Binary Tree All Operations as pseudocode
Tree Structure Each node x has these attributes: x.key: key stored in the node x.p: pointer to the parent node x.left: pointer to the left child x.right: pointer to the right child A tree T has: T.root: pointer to the root node Algorithms 1. Inorder Tree Walk Input: x (pointer to a node in the binary search tree) Output: None (prints keys in order) 1. If x ≠ null 2. Inorder-tree-walk(x.left) 3. Print x.key 4. Inorder-tree-walk(x.right) 2. Tree Search (Recursive) Input: x (pointer to subtree root), k (key to search) Output: Pointer to node with key k (or null if not found) 1. If x == null or k == x.key 2. Return x 3. If k < x.key 4. Return tree-search(x.left, k) 5. Else 6. Return tree-search(x.right, k) 3. Iterative Tree Search Input: x (pointer to subtree root), k (key to search) Output: Pointer to node with key k (or null if not found) 1. While x ≠ null and k ≠ x.key 2. If k < x.key 3. x = x.left 4. Else 5. x = x.right 6. Return x 4. Tree Minimum Input: x (pointer to non-null node) Output: Pointer to node with minimum key in the subtree 1. While x.left ≠ null 2. x = x.left 3. Return x 5. Tree Maximum Input: x (pointer to non-null node) Output: Pointer to node with maximum key in the subtree 1. While x.right ≠ null 2. x = x.right 3. Return x 6. Tree Insert Input: t (binary search tree), z (node to insert) Output: None (modifies tree by inserting z) 1. y = null 2. x = t.root 3. While x ≠ null 4. y = x 5. If z.key < x.key 6. x = x.left 7. Else 8. x = x.right 9. z.p = y 10. If y == null 11. t.root = z 12. Elseif z.key < y.key 13. y.left = z 14. Else 15. y.right = z 7. Transplant (Helper for Delete) Input: t (binary search tree), u (subtree to replace), v (replacing subtree) Output: None (modifies tree) 1. If u.p == null 2. t.root = v 3. Elseif u == u.p.left 4. u.p.left = v 5. Else 6. u.p.right = v 7. If v ≠ null 8. v.p = u.p 8. Tree Delete Input: t (binary search tree), z (node to delete) Output: None (modifies tree) 1. If z.left == null 2. Transplant(t, z, z.right) 3. Elseif z.right == null 4. Transplant(t, z, z.left) 5. Else 6. y = tree-minimum(z.right) 7. If y.p ≠ z 8. Transplant(t, y, y.right) 9. y.right = z.right 10. y.right.p = y 11. Transplant(t, z, y) 12. y.left = z.left 13. y.left.p = y Additional Tree Operations Size Input: T (binary tree) Output: Number of nodes in the tree 1. If T.root == Null 2. Return 0 3. count = 0 4. sizeHelper(T.root, count) 5. Return count Other Basic Operations isEmpty(): Returns true if tree is empty root(): Returns the root node parent(v): Returns parent of node v children(v): Returns list of children of node v leftChild(v): Returns left child of node v rightChild(v): Returns right child of node v sibling(v): Returns sibling of node v Traversal Algorithms Preorder Traversal Input: v (node) Output: None 1. If v == Null 2. Return 3. Visit v 4. If isInternal(v) 5. preorder(v.left) 6. preorder(v.right) Postorder Traversal Input: v (node) Output: None 1. If v == Null 2. Return 3. If isInternal(v) 4. postorder(v.left) 5. postorder(v.right) 6. Visit v Inorder Traversal Input: v (node) Output: None 1. If v == Null 2. Return 3. If v.left ≠ Null 4. inorder(v.left) 5. Visit v 6. If v.right ≠ Null 7. inorder(v.right) Euler Tour Traversal Input: v (node) Output: None 1. If v == null 2. Return 3. visitBeforeSubtrees(v) 4. If isInternal(v) 5. If v.left ≠ Null 6. eulerTour(v.left) 7. visitBetweenSubtrees(v) 8. If v.right ≠ Null 9. eulerTour(v.right) 10. visitAfterSubtrees(v) Time Complexity Summary Operation Time Complexity Inorder Walk O(n) Tree Search O(h) Tree Insert O(h) Tree Delete O(h) Size O(n) Traversals O(n) Note: h = height of the tree, n = number of nodes Euler