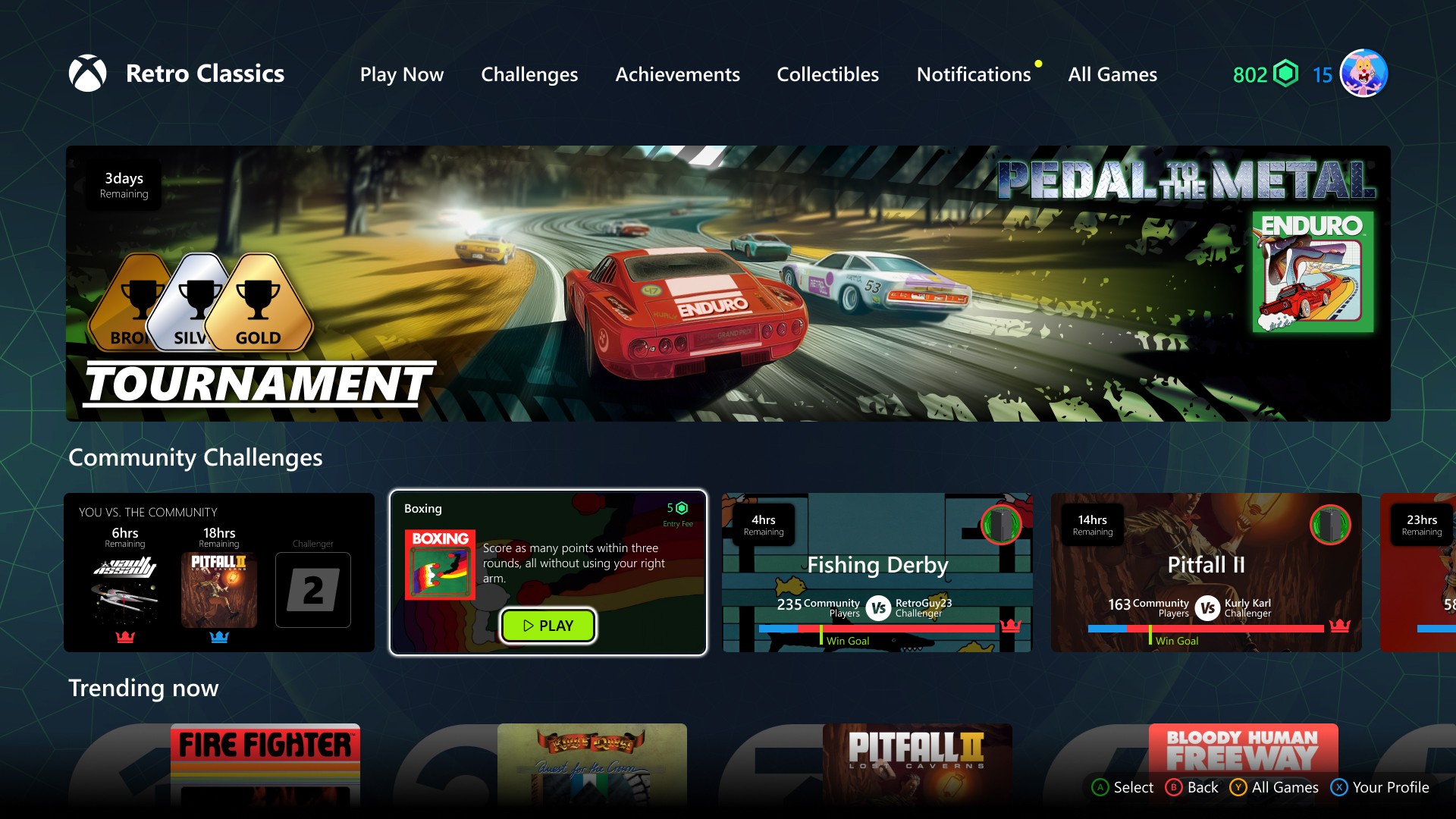
A Step-by-Step Implementation Tutorial for Building Modular AI Workflows Using Anthropic’s Claude Sonnet 3.7 through API and LangGraph
In this tutorial, we provide a practical guide for implementing LangGraph, a streamlined, graph-based AI orchestration framework, integrated seamlessly with Anthropic’s Claude API. Through detailed, executable code optimized for Google Colab, developers learn how to build and visualize AI workflows as interconnected nodes performing distinct tasks, such as generating concise answers, critically analyzing responses, and […] The post A Step-by-Step Implementation Tutorial for Building Modular AI Workflows Using Anthropic’s Claude Sonnet 3.7 through API and LangGraph appeared first on MarkTechPost.

