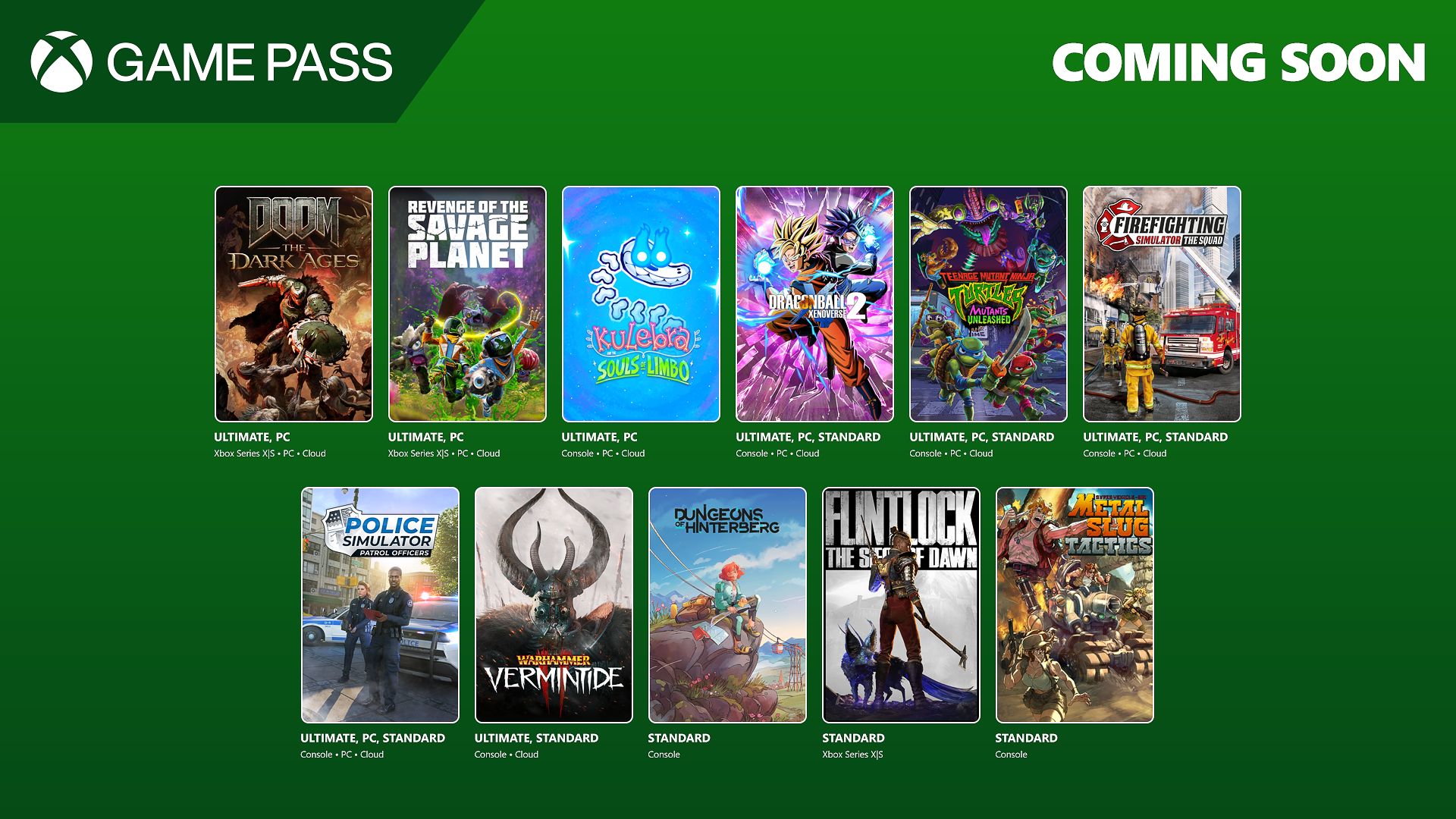
Educational Credentials in the Digital Age: Ensuring Authenticity and Portability
Introduction In today's interconnected world, verifying educational achievements has become increasingly important. Traditional paper certificates are susceptible to loss, damage, and forgery. Moreover, sharing these credentials across borders or institutions can be cumbersome. Digital credentials offer a solution—secure, verifiable, and easily shareable representations of academic accomplishments. This article explores how digital credentials, particularly those using decentralized identity technologies, are transforming the way we recognize and share educational achievements. The Limitations of Traditional Credentials Traditional educational credentials, such as paper diplomas and transcripts, have several drawbacks: Vulnerability to Fraud: Paper certificates can be easily forged, leading to issues in verifying the authenticity of an individual's qualifications. Inefficiency in Verification: Employers and institutions often have to contact issuing bodies directly to verify credentials, a process that can be time-consuming and prone to delays. Lack of Portability: Physical documents are not easily shareable, especially across international borders, making it difficult for individuals to present their qualifications when needed. Storage and Preservation Issues: Paper documents can be lost, damaged, or deteriorate over time, leading to potential loss of important records. The Rise of Digital Credentials Digital credentials address many of the shortcomings of traditional certificates. They are electronic representations of academic achievements that can be securely stored, easily shared, and quickly verified. These credentials often utilize technologies like blockchain and decentralized identifiers (DIDs) to ensure their authenticity and integrity. Understanding Decentralized Identity and Verifiable Credentials Decentralized identity (DID) is a framework that allows individuals to own and control their digital identities without relying on a central authority. In this model, users have unique identifiers stored on a blockchain, ensuring security and privacy. Verifiable credentials (VCs) are digital statements issued by a trusted authority (like a university) that attest to certain information about an individual. These credentials are cryptographically signed, making them tamper-evident and easily verifiable