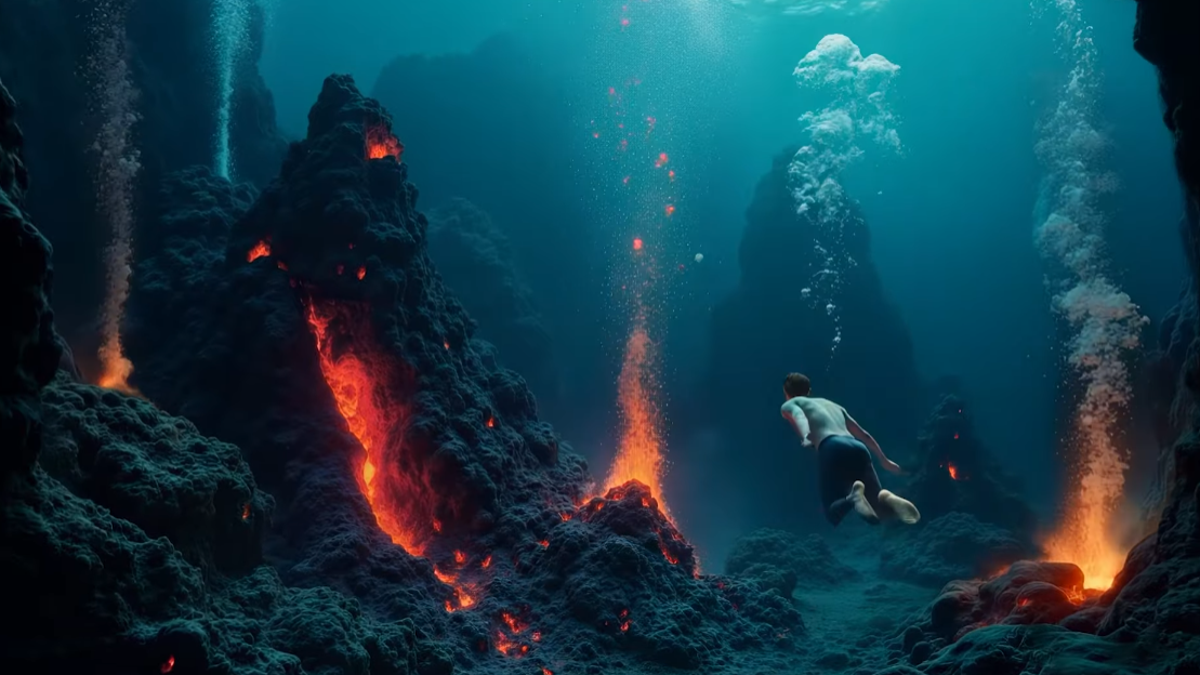React Suspense and Concurrent Rendering: The Future of Smooth UIs
Introduction React has always been at the forefront of building fast, interactive user interfaces. With React Suspense and Concurrent Rendering, the framework has significantly improved performance, responsiveness, and user experience. These features help manage asynchronous operations more efficiently while ensuring seamless UI updates. In this article, we’ll explore what React Suspense and Concurrent Rendering are, how they work, and why they matter for modern web applications. What is React Suspense? React Suspense is a feature that allows developers to handle asynchronous operations more smoothly, especially when dealing with data fetching. Instead of waiting for the entire data to load before rendering the UI, Suspense lets React show fallback UI components while the data is still being fetched. Why is Suspense Important? It improves user experience by preventing blank screens while waiting for data. It simplifies data fetching by handling loading states more efficiently. It works seamlessly with React Server Components and Concurrent Mode. Basic Example of React Suspense import React, { Suspense, lazy } from "react"; // Lazy load a component const Profile = lazy(() => import("./Profile")); function App() { return ( ); } export default App; Here, React Suspense displays the "Loading profile..." text while the Profile component is still being loaded asynchronously. What is Concurrent Rendering? Concurrent Rendering is a new rendering capability in React that helps improve app performance by allowing React to work on multiple UI updates simultaneously. Unlike traditional rendering, which blocks the UI until updates are finished, Concurrent Rendering enables: ✅ Interruptible rendering — React can pause rendering when needed. ✅ Smooth user interactions — Keeps UI responsive even with heavy computations. ✅ Better resource management — Prioritizes urgent updates over non-urgent ones. How Does Concurrent Rendering Work? With Concurrent Mode, React splits rendering into smaller chunks and prioritizes important UI updates, ensuring that slow operations don’t block user interactions. Example: Automatic Interruptions with startTransition import { useState, startTransition } from "react"; function SearchComponent({ data }) { const [query, setQuery] = useState(""); const [filteredData, setFilteredData] = useState(data); const handleSearch = (e) => { const value = e.target.value; setQuery(value); startTransition(() => { const results = data.filter((item) => item.toLowerCase().includes(value.toLowerCase()) ); setFilteredData(results); }); }; return ( {filteredData.map((item, index) => ( {item} ))} ); }
Introduction
React has always been at the forefront of building fast, interactive user interfaces. With React Suspense and Concurrent Rendering, the framework has significantly improved performance, responsiveness, and user experience. These features help manage asynchronous operations more efficiently while ensuring seamless UI updates.
In this article, we’ll explore what React Suspense and Concurrent Rendering are, how they work, and why they matter for modern web applications.
What is React Suspense?
