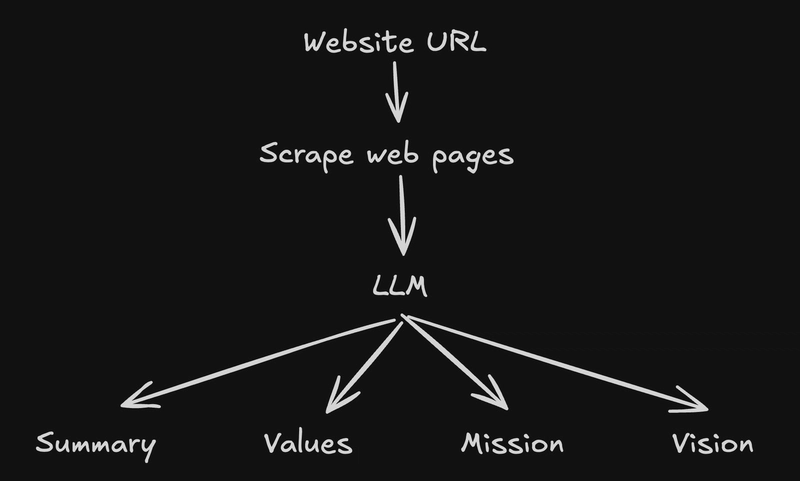
Transforming Venture Capital: The Role of Blockchain in the Future of Investment
Abstract This post explores how blockchain technology is redefining venture capital (VC) by enhancing transparency, liquidity, and access. We dive into the historical context of traditional VC, contrast it with blockchain-enabled innovations, and discuss core features like smart contracts, tokenization, and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). We also examine real-world examples, analyze challenges like regulatory hurdles and security concerns, and outline the future of blockchain in VC. For more details, see the Original Article. Introduction Venture capital has always played a crucial role in fostering innovation and fueling the growth of emerging technologies. However, traditional VC is often plagued by issues such as opacity, high entry barriers for new investors, and illiquidity. The advent of blockchain technology promises to change this landscape by introducing decentralized mechanisms which boost transparency and democratize investment opportunities. In this post, we explore how blockchain is transforming VC, review its core features, assess its real-life applications, and discuss future trends—all in a clear, technical yet accessible style. Background and Context Traditional Venture Capital Traditional VC typically involves complex networks of entrepreneurs, institutional investors, and intermediaries. The process is characterized by: Extensive due diligence: Investment decisions require deep legal vetting and financial analyses. Limited transparency: Information asymmetry often exists among stakeholders. High costs and illiquidity: Significant fees and long lock-in periods for investors are the norm. These issues have driven many to search for more efficient, transparent, and accessible investment models. Emergence of Blockchain Technology At its core, blockchain is a decentralized distributed ledger system that records transactions across many nodes. This distributed nature guarantees immutability and transparency. Beyond its association with cryptocurrencies, blockchain’s utility in sectors such as finance, supply chain, and now venture capital demonstrates its transformative power. Blockchain improves traditional VC practices by: Enabling smart contracts: Automating agreements based on preset conditions via smart contracts. Tokenization of assets: Dividing large investments into tokenized fractions allowing a broader, more inclusive investor base. Increasing liquidity: Secondary markets for tokens provide increased liquidity and flexible investment durations. Lowering costs: Reduced reliance on intermediaries minimizes transaction fees and legal costs. Core Concepts and Features Blockchain technology brings several key concepts to VC that redefine how investments are made and managed: Decentralization and Transparency Decentralization means that no single entity controls the data. This inherently builds trust among investors since every transaction is visible on a public ledger. Transparency is especially important in early-stage investments and project funding. Smart Contracts and Automation Smart contracts streamline the investment process. For example, a smart contract can automatically distribute funds to a startup when predefined conditions are met. This reduces manual intervention, lowers operational costs, and enhances security. Tokenization and Liquidity Tokenization divides a large investment into digital tokens. These tokens can be traded on digital exchanges, enabling investors to exit positions earlier and obtain liquidity. The ability to trade tokens even before the full maturation of a startup exemplifies the fusion of VC with decentralized finance (DeFi). Access and Democratization of Investing Traditional VC is usually limited to institutional investors and high-net-worth individuals. Blockchain bridges this gap by: Lowering entry barriers: Fractional ownership through tokenization enables broader community participation. Global investor pools: Digital assets and blockchain platforms allow participation regardless of geographic limitations. Integration with Other Technologies Blockchain’s potential is further enhanced when it interoperates with other emerging technologies. For instance, exploring arbitrum and Ethereum interoperability shows how scalability and efficiency can be improved, while platforms embracing arbitrum and De-Fi principles highlight novel investment opportunities. Additionally, evolving research on arbitrum and tokenomics illustrates dynamic models for incentive distribution. Below is a table contrasting traditional VC with blockchain-enabled VC: Feature Traditional VC Blockchain-Enabled VC Transparency Limited disclosure, reliant on intermediaries Open ledger ensures real-time, immutable transaction records Access Restricted to accredited investors Tokenization democratizes entry, offering

Abstract
This post explores how blockchain technology is redefining venture capital (VC) by enhancing transparency, liquidity, and access. We dive into the historical context of traditional VC, contrast it with blockchain-enabled innovations, and discuss core features like smart contracts, tokenization, and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). We also examine real-world examples, analyze challenges like regulatory hurdles and security concerns, and outline the future of blockchain in VC. For more details, see the Original Article.
