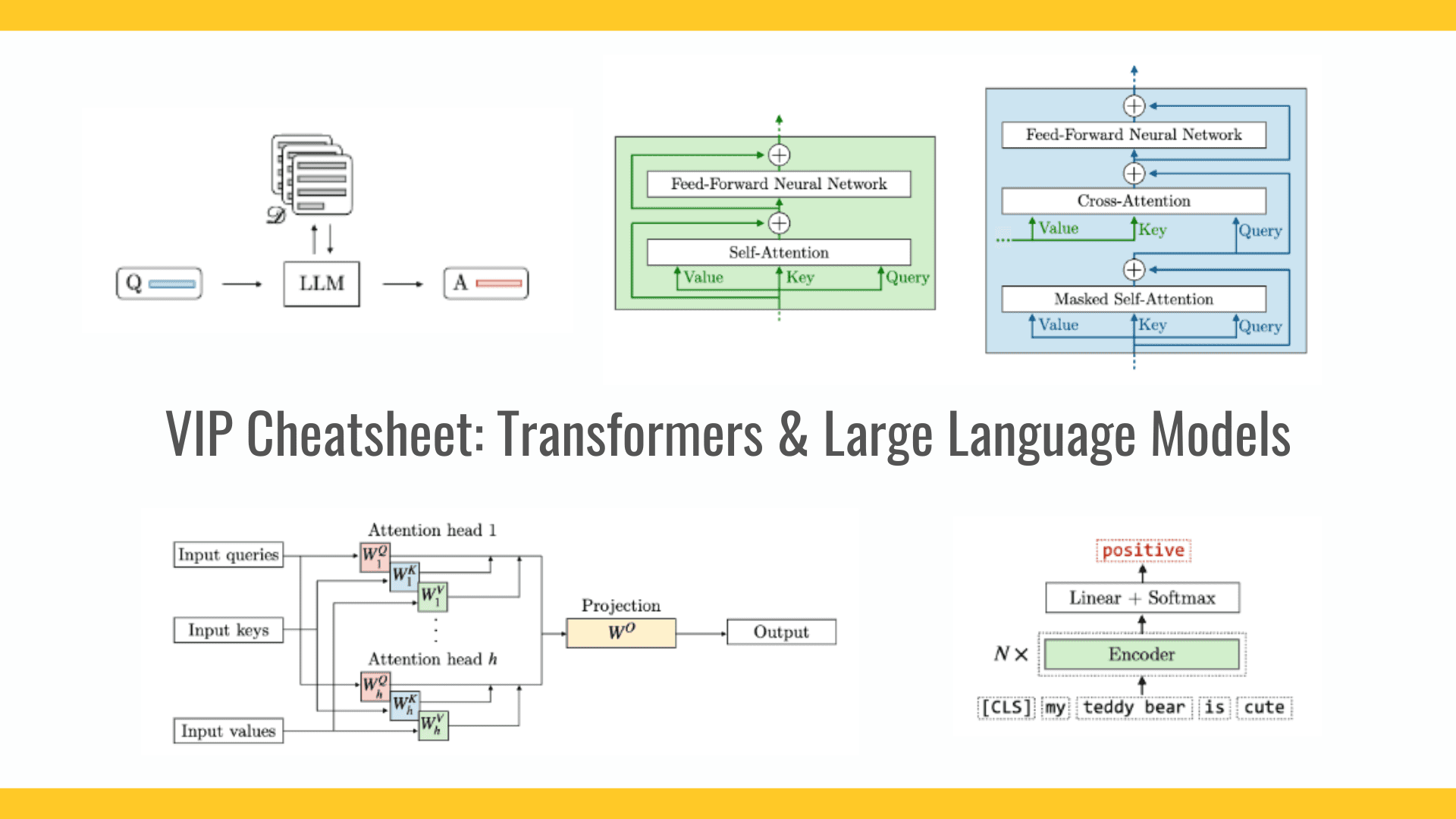
Tutorial 9: Handling User Input with Text Fields and Alerts
In this tutorial, we will create a simple iOS app that handles user input using a text field and shows alerts based on the user’s input. We will also use a timer to create a time-based challenge for the user. 1. Setup Your Project Open Xcode and create a new iOS project. Choose the Single View App template, and ensure you select Swift as the programming language. This tutorial will guide you on how to add the necessary UI elements and code. 2. Adding UI Elements In the storyboard file, drag and drop the following elements: UITextField: For entering the secret code. UIButton: For submitting the code. UILabel: To display the current level. UILabel: To show the remaining time on the timer. Connect these elements to your ViewController.swift file using @IBOutlet. 3. The Code Here’s the code you’ll need to add to ViewController.swift to handle the logic for this app. import UIKit class ViewController: UIViewController { // Outlets for UI elements @IBOutlet weak var codeTextField: UITextField! @IBOutlet weak var submitButton: UIButton! @IBOutlet weak var levelLabel: UILabel! @IBOutlet weak var timerLabel: UILabel! // Define the secret codes for each level let codes = ["1234", "5678", "91011", "121314"] // Define the current level and the timer var currentLevel = 0 var timer: Timer? var remainingTime = 10 var totalAttempts = 0 override func viewDidLoad() { super.viewDidLoad() startNewLevel() } // Action for the submit button @IBAction func submitCodeButtonTapped(_ sender: UIButton) { // Get the user input from the text field if let enteredCode = codeTextField.text, !enteredCode.isEmpty { totalAttempts += 1 checkCode(enteredCode) } else { showErrorAlert(message: "Please enter a code to proceed.") } } // Function to start a new level func startNewLevel() { // Reset the timer and update the UI for the new level levelLabel.text = "Level: \(currentLevel + 1)" remainingTime = 10 timerLabel.text = "Timer: \(remainingTime) sec" // Start a countdown timer startTimer() } // Timer functionality func startTimer() { // Invalidating any existing timer timer?.invalidate() // Create a new timer that updates every second timer = Timer.scheduledTimer(timeInterval: 1, target: self, selector: #selector(updateTimer), userInfo: nil, repeats: true) } @objc func updateTimer() { // Decrease remaining time by 1 second remainingTime -= 1 // Update the timer label timerLabel.text = "Timer: \(remainingTime) sec" // If time runs out, end the level with failure if remainingTime

