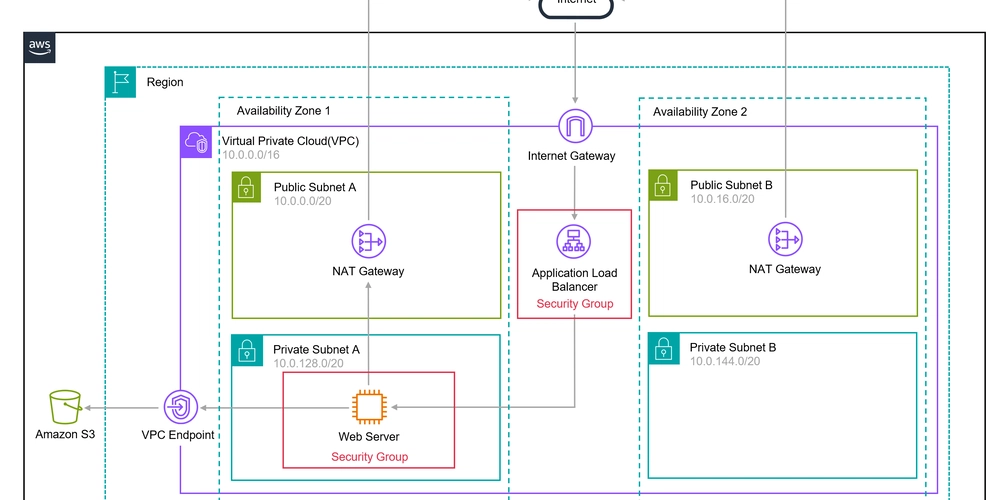
How Does Minikube Handle Storage Volumes in 2025?
Minikube continues to be a vital tool for developers looking to create Kubernetes clusters locally. As of 2025, Minikube's handling of storage volumes has evolved to enhance flexibility and performance. Understanding how Minikube manages storage is crucial for efficiently deploying and maintaining applications. This article delves into how Minikube manages storage volumes, offering insights into the new improvements and practices. Understanding Storage Volumes in Minikube Kubernetes employs volumes to manage persistent data; Minikube manages these volumes efficiently even in constrained local environments. In 2025, enhancements to Minikube have improved how volumes are created, assigned, and utilized across various nodes. Types of Storage Volumes Supported HostPath Volumes: Minikube supports HostPath volumes, which link nodes to directories on the host system. This setup is perfect for development and testing but should be used with caution in production. EmptyDir Volumes: These appear when a pod is assigned to a node and disappear upon pod termination. They're ideal for intermediate storage needs during app deployment. Persistent Volumes: Dynamic Provisioning: Minikube now supports dynamic provisioning out-of-the-box, significantly streamlining volume management. Storage Classes: Developers can define storage classes, improving storage abstraction and automating storage provisioning. Advanced Storage Features in 2025 1. Improved Performance By leveraging the latest disk I/O technologies, Minikube ensures that storage operations are both speedy and resource-efficient. New caching strategies reduce latency and enhance data retrieval times. 2. Enhanced Security Minikube now supports encryption for sensitive data stored in volumes. This layered approach provides an additional security layer, shielding data from unauthorized access. 3. Backup and Recovery Solutions Minikube includes integrated solutions for backing up and restoring data. These tools ensure data resilience and minimize downtime during disaster recovery operations. Setting Up Minikube For users looking to embark on their Minikube journey, here's a comprehensive guide on installing Minikube and Docker in Windows 10. Accessing Minikube from Outside Network To utilize Minikube beyond local development environments, you'll need to configure network settings for external access. Discover the steps necessary for accessing Minikube from outside your network. Removing a Minikube Cluster When it's time to decommission a Minikube setup, proper removal processes are essential to clean up resources. Follow the instructions on how to delete a Minikube cluster effectively. Conclusion Minikube's evolving capabilities in 2025 reflect its commitment to enhancing Kubernetes development. With advanced volume management, improved performance, and robust security measures, Minikube remains an indispensable tool for developers. By understanding and utilizing these storage features, you can maximize productivity and reliability in your development environment. Keywords: Minikube, storage volumes, Kubernetes, 2025, HostPath, EmptyDir, Persistent Volumes, dynamic provisioning, performance, security, backup and recovery. This markdown-formatted article is optimized with relevant keywords and embeds links to additional resources, providing a comprehensive take on Minikube's storage handling in 2025.