Introduction
Venture capital has always played a crucial role in fostering innovation and fueling the growth of emerging technologies. However, traditional VC is often plagued by issues such as opacity, high entry barriers for new investors, and illiquidity. The advent of blockchain technology promises to change this landscape by introducing decentralized mechanisms which boost transparency and democratize investment opportunities. In this post, we explore how blockchain is transforming VC, review its core features, assess its real-life applications, and discuss future trends—all in a clear, technical yet accessible style.
Background and Context
Traditional Venture Capital
Traditional VC typically involves complex networks of entrepreneurs, institutional investors, and intermediaries. The process is characterized by:
- Extensive due diligence: Investment decisions require deep legal vetting and financial analyses.
- Limited transparency: Information asymmetry often exists among stakeholders.
- High costs and illiquidity: Significant fees and long lock-in periods for investors are the norm.
These issues have driven many to search for more efficient, transparent, and accessible investment models.
Emergence of Blockchain Technology
At its core, blockchain is a decentralized distributed ledger system that records transactions across many nodes. This distributed nature guarantees immutability and transparency. Beyond its association with cryptocurrencies, blockchain’s utility in sectors such as finance, supply chain, and now venture capital demonstrates its transformative power.
Blockchain improves traditional VC practices by:
- Enabling smart contracts: Automating agreements based on preset conditions via smart contracts.
- Tokenization of assets: Dividing large investments into tokenized fractions allowing a broader, more inclusive investor base.
- Increasing liquidity: Secondary markets for tokens provide increased liquidity and flexible investment durations.
- Lowering costs: Reduced reliance on intermediaries minimizes transaction fees and legal costs.
Core Concepts and Features
Blockchain technology brings several key concepts to VC that redefine how investments are made and managed:
Decentralization and Transparency
Decentralization means that no single entity controls the data. This inherently builds trust among investors since every transaction is visible on a public ledger. Transparency is especially important in early-stage investments and project funding.
Smart Contracts and Automation
Smart contracts streamline the investment process. For example, a smart contract can automatically distribute funds to a startup when predefined conditions are met. This reduces manual intervention, lowers operational costs, and enhances security.
Tokenization and Liquidity
Tokenization divides a large investment into digital tokens. These tokens can be traded on digital exchanges, enabling investors to exit positions earlier and obtain liquidity. The ability to trade tokens even before the full maturation of a startup exemplifies the fusion of VC with decentralized finance (DeFi).
Access and Democratization of Investing
Traditional VC is usually limited to institutional investors and high-net-worth individuals. Blockchain bridges this gap by:
- Lowering entry barriers: Fractional ownership through tokenization enables broader community participation.
- Global investor pools: Digital assets and blockchain platforms allow participation regardless of geographic limitations.
Integration with Other Technologies
Blockchain’s potential is further enhanced when it interoperates with other emerging technologies. For instance, exploring arbitrum and Ethereum interoperability shows how scalability and efficiency can be improved, while platforms embracing arbitrum and De-Fi principles highlight novel investment opportunities. Additionally, evolving research on arbitrum and tokenomics illustrates dynamic models for incentive distribution.