by third parties. Benefits of Digital Credentials Enhanced Security: Digital credentials are cryptographically secured, reducing the risk of forgery and unauthorized alterations. Immediate Verification: Employers and institutions can instantly verify the authenticity of a credential without contacting the issuing body. Global Portability: Digital credentials can be shared electronically, facilitating international education and employment opportunities. User Control: Individuals have control over who can access their credentials, enhancing privacy and consent. Cost-Effective: Reduces administrative costs associated with issuing, storing, and verifying paper certificates. Real-World Applications Higher Education: Universities can issue digital diplomas that graduates can add to their digital wallets, making it easier to share with potential employers. Professional Certifications: Certifying bodies can provide digital badges that professionals can display on their online profiles, showcasing verified skills. Online Learning Platforms: MOOCs and e-learning platforms can issue verifiable certificates to learners, enhancing the credibility of online education. Challenges and Considerations While digital credentials offer numerous advantages, there are challenges to consider: Standardization: The lack of universal standards can lead to compatibility issues between different systems. Digital Divide: Access to technology is not uniform, and some individuals may face barriers in accessing or using digital credentials. Data Privacy: Ensuring that personal data is protected and used ethically is paramount. The Future of Educational Credentials As technology continues to evolve, digital credentials are poised to become the norm in educational and professional settings. Initiatives are underway to develop interoperable standards, enhance security measures, and promote widespread adoption. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning could further streamline the verification process, making it more efficient and reliable. Conclusion Digital credentials represent a significant advancement in how we document and share educational achievements. By leveraging technologies like decentralized identity and verifiable credentials, we can create a more secure, efficient, and user-centric system. As we embrace these innovations, it's essential to address the associated challenges to ensure that the benefits are accessible to all.