In this tutorial, we provide a practical guide for implementing LangGraph, a streamlined, graph-based AI orchestration framework, integrated seamlessly with Anthropic’s Claude API. Through detailed, executable code optimized for Google Colab, developers learn how to build and visualize AI workflows as interconnected nodes performing distinct tasks, such as generating concise answers, critically analyzing responses, and automatically composing technical blog content. The compact implementation highlights LangGraph’s intuitive node-graph architecture. It can manage complex sequences of Claude-powered natural language tasks, from basic question-answering scenarios to advanced content generation pipelines.
from getpass import getpass
import os
anthropic_key = getpass("Enter your Anthropic API key: ")
os.environ["ANTHROPIC_API_KEY"] = anthropic_key
print("Key set:", "ANTHROPIC_API_KEY" in os.environ)We securely prompt users to input their Anthropic API key using Python’s getpass module, ensuring sensitive data isn’t displayed. It then sets this key as an environment variable (ANTHROPIC_API_KEY) and confirms successful storage.
import os
import json
import requests
from typing import Dict, List, Any, Callable, Optional, Union
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from IPython.display import display, HTML, clear_outputWe import essential libraries for building and visualizing structured AI workflows. It includes modules for handling data (json, requests, dataclasses), graph creation and visualization (networkx, matplotlib), interactive notebook display (IPython.display), and type annotations (typing) for clarity and maintainability.
try:
import anthropic
except ImportError:
print("Installing anthropic package...")
!pip install -q anthropic
import anthropic
from anthropic import AnthropicWe ensure the anthropic Python package is available for use. It attempts to import the module and, if not found, automatically installs it using pip in a Google Colab environment. After installation, it imports the Anthropic client, essential for interacting with Claude models via the Anthropic API. 4o
@dataclass
class NodeConfig:
name: str
function: Callable
inputs: List[str] = field(default_factory=list)
outputs: List[str] = field(default_factory=list)
config: Dict[str, Any] = field(default_factory=dict)This NodeConfig data class defines the structure of each node in the LangGraph workflow. Each node has a name, an executable function, optional inputs and outputs, and an optional config dictionary to store additional parameters. This setup allows for modular, reusable node definitions for graph-based AI tasks.
class LangGraph:
def __init__(self, api_key: Optional[str] = None):
self.api_key = api_key or os.environ.get("ANTHROPIC_API_KEY")
if not self.api_key:
from google.colab import userdata
try:
self.api_key = userdata.get('ANTHROPIC_API_KEY')
if not self.api_key:
raise ValueError("No API key found")
except:
print("No Anthropic API key found in environment variables or Colab secrets.")
self.api_key = input("Please enter your Anthropic API key: ")
if not self.api_key:
raise ValueError("Please provide an Anthropic API key")
self.client = Anthropic(api_key=self.api_key)
self.graph = nx.DiGraph()
self.nodes = {}
self.state = {}
def add_node(self, node_config: NodeConfig):
self.nodes[node_config.name] = node_config
self.graph.add_node(node_config.name)
for input_node in node_config.inputs:
if input_node in self.nodes:
self.graph.add_edge(input_node, node_config.name)
return self
def claude_node(self, name: str, prompt_template: str, model: str = "claude-3-7-sonnet-20250219",
inputs: List[str] = None, outputs: List[str] = None, system_prompt: str = None):
"""Convenience method to create a Claude API node"""
inputs = inputs or []
outputs = outputs or [name + "_response"]
def claude_fn(state, **kwargs):
prompt = prompt_template
for k, v in state.items():
if isinstance(v, str):
prompt = prompt.replace(f"{{{k}}}", v)
message_params = {
"model": model,
"max_tokens": 1000,
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": prompt}]
}
if system_prompt:
message_params["system"] = system_prompt
response = self.client.messages.create(**message_params)
