OpenAI’s new image generator aims to be practical enough for designers and advertisers
OpenAI has released a new image generator that’s designed less for typical surrealist AI art and more for highly controllable and practical creation of visuals—a sign that OpenAI thinks its tools are ready for use in fields like advertising and graphic design. The image generator, which is now part of the company’s GPT-4o model, was…

OpenAI has released a new image generator that’s designed less for typical surrealist AI art and more for highly controllable and practical creation of visuals—a sign that OpenAI thinks its tools are ready for use in fields like advertising and graphic design.
The image generator, which is now part of the company’s GPT-4o model, was promised by OpenAI last May but wasn’t released. Requests for generated images on ChatGPT were filled by an older image generator called DALL-E. OpenAI has been tweaking the new model since then and will now release it over the coming weeks to all tiers of users starting today, replacing the older one.
The new model makes progress on technical issues that have plagued AI image generators for years. While most have been great at creating fantastical images or realistic deepfakes, they’ve been terrible at something called binding, which refers to the ability to identify certain objects correctly and put them in their proper place (like a sign that says “hot dogs” properly placed above a food cart, not somewhere else in the image).
It was only a few years ago that models started to succeed at things like “Put the red cube on top of the blue cube,” a feature that is essential for any creative professional use of AI. Generators also struggle with text generation, typically creating distorted jumbles of letter shapes that look more like captchas than readable text.
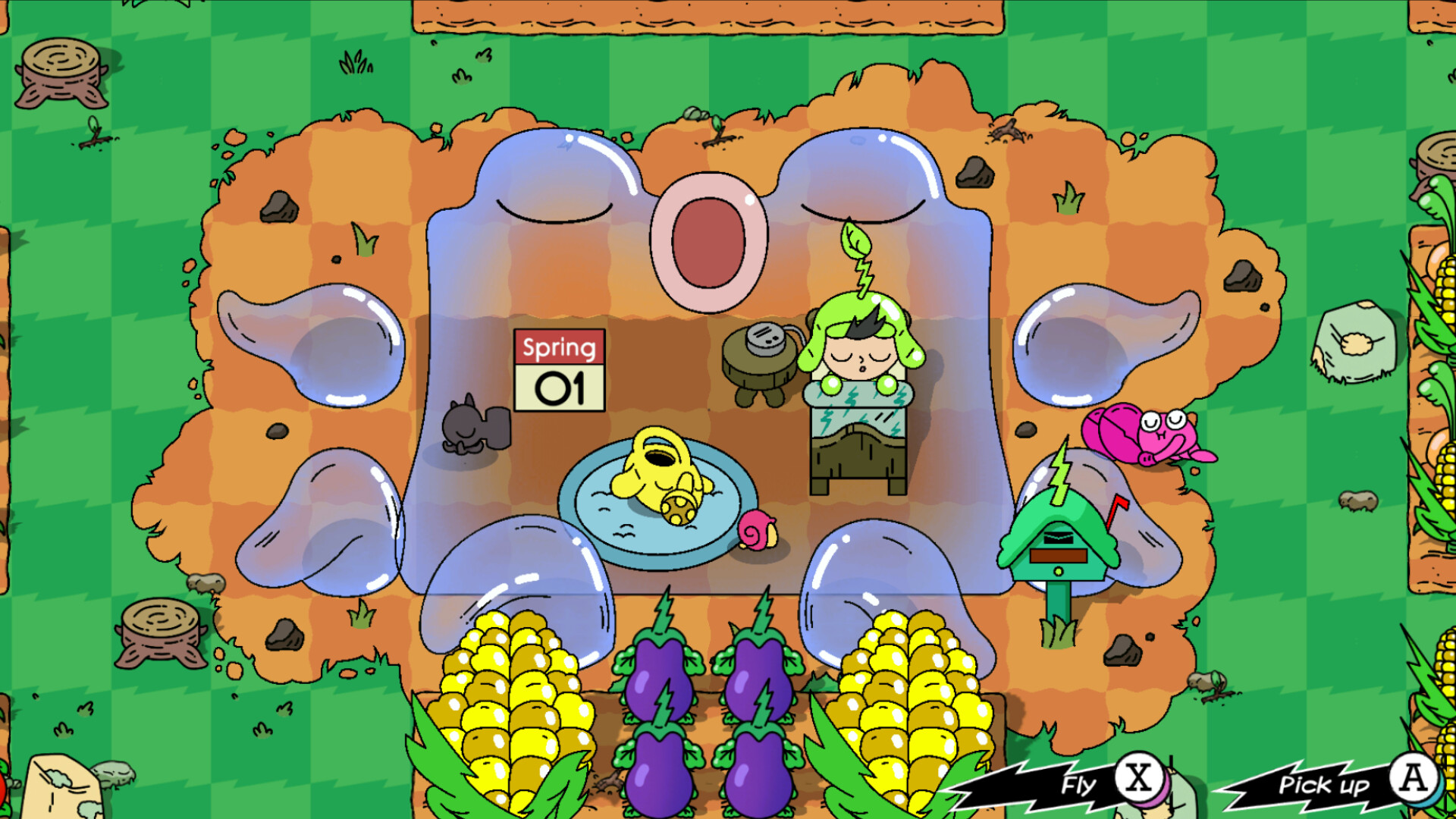
Example images from OpenAI show progress here. The model is able to generate 12 discrete graphics within a single image—like a cat emoji or a lightning bolt—and place them in proper order. Another shows four cocktails accompanied by recipe cards with accurate, legible text. More images show comic strips with text bubbles, mock advertisements, and instructional diagrams. The model also allows you to upload images to be modified, and it will be available in the video generator Sora as well as in GPT-4o.
It’s “a new tool for communication,” says Gabe Goh, the lead designer on the generator at OpenAI. Kenji Hata, a researcher at OpenAI who also worked on the tool, puts it a different way: “I think the whole idea is that we’re going away from, like, beautiful art.” It can still do that, he clarifies, but it will do more useful things too. “You can actually make images work for you,” he says, “and not just just look at them.”
It’s a clear sign that OpenAI is positioning the tool to be used more by creative professionals: think graphic designers, ad agencies, social media managers, or illustrators. But in entering this domain, OpenAI has two paths, both difficult.