In this tutorial, we will create a simple iOS app that handles user input using a text field and shows alerts based on the user’s input. We will also use a timer to create a time-based challenge for the user.
1. Setup Your Project
Open Xcode and create a new iOS project. Choose the Single View App template, and ensure you select Swift as the programming language. This tutorial will guide you on how to add the necessary UI elements and code.
2. Adding UI Elements
In the storyboard file, drag and drop the following elements:
-
UITextField: For entering the secret code. -
UIButton: For submitting the code. -
UILabel: To display the current level. -
UILabel: To show the remaining time on the timer.
Connect these elements to your ViewController.swift file using @IBOutlet.
3. The Code
Here’s the code you’ll need to add to ViewController.swift to handle the logic for this app.
import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController {
// Outlets for UI elements
@IBOutlet weak var codeTextField: UITextField!
@IBOutlet weak var submitButton: UIButton!
@IBOutlet weak var levelLabel: UILabel!
@IBOutlet weak var timerLabel: UILabel!
// Define the secret codes for each level
let codes = ["1234", "5678", "91011", "121314"]
// Define the current level and the timer
var currentLevel = 0
var timer: Timer?
var remainingTime = 10
var totalAttempts = 0
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
startNewLevel()
}
// Action for the submit button
@IBAction func submitCodeButtonTapped(_ sender: UIButton) {
// Get the user input from the text field
if let enteredCode = codeTextField.text, !enteredCode.isEmpty {
totalAttempts += 1
checkCode(enteredCode)
} else {
showErrorAlert(message: "Please enter a code to proceed.")
}
}
// Function to start a new level
func startNewLevel() {
// Reset the timer and update the UI for the new level
levelLabel.text = "Level: \(currentLevel + 1)"
remainingTime = 10
timerLabel.text = "Timer: \(remainingTime) sec"
// Start a countdown timer
startTimer()
}
// Timer functionality
func startTimer() {
// Invalidating any existing timer
timer?.invalidate()
// Create a new timer that updates every second
timer = Timer.scheduledTimer(timeInterval: 1, target: self, selector: #selector(updateTimer), userInfo: nil, repeats: true)
}
@objc func updateTimer() {
// Decrease remaining time by 1 second
remainingTime -= 1
// Update the timer label
timerLabel.text = "Timer: \(remainingTime) sec"
// If time runs out, end the level with failure
if remainingTime <= 0 {
timer?.invalidate()
showFailureAlert(message: "Time's up! Mission failed.")
}
}
// Function to check the entered code
func checkCode(_ enteredCode: String) {
// Check if the entered code is correct
if enteredCode == codes[currentLevel] {
showSuccessAlert(message: "Correct! Proceed to the next level.")
} else {
showFailureAlert(message: "Incorrect code. Try again!")
}
}
// Show success alert
func showSuccessAlert(message: String) {
let alertController = UIAlertController(title: "Success!", message: message, preferredStyle: .alert)
alertController.addAction(UIAlertAction(title: "Next Level", style: .default, handler: { _ in
self.currentLevel += 1
if self.currentLevel < self.codes.count {
self.startNewLevel()
} else {
self.showMissionCompleteAlert()
}
}))
self.present(alertController, animated: true, completion: nil)
}
// Show failure alert
func showFailureAlert(message: String) {
let alertController = UIAlertController(title: "Failure", message: message, preferredStyle: .alert)
alertController.addAction(UIAlertAction(title: "Retry", style: .default, handler: nil))
self.present(alertController, animated: true, completion: nil)
}
// Show error alert (e.g., empty text field)
func showErrorAlert(message: String) {
let alertController = UIAlertController(title: "Error", message: message, preferredStyle: .alert)
alertController.addAction(UIAlertAction(title: "Okay", style: .default, handler: nil))
self.present(alertController, animated: true, completion: nil)
}
// Show mission complete alert
func showMissionCompleteAlert() {
let alertController = UIAlertController(title: "Mission Complete!", message: "You've successfully completed all levels.", preferredStyle: .alert)
alertController.addAction(UIAlertAction(title: "Play Again", style: .default, handler: { _ in
self.resetGame()
}))
self.present(alertController, animated: true, completion: nil)
}
// Reset game after completing all levels
func resetGame() {
currentLevel = 0
totalAttempts = 0
startNewLevel()
}
}
4. Testing the App
Once you have completed the code, run the app in the simulator. Enter a code into the text field, tap the submit button, and see how the alerts and timer interact with the user’s input.
5. Conclusion
In this tutorial, we’ve built an app that challenges users to enter secret codes under a time limit. With user input handling, alerts, and timers, this app demonstrates key features that can be adapted to many types of iOS applications.
Happy coding!



























































