NASA’s Curiosity rover has found the longest chain carbon molecules yet on Mars
It’s a significant finding in the search for alien life.
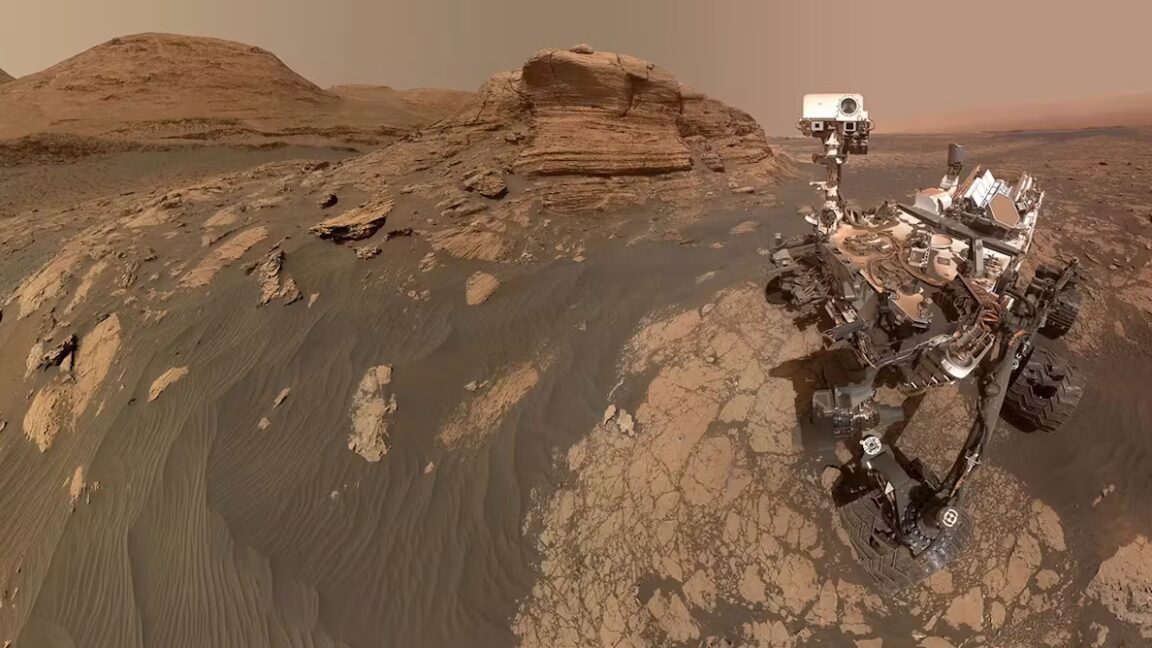

NASA’s Curiosity Mars rover has detected the largest organic (carbon-containing) molecules ever found on the red planet. The discovery is one of the most significant findings in the search for evidence of past life on Mars. This is because, on Earth at least, relatively complex, long-chain carbon molecules are involved in biology. These molecules could actually be fragments of fatty acids, which are found in, for example, the membranes surrounding biological cells.
Scientists think that, if life ever emerged on Mars, it was probably microbial in nature. Because microbes are so small, it’s difficult to be definitive about any potential evidence for life found on Mars. Such evidence needs more powerful scientific instruments that are too large to be put on a rover.
The organic molecules found by Curiosity consist of carbon atoms linked in long chains, with other elements bonded to them, like hydrogen and oxygen. They come from a 3.7-billion-year-old rock dubbed Cumberland, encountered by the rover at a presumed dried-up lakebed in Mars’s Gale Crater. Scientists used the Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM) instrument on the NASA rover to make their discovery.


