One, it can target the skilled professionals who have long used programs like Adobe Photoshop, which is also investing heavily in AI tools that can fill images with generative AI.
“Adobe really has a stranglehold on this market, and they’re moving fast enough that I don’t know how compelling it is for people to switch,” says David Raskino, the cofounder and chief technical officer of Irreverent Labs, which works on AI video generation.
The second option is to target casual designers who have flocked to tools like Canva (which has also been investing in AI). This is an audience that may not have ever needed technically demanding software like Photoshop but would use more casual design tools to create visuals. To succeed here, OpenAI would have to lure people away from platforms built for design in hopes that the speed and quality of its own image generator would make the switch worth it (at least for part of the design process).
It’s also possible the tool will simply be used as many image generators are now: to create quick visuals that are “good enough” to accompany social media posts. But with OpenAI planning massive investments, including participation in the $500 billion Stargate project to build new data centers at unprecedented scale, it’s hard to imagine that the image generator won’t play some ambitious moneymaking role.
Regardless, the fact that OpenAI’s new image generator has pushed through notable technical hurdles has raised the bar for other AI companies. Clearing those hurdles likely required lots of very specific data, Raskino says, like millions of images in which text is properly displayed at lots of different angles and orientations. Now competing image generators will have to match those achievements to keep up.
“The pace of innovation should increase here,” Raskino says.

































































![iOS 19 Leak: First Look at Alleged VisionOS Inspired Redesign [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96824/96824/96824-640.jpg)

![OpenAI Announces 4o Image Generation [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96821/96821/96821-640.jpg)











![Do you care about Find My Device privacy settings? [Poll]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2024/06/Chipolo-One-Point-with-Find-My-Device-app.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)





























































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 140]: New AGI Warnings, OpenAI Suggests Government Policy, Sam Altman Teases Creative Writing Model, Claude Web Search & Apple’s AI Woes](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20140%20cover.png)
![[The AI Show Episode 139]: The Government Knows AGI Is Coming, Superintelligence Strategy, OpenAI’s $20,000 Per Month Agents & Top 100 Gen AI Apps](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20139%20cover-2.png)






















































































































































.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=80&format=jpg&auto=webp#)