![Apple Watch Series 10 Prototype with Mystery Sensor Surfaces [Images]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96892/96892/96892-640.jpg)

![Get Up to 69% Off Anker and Eufy Products on Final Day of Amazon's Big Spring Sale [Deal]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96888/96888/96888-640.jpg)
![Apple Officially Releases macOS Sequoia 15.4 [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96887/96887/96887-640.jpg)












![What’s new in Android’s March 2025 Google System Updates [U: 3/31]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/01/google-play-services-1.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)













-xl-xl.jpg)




















































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 141]: Road to AGI (and Beyond) #1 — The AI Timeline is Accelerating](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20141.1.png)
![[The AI Show Episode 140]: New AGI Warnings, OpenAI Suggests Government Policy, Sam Altman Teases Creative Writing Model, Claude Web Search & Apple’s AI Woes](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20140%20cover.png)
![[The AI Show Episode 139]: The Government Knows AGI Is Coming, Superintelligence Strategy, OpenAI’s $20,000 Per Month Agents & Top 100 Gen AI Apps](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20139%20cover-2.png)













































































































![Is this a suitable approach to architect a flutter app? [closed]](https://i.sstatic.net/4hMHGb1L.png)

















![From broke musician to working dev. How college drop-out Ryan Furrer taught himself to code [Podcast #166]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743189826063/2080cde4-6fc0-46fb-b98d-b3d59841e8c4.png?#)




























-1280x720.jpg?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=80&format=jpg&auto=webp#)


























































