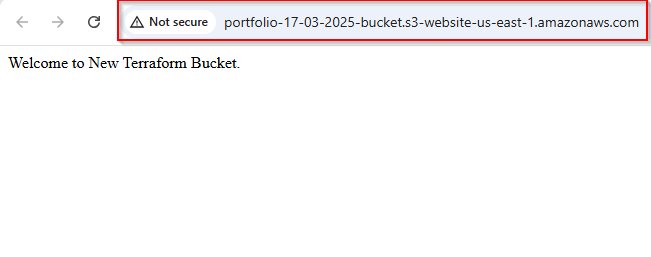
Step 4: Output the Website Endpoint
Finally, we'll output the website endpoint so we can easily access it after the deployment.
output "website_endpoint" {
value = "http://${aws_s3_bucket.portfolibucket.website_endpoint}"
}
Step 5: Prevent My VPC been Destroy
We'll also prevent my VPC been destroy.
resource "aws_vpc" "myvpc" {
cidr_block = "172.16.0.0/16"
lifecycle {
prevent_destroy = true
}
}
This configuration creates a VPC with a CIDR block of 172.16.0.0/16.
Step 6: Apply the Configuration
With all the resources defined, we can now apply the configuration using Terraform.
terraform init
terraform apply --auto-approve
This will create the S3 bucket, set up the public access block, define the bucket policy, and prevent my VPC been destroy.
Conclusion
In this blog post, we've walked through the process of setting up an S3 bucket using Terraform. This setup is useful for hosting a static website on S3 and managing infrastructure as code with Terraform. I hope you found this guide helpful. Happy coding!
Check my previous post; how to create EC2 in full details?
Feel free to leave any questions or comments below.
Similar code found with 1 license type




























































![Apple C1 vs Qualcomm Modem Performance [Speedtest]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96767/96767/96767-640.jpg)
![Apple Studio Display On Sale for $1249 [Lowest Price Ever]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96770/96770/96770-640.jpg)












![[Fixed] Chromecast (2nd gen) and Audio can’t Cast in ‘Untrusted’ outage](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2019/08/chromecast_audio_1.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)


























































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 139]: The Government Knows AGI Is Coming, Superintelligence Strategy, OpenAI’s $20,000 Per Month Agents & Top 100 Gen AI Apps](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20139%20cover-2.png)


![[The AI Show Episode 138]: Introducing GPT-4.5, Claude 3.7 Sonnet, Alexa+, Deep Research Now in ChatGPT Plus & How AI Is Disrupting Writing](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20138%20cover.png)