In today's interconnected world, verifying educational achievements has become increasingly important. Traditional paper certificates are susceptible to loss, damage, and forgery. Moreover, sharing these credentials across borders or institutions can be cumbersome. Digital credentials offer a solution—secure, verifiable, and easily shareable representations of academic accomplishments. This article explores how digital credentials, particularly those using decentralized identity technologies, are transforming the way we recognize and share educational achievements.
The Limitations of Traditional Credentials
Traditional educational credentials, such as paper diplomas and transcripts, have several drawbacks:
Vulnerability to Fraud: Paper certificates can be easily forged, leading to issues in verifying the authenticity of an individual's qualifications.
Inefficiency in Verification: Employers and institutions often have to contact issuing bodies directly to verify credentials, a process that can be time-consuming and prone to delays.
Lack of Portability: Physical documents are not easily shareable, especially across international borders, making it difficult for individuals to present their qualifications when needed.
Storage and Preservation Issues: Paper documents can be lost, damaged, or deteriorate over time, leading to potential loss of important records.
The Rise of Digital Credentials
Digital credentials address many of the shortcomings of traditional certificates. They are electronic representations of academic achievements that can be securely stored, easily shared, and quickly verified. These credentials often utilize technologies like blockchain and decentralized identifiers (DIDs) to ensure their authenticity and integrity.
Understanding Decentralized Identity and Verifiable Credentials
Decentralized identity (DID) is a framework that allows individuals to own and control their digital identities without relying on a central authority. In this model, users have unique identifiers stored on a blockchain, ensuring security and privacy.
Verifiable credentials (VCs) are digital statements issued by a trusted authority (like a university) that attest to certain information about an individual. These credentials are cryptographically signed, making them tamper-evident and easily verifiable by third parties.
Benefits of Digital Credentials
Enhanced Security: Digital credentials are cryptographically secured, reducing the risk of forgery and unauthorized alterations.
Immediate Verification: Employers and institutions can instantly verify the authenticity of a credential without contacting the issuing body.
Global Portability: Digital credentials can be shared electronically, facilitating international education and employment opportunities.
User Control: Individuals have control over who can access their credentials, enhancing privacy and consent.
Cost-Effective: Reduces administrative costs associated with issuing, storing, and verifying paper certificates.
Real-World Applications
Higher Education: Universities can issue digital diplomas that graduates can add to their digital wallets, making it easier to share with potential employers.
Professional Certifications: Certifying bodies can provide digital badges that professionals can display on their online profiles, showcasing verified skills.
Online Learning Platforms: MOOCs and e-learning platforms can issue verifiable certificates to learners, enhancing the credibility of online education.
Challenges and Considerations
While digital credentials offer numerous advantages, there are challenges to consider:
Standardization: The lack of universal standards can lead to compatibility issues between different systems.
Digital Divide: Access to technology is not uniform, and some individuals may face barriers in accessing or using digital credentials.
Data Privacy: Ensuring that personal data is protected and used ethically is paramount.
The Future of Educational Credentials
As technology continues to evolve, digital credentials are poised to become the norm in educational and professional settings. Initiatives are underway to develop interoperable standards, enhance security measures, and promote widespread adoption. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning could further streamline the verification process, making it more efficient and reliable.
Conclusion
Digital credentials represent a significant advancement in how we document and share educational achievements. By leveraging technologies like decentralized identity and verifiable credentials, we can create a more secure, efficient, and user-centric system. As we embrace these innovations, it's essential to address the associated challenges to ensure that the benefits are accessible to all.








































































![Apple Shares Official Trailer for 'Echo Valley' Starring Julianne Moore, Sydney Sweeney, Domhnall Gleeson [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97250/97250/97250-640.jpg)

![Netflix Unveils Redesigned TV Interface With Smarter Recommendations [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97249/97249/97249-640.jpg)
















































































































_Wavebreakmedia_Ltd_IFE-240611_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)

_Alexey_Kotelnikov_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)






















































































































![[The AI Show Episode 146]: Rise of “AI-First” Companies, AI Job Disruption, GPT-4o Update Gets Rolled Back, How Big Consulting Firms Use AI, and Meta AI App](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20146%20cover.png)


























































































































































































-Pokemon-GO---Official-Gigantamax-Pokemon-Trailer-00-02-12.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)








.jpg?#)