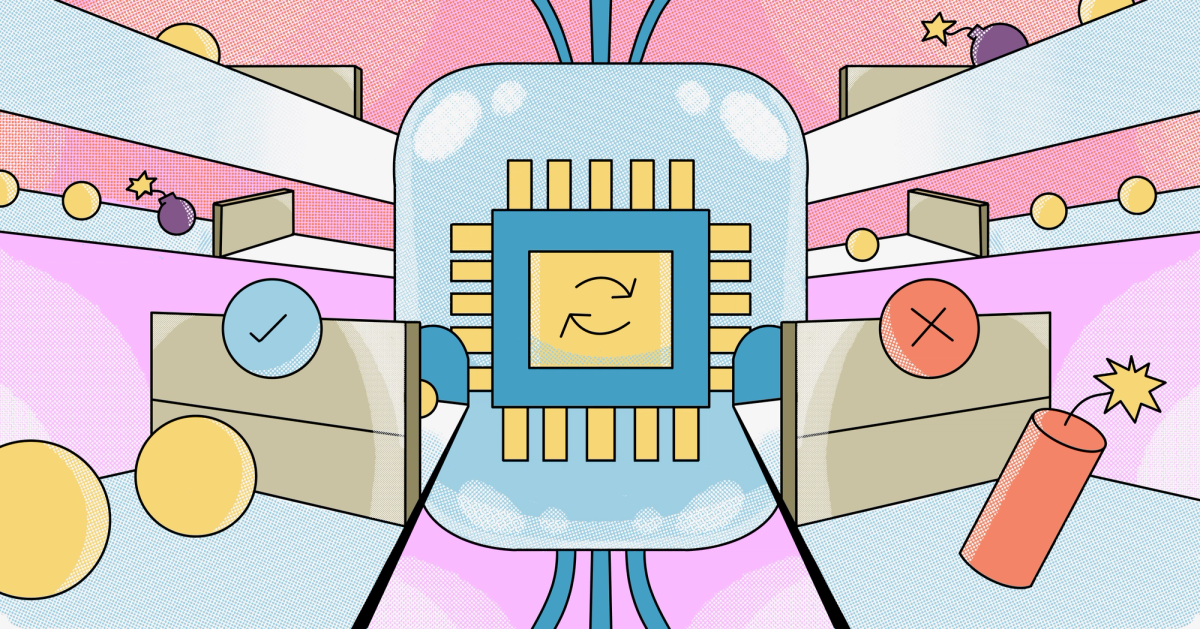
Understanding the Key Differences between AI vs. Automation
In today’s tech-driven world, terms like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and automation are often used interchangeably, but they serve very different purposes. While both improve efficiency and reduce human effort, their capabilities and applications vary significantly. This article explores the distinctions between AI and automation, their use cases, and how businesses leverage them. 1. What is Automation? Automation refers to using technology to perform repetitive, rule-based tasks without human intervention. It follows predefined instructions and does not learn or adapt on its own. Key Features of Automation: ✔ Rule-based: Operates on fixed "if-then" logic. ✔ No learning capability: Cannot improve without reprogramming. ✔ Consistency: Performs tasks the same way every time. ✔ Reduces human effort: Ideal for manual, repetitive work. Examples of Automation: Manufacturing robots assembling cars. Email autoresponders sending pre-written replies. Payroll software processing salaries automatically. 2. What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)? AI refers to systems that mimic human intelligence, enabling machines to learn, reason, and make decisions. Unlike automation, AI can analyze data, recognize patterns, and improve over time. Key Features of AI: ✔ Learning & Adaptation: Uses machine learning (ML) to improve from data. ✔ Decision-making: Can handle uncertainty and make predictions. ✔ Handles unstructured data: Processes text, images, and speech. ✔ Human-like reasoning: Powers chatbots, recommendation engines, and more. Examples of AI: ChatGPT & virtual assistants (Siri, Alexa) understanding natural language. Self-driving cars making real-time traffic decisions. Fraud detection systems analyzing transaction patterns. 3. Key Differences Between AI and Automation Aspect Automation Artificial Intelligence (AI) Intelligence Follows fixed rules, no learning. Learns from data, adapts, and improves. Flexibility Works only in structured environments. Handles unstructured, dynamic scenarios. Decision-making No decision-making, just execution. Makes predictions and decisions. Human-like Ability No cognitive functions. Simulates reasoning, perception, and learning. Examples Robotic arms, scheduled scripts. Facial recognition, AI chatbots, recommendation systems. 4. How AI and Automation Work Together While different, AI and automation often complement each other: Robotic Process Automation (RPA) + AI = Smarter automation that handles exceptions (e.g., processing invoices with varying formats). AI-powered chatbots automate customer service while understanding natural language. Smart factories use AI-driven robots that adapt to production changes. 5. Which One Should You Use? Choose Automation if: You need to streamline repetitive, predictable tasks (e.g., data entry, assembly lines). Choose AI if: You need intelligent decision-making, pattern recognition, or interaction with unstructured data (e.g., customer support, medical diagnosis). Conclusion While automation replaces manual work with machines, AI enhances machines with human-like intelligence. Businesses benefit most by combining both—using automation for efficiency and AI for smarter decision-making.

