Layer by Layer: The OSI Model: Layer 3
Preamble: This space will be utilized to synthesize my notes and help improve my learning process while I study for the CompTIA Network+ N10-009 certification exam. Please follow along for more Network+ notes and feel free to ask any questions or, if I get something wrong, offer suggestions to correct any mistakes. Network Layer (Layer 3) This layer is responsible for moving data to other networks. While the data-link layer is responsible for forwarding data using a hardware address within a single segment the Network layer moves data around networks by using logical addressing and host IDs. The Network layer encapsulates data into a PDU called a packet and it is given a destination networking address. The most common for of networking address is an Internet Protocol (IP) address. The packet is then forwarded by a device called a router and it will move from one router to the next (hop) until it reaches its final destination. Microsoft Windows Command Prompt showing the results of the ipconfig command. Devices that Operate on the Network Layer Router: Network device that is used to connect different networks together. It utilizes PDUs called Packets and logical addressing. They use protocols to determine the best path to send the packet like: RIP (Routing Information Protocol) OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Firewalls: Enforces rules to prevent unauthorized traffic into or out of a network. It utilizes Access Control Lists (ACLs) to filter network traffic. Layer 3 switches: These are switches that have routing capabilities and can route traffic between different VLANs and IP networks. Ideal for larger networks that require inter-VLAN routing and efficient traffic management. Used in core network environments to improve performance and scalability. Thanks for joining me to learn more about Layer 3, the Network layer. Next we will peer into Layer 4, the Transport layer.
Preamble:
This space will be utilized to synthesize my notes and help improve my learning process while I study for the CompTIA Network+ N10-009 certification exam. Please follow along for more Network+ notes and feel free to ask any questions or, if I get something wrong, offer suggestions to correct any mistakes.
Network Layer (Layer 3)
This layer is responsible for moving data to other networks. While the data-link layer is responsible for forwarding data using a hardware address within a single segment the Network layer moves data around networks by using logical addressing and host IDs. The Network layer encapsulates data into a PDU called a packet and it is given a destination networking address. The most common for of networking address is an Internet Protocol (IP) address. The packet is then forwarded by a device called a router and it will move from one router to the next (hop) until it reaches its final destination.
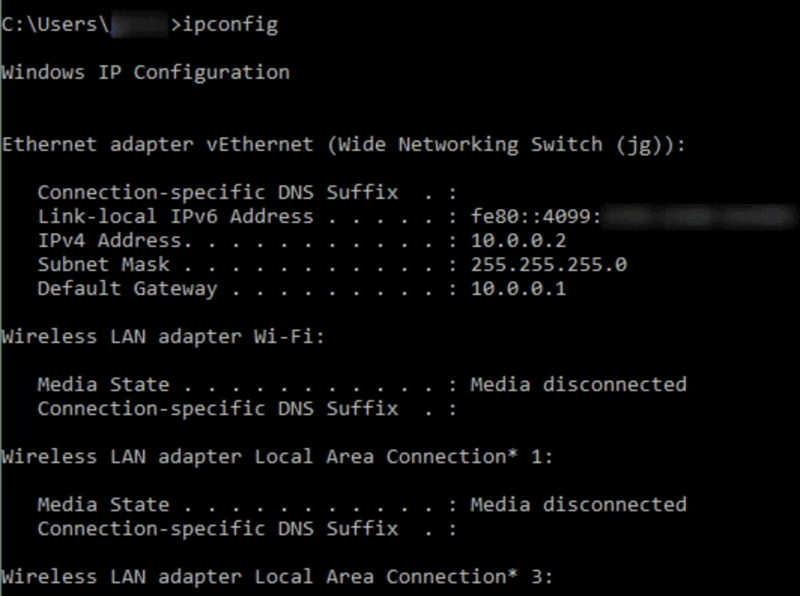
 Microsoft Windows Command Prompt showing the results of the ipconfig command.
Microsoft Windows Command Prompt showing the results of the ipconfig command.
Devices that Operate on the Network Layer
Router: Network device that is used to connect different networks together. It utilizes PDUs called Packets and logical addressing. They use protocols to determine the best path to send the packet like:
- RIP (Routing Information Protocol)
- OSPF (Open Shortest Path First)
- BGP (Border Gateway Protocol)
Firewalls: Enforces rules to prevent unauthorized traffic into or out of a network. It utilizes Access Control Lists (ACLs) to filter network traffic.
Layer 3 switches: These are switches that have routing capabilities and can route traffic between different VLANs and IP networks. Ideal for larger networks that require inter-VLAN routing and efficient traffic management. Used in core network environments to improve performance and scalability.
Thanks for joining me to learn more about Layer 3, the Network layer. Next we will peer into Layer 4, the Transport layer.


































































![Redesigned Plastic Apple Watch SE in 'Serious Jeopardy' [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96789/96789/96789-640.jpg)
![Apple Watch to Gain Cameras in Future Models [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96790/96790/96790-640.jpg)
![Apple M4 Mac Mini on Sale for $499 [Lowest Price Ever]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96788/96788/96788-640.jpg)
![Apple Shares First Look and Premiere Date for 'The Buccaneers' Season Two [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96786/96786/96786-640.jpg)














![Google updates Circle to Search with transparent navigation bar [U]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/01/galaxy-s25-circle-to-search-1.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)























































































_robertharding_Alamy.jpg?#)





































































![[The AI Show Episode 139]: The Government Knows AGI Is Coming, Superintelligence Strategy, OpenAI’s $20,000 Per Month Agents & Top 100 Gen AI Apps](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20139%20cover-2.png)


![[The AI Show Episode 138]: Introducing GPT-4.5, Claude 3.7 Sonnet, Alexa+, Deep Research Now in ChatGPT Plus & How AI Is Disrupting Writing](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20138%20cover.png)














































































































![From hating coding to programming satellites at age 37 with Francesco Ciulla [Podcast #165]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1742585568977/09b25b8e-8c92-4f4b-853f-64b7f7915980.png?#)




![[DEALS] The All-in-One CompTIA Certification Prep Courses Bundle (90% off) & Other Deals Up To 98% Off – Offers End Soon!](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)
































.png?#)