return response.content[0].text
node_config = NodeConfig(
name=name,
function=claude_fn,
inputs=inputs,
outputs=outputs,
config={"model": model, "prompt_template": prompt_template}
)
return self.add_node(node_config)
def transform_node(self, name: str, transform_fn: Callable,
inputs: List[str] = None, outputs: List[str] = None):
"""Add a data transformation node"""
inputs = inputs or []
outputs = outputs or [name + "_output"]
node_config = NodeConfig(
name=name,
function=transform_fn,
inputs=inputs,
outputs=outputs
)
return self.add_node(node_config)
def visualize(self):
"""Visualize the graph"""
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
pos = nx.spring_layout(self.graph)
nx.draw(self.graph, pos, with_labels=True, node_color="lightblue",
node_size=1500, arrowsize=20, font_size=10)
plt.title("LangGraph Flow")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
print("\nGraph Structure:")
for node in self.graph.nodes():
successors = list(self.graph.successors(node))
if successors:
print(f" {node} → {', '.join(successors)}")
else:
print(f" {node} (endpoint)")
print()
def _get_execution_order(self):
"""Determine execution order based on dependencies"""
try:
return list(nx.topological_sort(self.graph))
except nx.NetworkXUnfeasible:
raise ValueError("Graph contains a cycle")
def execute(self, initial_state: Dict[str, Any] = None):
"""Execute the graph in topological order"""
self.state = initial_state or {}
execution_order = self._get_execution_order()
print("Executing LangGraph flow:")
for node_name in execution_order:
print(f"- Running node: {node_name}")
node = self.nodes[node_name]
inputs = {k: self.state.get(k) for k in node.inputs if k in self.state}
result = node.function(self.state, **inputs)
if len(node.outputs) == 1:
self.state[node.outputs[0]] = result
elif isinstance(result, (list, tuple)) and len(result) == len(node.outputs):
for i, output_name in enumerate(node.outputs):
self.state[output_name] = result[i]
print("Execution completed!")
return self.state
def run_example(question="What are the key benefits of using a graph-based architecture for AI workflows?"):
"""Run an example LangGraph flow with a predefined question"""
print(f"Running example with question: '{question}'")
graph = LangGraph()
def question_provider(state, **kwargs):
return question
graph.transform_node(
name="question_provider",
transform_fn=question_provider,
outputs=["user_question"]
)
graph.claude_node(
name="question_answerer",
prompt_template="Answer this question clearly and concisely: {user_question}",
inputs=["user_question"],
outputs=["answer"],
system_prompt="You are a helpful AI assistant."
)
graph.claude_node(
name="answer_analyzer",
prompt_template="Analyze if this answer addresses the question well: Question: {user_question}\nAnswer: {answer}",
inputs=["user_question", "answer"],
outputs=["analysis"],
system_prompt="You are a critical evaluator. Be brief but thorough."
)
graph.visualize()
result = graph.execute()
print("\n" + "="*50)
print("EXECUTION RESULTS:")
print("="*50)
print(f"\n Read More
Read More







































































![Apple Leads Global Wireless Earbuds Market in Q1 2025 [Chart]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97394/97394/97394-640.jpg)

![OpenAI Acquires Jony Ive's 'io' to Build Next-Gen AI Devices [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97399/97399/97399-640.jpg)














![YouTube rolling out updated miniplayer on Android, iPhone [U]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2024/11/YouTube-Android-app-1.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)

























































































.webp?#)






_Alan_Wilson_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)













































































































![[The AI Show Episode 148]: Microsoft’s Quiet AI Layoffs, US Copyright Office’s Bombshell AI Guidance, 2025 State of Marketing AI Report, and OpenAI Codex](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20148%20cover%20%281%29.png)