Recovering Water From Cooling Tower Plumes With Plume Abatement
As a common feature with thermal power plants, cooling towers enable major water savings compared to straight through cooling methods. Even so, the big clouds of water vapor above them …read more



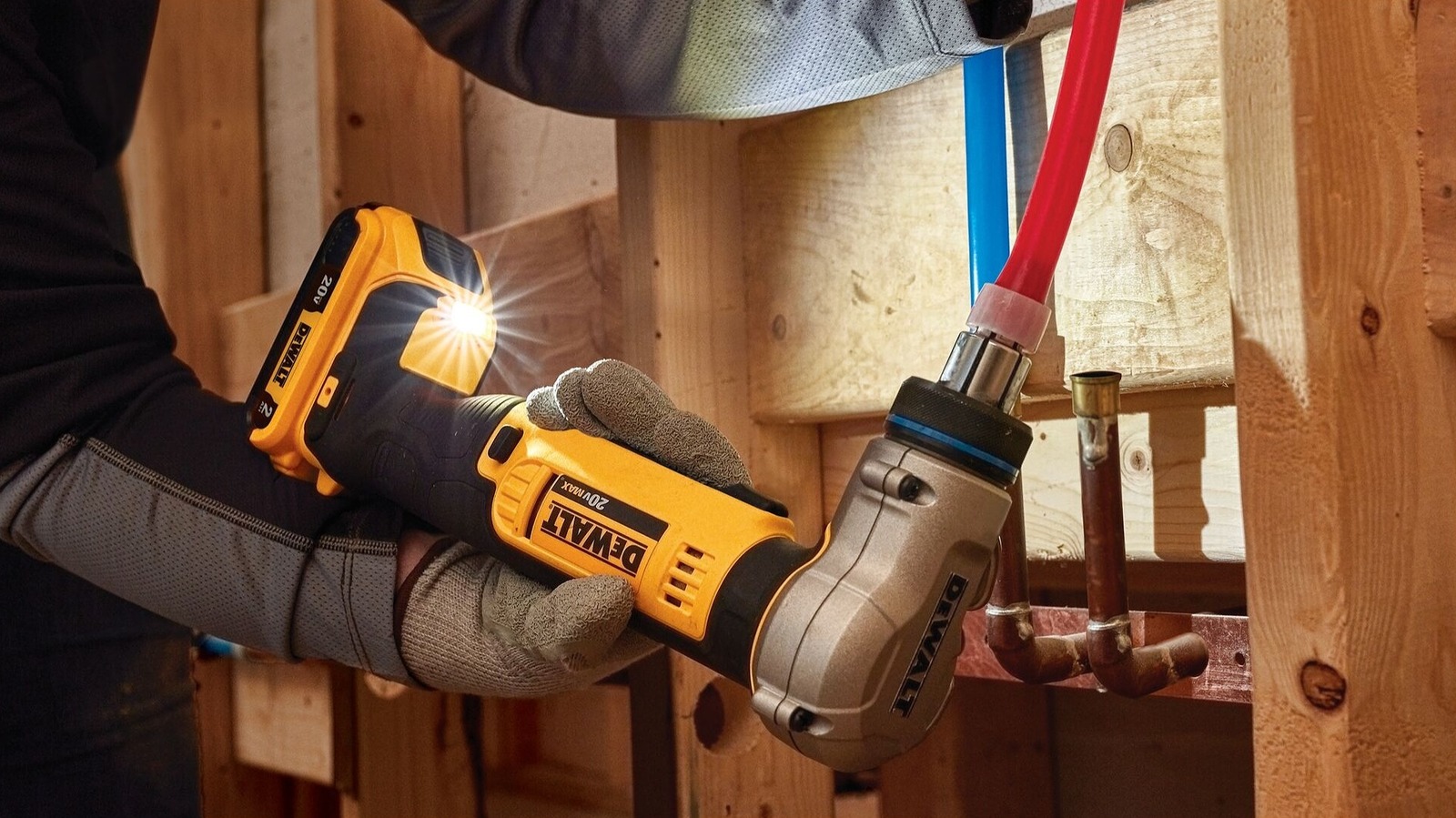
As a common feature with thermal power plants, cooling towers enable major water savings compared to straight through cooling methods. Even so, the big clouds of water vapor above them are a clear indication of how much cooling water is still effectively lost, with water vapor also having a negative impact on the environment. Using so-called plume abatement the amount of water vapor making it into the environment can be reduced, with recently a trial taking place at a French nuclear power plant.
This trial featured electrostatic droplet capture by US-based Infinite Cooling, which markets it as able to be retrofitted to existing cooling towers and similar systems, including the condensers of office HVAC systems. The basic principle as the name suggests involves capturing the droplets that form as the heated, saturated air leaves the cooling tower, in this case with an electrostatic charge. The captured droplets are then led to a reservoir from which it can be reused in the cooling system. This reduces both the visible plume and the amount of cooling water used.
In a 2021 review article by [Shuo Li] and [M.R. Flynn] in Environmental Fluid Mechanics the different approaches to plume abatement are looked at. Traditional plume abatement designs use parallel streams of air, with the goal being to have condensation commence as early as possible rather than after having been exhausted into the surrounding air. Some methods used a mesh cover to provide a surface to condense on, while a commercially available technology are condensing modules which use counterflow in an air-to-air heat exchanger.
Other commercial solutions include low-profile, forced-draft hybrid cooling towers, yet it seems that electrostatic droplet capture is a rather new addition here. With even purely passive systems already seeing ~10% recapturing of lost cooling water, these active methods may just be the ticket to significantly reduce cooling water needs without being forced to look at (expensive) dry cooling methods.
Top image: The French Chinon nuclear power plant with its low-profile, forced-draft cooling towers. (Credit: EDF/Marc Mourceau)





































































![Jony Ive and OpenAI Working on AI Device With No Screen [Kuo]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97401/97401/97401-640.jpg)

![Anthropic Unveils Claude 4 Models That Could Power Apple Xcode AI Assistant [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97407/97407/97407-640.jpg)
![Apple Accelerates Smart Glasses for 2026, Cancels Watch With Camera [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97408/97408/97408-640.jpg)


























-xl.jpg)












































































.webp?#)



_David_Hall_-Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)
_Andriy_Popov_Alamy_Stock_Photo.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)

















































































































![[The AI Show Episode 148]: Microsoft’s Quiet AI Layoffs, US Copyright Office’s Bombshell AI Guidance, 2025 State of Marketing AI Report, and OpenAI Codex](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20148%20cover%20%281%29.png)































































































































































![Laid off but not afraid with X-senior Microsoft Dev MacKevin Fey [Podcast #173]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1747965474270/ae29dc33-4231-47b2-afd1-689b3785fb79.png?#)






















-1-52-screenshot.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)

.png?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=70&format=jpg&auto=webp#)







































