Below is a table contrasting traditional VC with blockchain-enabled VC:
| Feature | Traditional VC | Blockchain-Enabled VC |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | Limited disclosure, reliant on intermediaries | Open ledger ensures real-time, immutable transaction records |
| Access | Restricted to accredited investors | Tokenization democratizes entry, offering fractional ownership |
| Liquidity | Long lock-in periods, high exit barriers | Secondary markets for tokens provide liquidity |
| Cost Efficiency | High operational and legal fees | Automated smart contracts cut down intermediary costs |
| Speed & Efficiency | Slow due diligence and legal processes | Automated workflows expedite the investment lifecycle |
Applications and Use Cases
Blockchain is already transforming several aspects of venture capital. Here we present practical use cases across different platforms:
ICOs and STOs
Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) and Security Token Offerings (STOs) have revolutionized how early-stage capital is raised. Instead of extensive paperwork, startups issue tokens that represent equity or utility. More information on ICOs can be found here.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
DAOs utilize blockchain to create community-driven investment funds. Participants vote on investment decisions, ensuring collective decision-making and shared responsibility. Learn more about DAOs and their potential impact on VC.
Tokenized Equity Platforms
Platforms such as Republic and Swarm illustrate how startups can tokenize their assets. This approach demystifies traditional VC and offers enhanced liquidity for both startups and investors.
Integration with DeFi
The integration of blockchain with decentralized finance (DeFi) exemplifies one of the most promising trends. With DeFi protocols, investors can not only access funding opportunities but also leverage advanced financial instruments for yield farming and liquidity provision. These innovations help to mitigate long-standing liquidity issues in VC.
Additional Real-World Examples
- Platform: Republic – This platform enables global participation by allowing investors to purchase tokenized equity at lower thresholds.
- Platform: Swarm – Swarm network uses blockchain to fractionalize investments, making it easier for startups to source funds.
- Funding via DAOs – Community-governed DAOs enable a decentralized approach to fund allocation, which has been pivotal in early-stage tech ventures.
Useful Resources on Blockchain and Innovation
For those looking to expand their knowledge or get involved with blockchain-based VC, consider exploring:
- IBM's explanation of what is blockchain
- Guidelines on sustainable blockchain practices
Challenges and Limitations
While the promise of blockchain in venture capital is immense, several challenges must be acknowledged:
Regulatory and Legal Concerns
- Regulation Variance: Jurisdictions vary widely in terms of how cryptocurrencies and tokenized assets are regulated. This can lead to legal uncertainties.
- Compliance Costs: Despite reduced intermediary costs, navigating the complex regulatory landscape might require further legal expertise.
Technological Complexity
- Integration Challenges: Merging traditional financial systems with blockchain infrastructures requires significant research, development, and expertise.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Blockchain, though secure by design, is not immune to hacks. Smart contracts and digital wallets must be rigorously audited to avoid breaches.
Market Adoption and Liquidity Management
- Fragmentation: Many blockchain VC platforms are still in early development, resulting in a fragmented ecosystem.
- Investor Education: A steep learning curve may deter new investors who are unfamiliar with digital assets and decentralized protocols.
Below is a bullet list summarizing key challenges:
- Regulatory hurdles and legal complexities
- Integration and interoperability issues
- Potential security vulnerabilities
- Market fragmentation and investor education gaps
Future Outlook and Innovations
The future of blockchain in venture capital is poised to evolve rapidly. Here are some trends and innovations to watch:
Widespread Adoption
As blockchain becomes more mainstream, it is expected that more traditional VC firms will integrate blockchain-based systems to complement their existing frameworks. This fusion of decentralization and conventional investment practices could lead to more robust, transparent markets.
Enhanced DeFi Integration
Further convergence with DeFi will likely bring new financial instruments and funding mechanisms. Innovations such as yield enhancement strategies and liquidity pools specifically tailored for VC investments could emerge, further democratizing the process.
Improved Regulatory Frameworks
Anticipated advancements in legal clarity and international regulatory frameworks will enable smoother blockchain adoption. Such developments could encourage both startups and institutional investors to break into the blockchain VC sphere with greater confidence.
Decentralized Governance Models
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) are expected to evolve with more sophisticated governance mechanisms. Increased community participation may lead to more efficient, transparent, and democratic funding models.