Minikube continues to be a vital tool for developers looking to create Kubernetes clusters locally. As of 2025, Minikube's handling of storage volumes has evolved to enhance flexibility and performance. Understanding how Minikube manages storage is crucial for efficiently deploying and maintaining applications. This article delves into how Minikube manages storage volumes, offering insights into the new improvements and practices.
Understanding Storage Volumes in Minikube
Kubernetes employs volumes to manage persistent data; Minikube manages these volumes efficiently even in constrained local environments. In 2025, enhancements to Minikube have improved how volumes are created, assigned, and utilized across various nodes.
Types of Storage Volumes Supported
HostPath Volumes: Minikube supports HostPath volumes, which link nodes to directories on the host system. This setup is perfect for development and testing but should be used with caution in production.
EmptyDir Volumes: These appear when a pod is assigned to a node and disappear upon pod termination. They're ideal for intermediate storage needs during app deployment.
-
Persistent Volumes:
- Dynamic Provisioning: Minikube now supports dynamic provisioning out-of-the-box, significantly streamlining volume management.
- Storage Classes: Developers can define storage classes, improving storage abstraction and automating storage provisioning.
Advanced Storage Features in 2025
1. Improved Performance
By leveraging the latest disk I/O technologies, Minikube ensures that storage operations are both speedy and resource-efficient. New caching strategies reduce latency and enhance data retrieval times.
2. Enhanced Security
Minikube now supports encryption for sensitive data stored in volumes. This layered approach provides an additional security layer, shielding data from unauthorized access.
3. Backup and Recovery Solutions
Minikube includes integrated solutions for backing up and restoring data. These tools ensure data resilience and minimize downtime during disaster recovery operations.
Setting Up Minikube
For users looking to embark on their Minikube journey, here's a comprehensive guide on installing Minikube and Docker in Windows 10.
Accessing Minikube from Outside Network
To utilize Minikube beyond local development environments, you'll need to configure network settings for external access. Discover the steps necessary for accessing Minikube from outside your network.
Removing a Minikube Cluster
When it's time to decommission a Minikube setup, proper removal processes are essential to clean up resources. Follow the instructions on how to delete a Minikube cluster effectively.
Conclusion
Minikube's evolving capabilities in 2025 reflect its commitment to enhancing Kubernetes development. With advanced volume management, improved performance, and robust security measures, Minikube remains an indispensable tool for developers. By understanding and utilizing these storage features, you can maximize productivity and reliability in your development environment.
Keywords: Minikube, storage volumes, Kubernetes, 2025, HostPath, EmptyDir, Persistent Volumes, dynamic provisioning, performance, security, backup and recovery.
This markdown-formatted article is optimized with relevant keywords and embeds links to additional resources, providing a comprehensive take on Minikube's storage handling in 2025.






























































![Get Up to 69% Off Anker and Eufy Products on Final Day of Amazon's Big Spring Sale [Deal]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96888/96888/96888-640.jpg)
![Apple Officially Releases macOS Sequoia 15.4 [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96887/96887/96887-640.jpg)












![What’s new in Android’s March 2025 Google System Updates [U: 3/31]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/01/google-play-services-1.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)


![Oppo ditches Alert Slider in teaser for smaller Find X8s, five-camera Find X8 Ultra [Gallery]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/03/oppo-find-x8s-ultra-teaser-1.jpg?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)











-xl-xl.jpg)






















































































































































