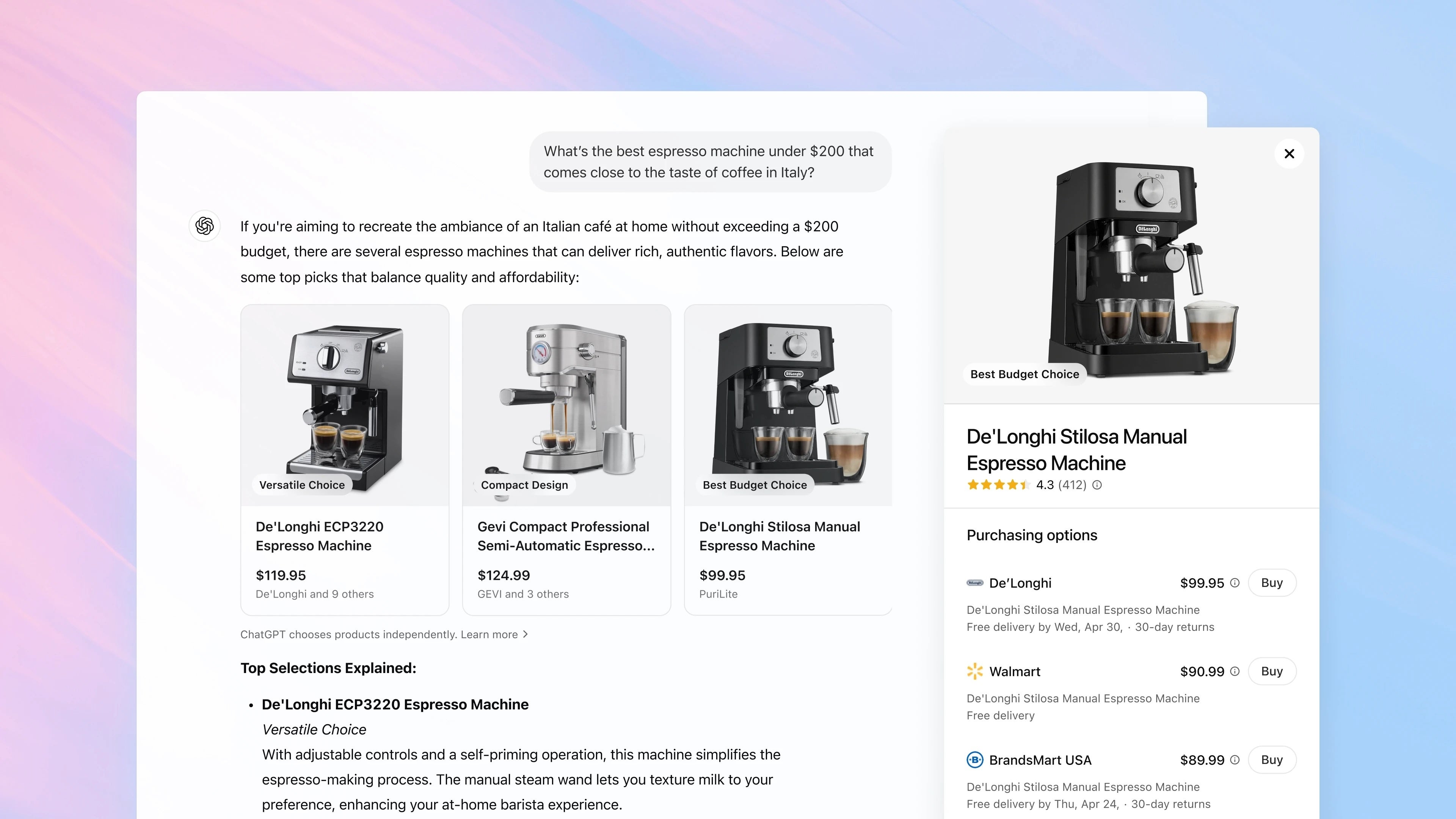
Car Subscription Features Raise Your Risk of Government Surveillance, Police Records Show
An anonymous reader quotes a report from Wired: Automakers are increasingly pushing consumers to accept monthly and annual fees to unlock preinstalled safety and performance features, from hands-free driving systems and heated seats to cameras that can automatically record accident situations. But the additional levels of internet connectivity this subscription model requires can increase drivers' exposure to government surveillance and the likelihood of being caught up in police investigations. A cache of more than two dozen police records recently reviewed by WIRED show US law enforcement agencies regularly trained on how to take advantage of "connected cars," with subscription-based features drastically increasing the amount of data that can be accessed during investigations. The records make clear that law enforcement's knowledge of the surveillance far exceeds that of the public and reveal how corporate policies and technologies -- not the law -- determine driver privacy. "Each manufacturer has their whole protocol on how the operating system in the vehicle utilizes telematics, mobile Wi-Fi, et cetera," one law enforcement officer noted in a presentation prepared by the California State Highway Patrol (CHP) and reviewed by WIRED. The presentation, while undated, contains statistics on connected cars for the year 2024. "If the vehicle has an active subscription," they add, "it does create more data." The CHP presentation, obtained by government transparency nonprofit Property of the People via a public records request, trains police on how to acquire data based on a variety of hypothetical scenarios, each describing how vehicle data can be acquired based on the year, make, and model of a vehicle. The presentation acknowledges that access to data can ultimately be limited due to choices made by not only vehicle manufacturers but the internet service providers on which connected devices rely. One document notes, for instance, that when a General Motors vehicle is equipped with an active OnStar subscription, it will transmit data -- revealing its location -- roughly twice as often as a Ford vehicle. Different ISPs appear to have not only different capabilities but policies when it comes to responding to government requests for information. Police may be able to rely on AT&T to help identify certain vehicles based on connected devices active in the car but lack the ability to do so when the device relies on a T-Mobile or Verizon network instead. [...] Nearly all subscription-based car features rely on devices that come preinstalled in a vehicle, with a cellular connection necessary only to enable the automaker's recurring-revenue scheme. The ability of car companies to charge users to activate some features is effectively the only reason the car's systems need to communicate with cell towers. The police documents note that companies often hook customers into adopting the services through free trial offers, and in some cases the devices are communicating with cell towers even when users decline to subscribe. Read more of this story at Slashdot.