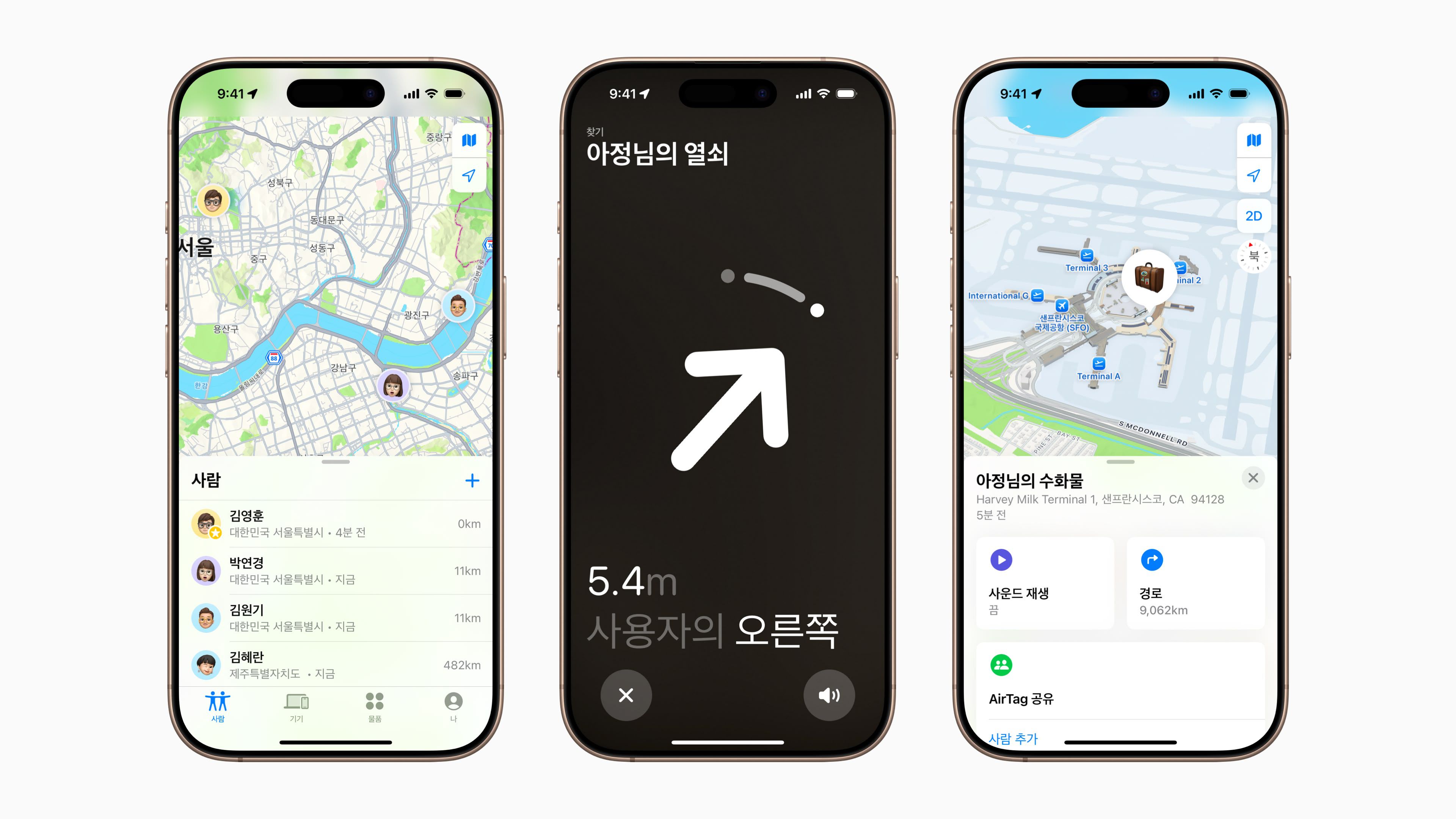

































![Apple Watch Series 10 Prototype with Mystery Sensor Surfaces [Images]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96892/96892/96892-640.jpg)

![Get Up to 69% Off Anker and Eufy Products on Final Day of Amazon's Big Spring Sale [Deal]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96888/96888/96888-640.jpg)
![Apple Officially Releases macOS Sequoia 15.4 [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96887/96887/96887-640.jpg)












![What’s new in Android’s March 2025 Google System Updates [U: 3/31]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/01/google-play-services-1.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)













-xl-xl.jpg)



















































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 141]: Road to AGI (and Beyond) #1 — The AI Timeline is Accelerating](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20141.1.png)
![[The AI Show Episode 140]: New AGI Warnings, OpenAI Suggests Government Policy, Sam Altman Teases Creative Writing Model, Claude Web Search & Apple’s AI Woes](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20140%20cover.png)
![[The AI Show Episode 139]: The Government Knows AGI Is Coming, Superintelligence Strategy, OpenAI’s $20,000 Per Month Agents & Top 100 Gen AI Apps](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20139%20cover-2.png)