In today’s tech-driven world, terms like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and automation are often used interchangeably, but they serve very different purposes. While both improve efficiency and reduce human effort, their capabilities and applications vary significantly. This article explores the distinctions between AI and automation, their use cases, and how businesses leverage them.
1. What is Automation?
Automation refers to using technology to perform repetitive, rule-based tasks without human intervention. It follows predefined instructions and does not learn or adapt on its own.
Key Features of Automation:
✔ Rule-based: Operates on fixed "if-then" logic.
✔ No learning capability: Cannot improve without reprogramming.
✔ Consistency: Performs tasks the same way every time.
✔ Reduces human effort: Ideal for manual, repetitive work.
Examples of Automation:
- Manufacturing robots assembling cars.
- Email autoresponders sending pre-written replies.
- Payroll software processing salaries automatically.
2. What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
AI refers to systems that mimic human intelligence, enabling machines to learn, reason, and make decisions. Unlike automation, AI can analyze data, recognize patterns, and improve over time.
Key Features of AI:
✔ Learning & Adaptation: Uses machine learning (ML) to improve from data.
✔ Decision-making: Can handle uncertainty and make predictions.
✔ Handles unstructured data: Processes text, images, and speech.
✔ Human-like reasoning: Powers chatbots, recommendation engines, and more.
Examples of AI:
- ChatGPT & virtual assistants (Siri, Alexa) understanding natural language.
- Self-driving cars making real-time traffic decisions.
- Fraud detection systems analyzing transaction patterns.
3. Key Differences Between AI and Automation
| Aspect | Automation | Artificial Intelligence (AI) |
|---|---|---|
| Intelligence | Follows fixed rules, no learning. | Learns from data, adapts, and improves. |
| Flexibility | Works only in structured environments. | Handles unstructured, dynamic scenarios. |
| Decision-making | No decision-making, just execution. | Makes predictions and decisions. |
| Human-like Ability | No cognitive functions. | Simulates reasoning, perception, and learning. |
| Examples | Robotic arms, scheduled scripts. | Facial recognition, AI chatbots, recommendation systems. |
4. How AI and Automation Work Together
While different, AI and automation often complement each other:
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA) + AI = Smarter automation that handles exceptions (e.g., processing invoices with varying formats).
- AI-powered chatbots automate customer service while understanding natural language.
- Smart factories use AI-driven robots that adapt to production changes.
5. Which One Should You Use?
- Choose Automation if: You need to streamline repetitive, predictable tasks (e.g., data entry, assembly lines).
- Choose AI if: You need intelligent decision-making, pattern recognition, or interaction with unstructured data (e.g., customer support, medical diagnosis).
Conclusion
While automation replaces manual work with machines, AI enhances machines with human-like intelligence. Businesses benefit most by combining both—using automation for efficiency and AI for smarter decision-making.









































































![Apple Ships 55 Million iPhones, Claims Second Place in Q1 2025 Smartphone Market [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/97185/97185/97185-640.jpg)













![Android Auto light theme surfaces for the first time in years and looks nearly finished [Gallery]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2023/01/android-auto-dashboard-1.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)





























































































_Andreas_Prott_Alamy.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale#)




























































































































![[The AI Show Episode 145]: OpenAI Releases o3 and o4-mini, AI Is Causing “Quiet Layoffs,” Executive Order on Youth AI Education & GPT-4o’s Controversial Update](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20145%20cover.png)





























































































































































![[DEALS] Mail Backup X Individual Edition: Lifetime Subscription (72% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)































































