Cross-Chain Interoperability
Efforts to improve interoperability between various blockchain networks (e.g., through projects like arbitrum and Ethereum interoperability) will help in merging different digital ecosystems into a unified marketplace. This could expand the instant liquidity and broaden investment horizons.
Voices from the Community
The influential posts on platforms like Dev.to and articles such as License Token Revolutionizing Open Source Licensing discuss similar trends. Moreover, insights from Crowdfunding for Blockchain Startups highlight how these innovations are empowering decentralized funding models.
Summary
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing venture capital by addressing traditional challenges of transparency, liquidity, and accessibility. In summary:
- Blockchain advantages: Automation via smart contracts, tokenization of assets, and decentralized governance lead to significant improvements in traditional VC practices.
- Practical applications: ICOs, DAOs, and tokenized equity platforms are already disrupting the status quo.
- Challenges remain: Regulatory uncertainties, technological integration issues, and security vulnerabilities need ongoing attention.
- The future is promising: Enhanced interoperability, growing DeFi integration, and evolving regulatory frameworks indicate a bright future for blockchain-powered venture capital.
As blockchain technology continues to mature, its integration with venture capital could lead to a more inclusive, efficient, and transparent investment environment. Both investors and entrepreneurs stand to benefit from these advancements, as seen in the growing adoption of tokenized assets and decentralized funding platforms.
For those who wish to explore more on the subject, consider reading related insights on:
- What is blockchain?
- Smart Contracts on Blockchain
- Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs)
- Understanding DAOs
- Sustainable Blockchain Practices
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is reshaping the venture capital landscape by reducing barriers to entry, improving transparency, and boosting liquidity. The integration of innovation—such as smart contracts and asset tokenization—creates a new paradigm that is set to democratize investment opportunities. Despite challenges related to regulatory compliance and technology integration, the future of blockchain-powered VC looks bright and promises to revolutionize the way capital is raised and managed.
In a world where decentralization and digital economies continue to expand, staying updated with these innovations is crucial. Embrace the future with blockchain-enabled VC and be part of an evolving ecosystem that is redefining investment norms.
Key Takeaways:
- Blockchain disrupts traditional VC: By introducing decentralized ledgers, smart contracts, and tokenization.
- Real-world examples such as Republic, Swarm, and DAOs illustrate practical applications.
- Challenges like regulation and security must be overcome to unlock full potential.
- The future integration with DeFi and cross-chain interoperability will further empower investors.
Whether you are a seasoned venture capitalist or a new investor, understanding these emerging trends is essential for navigating the rapidly evolving financial landscape. Explore the resources and case studies shared in this post to get a deeper insight into how blockchain is transforming venture capital—and prepare yourself for the future of decentralized investment.









































































![Apple Shares Trailer for First Immersive Feature Film 'Bono: Stories of Surrender' [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97168/97168/97168-640.jpg)
![New Hands-On iPhone 17 Dummy Video Shows Off Ultra-Thin Air Model, Updated Pro Designs [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97171/97171/97171-640.jpg)
![Apple Restructures Global Affairs and Apple Music Teams [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97162/97162/97162-640.jpg)

















![Apple testing Stage Manager for iPhone, Photographic Styles for video, and more [Video]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5mac.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/6/2025/04/iOS-Decoded-iOS-18.5.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)



















































































.webp?#)




_Jochen_Tack_Alamy.png?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)




























































































































![[The AI Show Episode 145]: OpenAI Releases o3 and o4-mini, AI Is Causing “Quiet Layoffs,” Executive Order on Youth AI Education & GPT-4o’s Controversial Update](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20145%20cover.png)