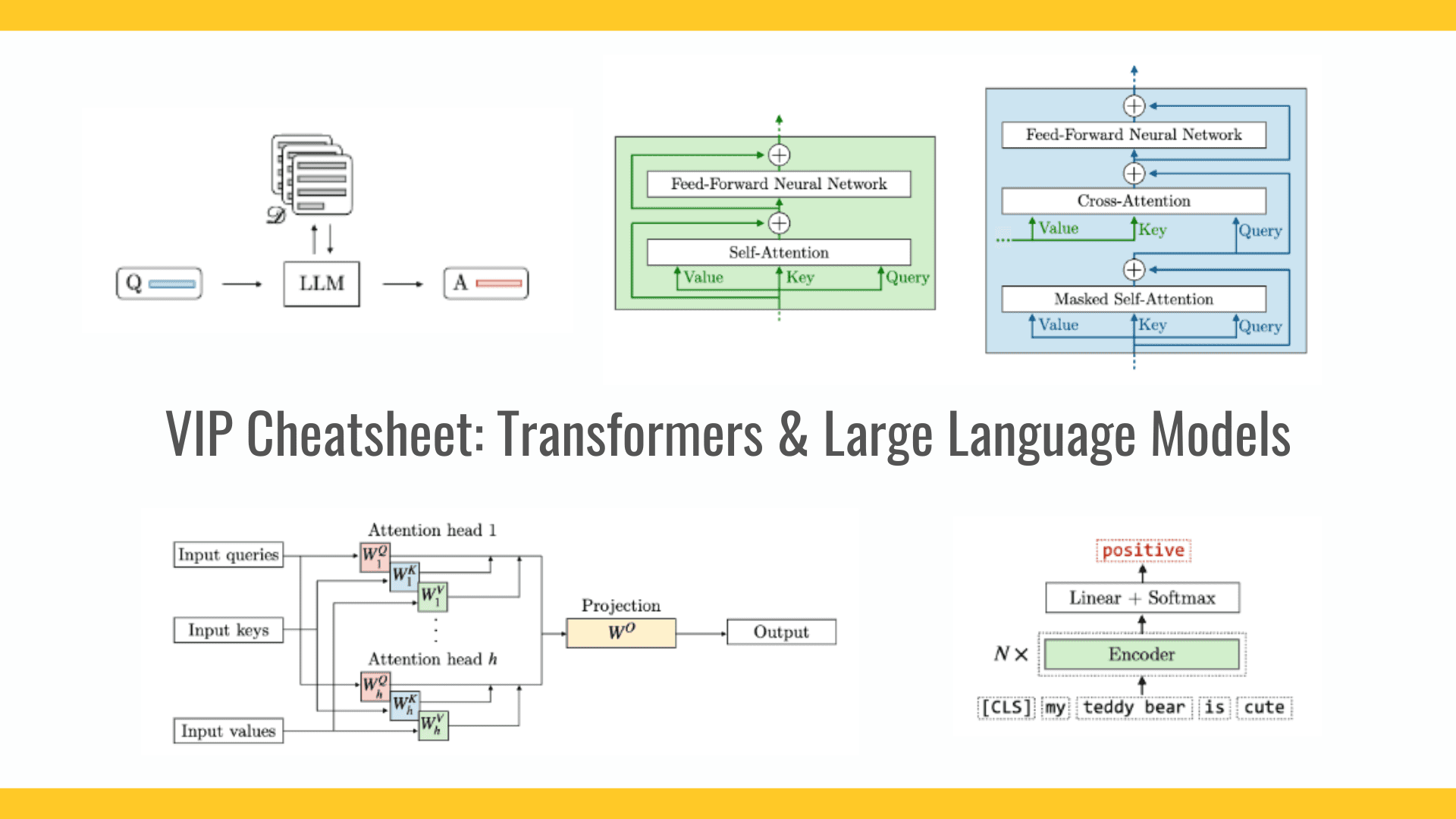
![[The AI Show Episode 141]: Road to AGI (and Beyond) #1 — The AI Timeline is Accelerating](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20141.1.png)
![[The AI Show Episode 140]: New AGI Warnings, OpenAI Suggests Government Policy, Sam Altman Teases Creative Writing Model, Claude Web Search & Apple’s AI Woes](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20140%20cover.png)
![[The AI Show Episode 139]: The Government Knows AGI Is Coming, Superintelligence Strategy, OpenAI’s $20,000 Per Month Agents & Top 100 Gen AI Apps](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20139%20cover-2.png)



























































































































![From broke musician to working dev. How college drop-out Ryan Furrer taught himself to code [Podcast #166]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743189826063/2080cde4-6fc0-46fb-b98d-b3d59841e8c4.png?#)



























-1280x720.jpg?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=80&format=jpg&auto=webp#)