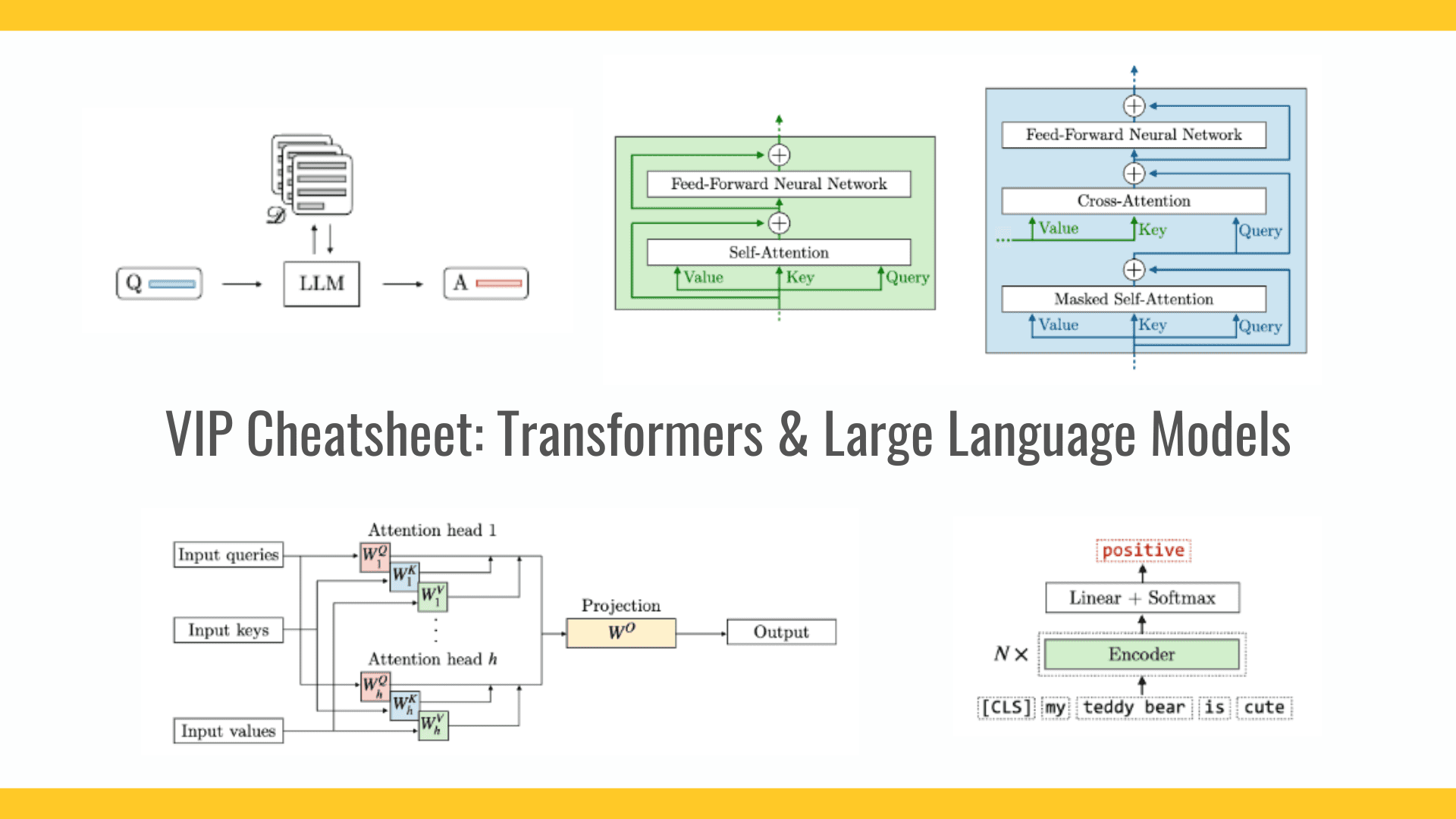























































































![Is this a suitable approach to architect a flutter app? [closed]](https://i.sstatic.net/4hMHGb1L.png)

















![From broke musician to working dev. How college drop-out Ryan Furrer taught himself to code [Podcast #166]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743189826063/2080cde4-6fc0-46fb-b98d-b3d59841e8c4.png?#)




























-1280x720.jpg?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=80&format=jpg&auto=webp#)


























