React Suspense is a feature that allows developers to handle asynchronous operations more smoothly, especially when dealing with data fetching. Instead of waiting for the entire data to load before rendering the UI, Suspense lets React show fallback UI components while the data is still being fetched.
Why is Suspense Important?
- It improves user experience by preventing blank screens while waiting for data.
- It simplifies data fetching by handling loading states more efficiently.
- It works seamlessly with React Server Components and Concurrent Mode.
Basic Example of React Suspense
import React, { Suspense, lazy } from "react";
// Lazy load a component
const Profile = lazy(() => import("./Profile"));
function App() {
return (
<Suspense fallback={<div>Loading profile...</div>}>
<Profile />
</Suspense>
);
}
export default App;
Here, React Suspense displays the "Loading profile..." text while the Profile component is still being loaded asynchronously.
What is Concurrent Rendering?
Concurrent Rendering is a new rendering capability in React that helps improve app performance by allowing React to work on multiple UI updates simultaneously. Unlike traditional rendering, which blocks the UI until updates are finished, Concurrent Rendering enables:
✅ Interruptible rendering — React can pause rendering when needed.
✅ Smooth user interactions — Keeps UI responsive even with heavy computations.
✅ Better resource management — Prioritizes urgent updates over non-urgent ones.
How Does Concurrent Rendering Work?
With Concurrent Mode, React splits rendering into smaller chunks and prioritizes important UI updates, ensuring that slow operations don’t block user interactions.
Example: Automatic Interruptions with startTransition
import { useState, startTransition } from "react";
function SearchComponent({ data }) {
const [query, setQuery] = useState("");
const [filteredData, setFilteredData] = useState(data);
const handleSearch = (e) => {
const value = e.target.value;
setQuery(value);
startTransition(() => {
const results = data.filter((item) =>
item.toLowerCase().includes(value.toLowerCase())
);
setFilteredData(results);
});
};
return (
<div>
<input type="text" value={query} onChange={handleSearch} />
<ul>
{filteredData.map((item, index) => (
<li key={index}>{item}</li>
))}
</ul>
</div>
);
}





























































![Apple C1 vs Qualcomm Modem Performance [Speedtest]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96767/96767/96767-640.jpg)
![Apple Studio Display On Sale for $1249 [Lowest Price Ever]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96770/96770/96770-640.jpg)












![[Fixed] Chromecast (2nd gen) and Audio can’t Cast in ‘Untrusted’ outage](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2019/08/chromecast_audio_1.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)
























































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 139]: The Government Knows AGI Is Coming, Superintelligence Strategy, OpenAI’s $20,000 Per Month Agents & Top 100 Gen AI Apps](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20139%20cover-2.png)


![[The AI Show Episode 138]: Introducing GPT-4.5, Claude 3.7 Sonnet, Alexa+, Deep Research Now in ChatGPT Plus & How AI Is Disrupting Writing](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20138%20cover.png)