Read more of this story at Slashdot.




























![Apple Seeds Fourth Beta of iOS 18.5 to Developers [Update: Public Beta Available]](https://images.macrumors.com/t/uSxxRefnKz3z3MK1y_CnFxSg8Ak=/2500x/article-new/2025/04/iOS-18.5-Feature-Real-Mock.jpg)
![Apple Seeds Fourth Beta of macOS Sequoia 15.5 [Update: Public Beta Available]](https://images.macrumors.com/t/ne62qbjm_V5f4GG9UND3WyOAxE8=/2500x/article-new/2024/08/macOS-Sequoia-Night-Feature.jpg)






































![Apple Seeds watchOS 11.5 Beta 4 to Developers [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97147/97147/97147-640.jpg)
![Apple Seeds visionOS 2.5 Beta 4 to Developers [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97150/97150/97150-640.jpg)
![Apple Seeds tvOS 18.5 Beta 4 to Developers [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97153/97153/97153-640.jpg)
![Apple Releases macOS Sequoia 15.5 Beta 4 to Developers [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97155/97155/97155-640.jpg)








































































































_NicoElNino_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)























































































































![[The AI Show Episode 144]: ChatGPT’s New Memory, Shopify CEO’s Leaked “AI First” Memo, Google Cloud Next Releases, o3 and o4-mini Coming Soon & Llama 4’s Rocky Launch](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20144%20cover.png)

































































































































































































.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)
.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)

































