Tour Example The Euler Tour captures all tree traversal information in a single walk: Each node is visited exactly 3 times Combines preorder, inorder, and postorder traversals Example Tree Expression The Euler Tour can help evaluate complex tree expressions: ((3+1)×(9−5))−(3×(7−4)+6) This demonstrates how Euler Tour can be used to systematically process and evaluate tree-based mathematical expressions. Binary Search Tree Operations Complexity Table Operation Time Complexity (Big-O) inorder-tree-walk O(n) tree-search O(h) iterative-tree-search O(h) tree-minimum O(h) tree-maximum O(h) tree-insert O(h) tree-delete O(h) transplant O(1) size O(n) isEmpty O(1) root O(1) parent O(1) children O(1) leftChild O(1) rightChild O(1) sibling O(1) isIn
Tree Structure
Each node x has these attributes:
-
x.key: key stored in the node -
x.p: pointer to the parent node -
x.left: pointer to the left child -
x.right: pointer to the right child
A tree T has:
-
T.root: pointer to the root node
Algorithms
1. Inorder Tree Walk
Input: x (pointer to a node in the binary search tree)
Output: None (prints keys in order)
1. If x ≠ null
2. Inorder-tree-walk(x.left)
3. Print x.key
4. Inorder-tree-walk(x.right)
2. Tree Search (Recursive)
Input: x (pointer to subtree root), k (key to search)
Output: Pointer to node with key k (or null if not found)
1. If x == null or k == x.key
2. Return x
3. If k < x.key
4. Return tree-search(x.left, k)
5. Else
6. Return tree-search(x.right, k)
3. Iterative Tree Search
Input: x (pointer to subtree root), k (key to search)
Output: Pointer to node with key k (or null if not found)
1. While x ≠ null and k ≠ x.key
2. If k < x.key
3. x = x.left
4. Else
5. x = x.right
6. Return x
4. Tree Minimum
Input: x (pointer to non-null node)
Output: Pointer to node with minimum key in the subtree
1. While x.left ≠ null
2. x = x.left
3. Return x
5. Tree Maximum
Input: x (pointer to non-null node)
Output: Pointer to node with maximum key in the subtree
1. While x.right ≠ null
2. x = x.right
3. Return x
6. Tree Insert
Input: t (binary search tree), z (node to insert)
Output: None (modifies tree by inserting z)
1. y = null
2. x = t.root
3. While x ≠ null
4. y = x
5. If z.key < x.key
6. x = x.left
7. Else
8. x = x.right
9. z.p = y
10. If y == null
11. t.root = z
12. Elseif z.key < y.key
13. y.left = z
14. Else
15. y.right = z
7. Transplant (Helper for Delete)
Input: t (binary search tree), u (subtree to replace), v (replacing subtree)
Output: None (modifies tree)
1. If u.p == null
2. t.root = v
3. Elseif u == u.p.left
4. u.p.left = v
5. Else
6. u.p.right = v
7. If v ≠ null
8. v.p = u.p
8. Tree Delete
Input: t (binary search tree), z (node to delete)
Output: None (modifies tree)
1. If z.left == null
2. Transplant(t, z, z.right)
3. Elseif z.right == null
4. Transplant(t, z, z.left)
5. Else
6. y = tree-minimum(z.right)
7. If y.p ≠ z
8. Transplant(t, y, y.right)
9. y.right = z.right
10. y.right.p = y
11. Transplant(t, z, y)
12. y.left = z.left
13. y.left.p = y
Additional Tree Operations
Size
Input: T (binary tree)
Output: Number of nodes in the tree
1. If T.root == Null
2. Return 0
3. count = 0
4. sizeHelper(T.root, count)
5. Return count
Other Basic Operations
-
isEmpty(): Returns true if tree is empty -
root(): Returns the root node -
parent(v): Returns parent of node v -
children(v): Returns list of children of node v -
leftChild(v): Returns left child of node v -
rightChild(v): Returns right child of node v -
sibling(v): Returns sibling of node v
Traversal Algorithms
Preorder Traversal
Input: v (node)
Output: None
1. If v == Null
2. Return
3. Visit v
4. If isInternal(v)
5. preorder(v.left)
6. preorder(v.right)
Postorder Traversal
Input: v (node)
Output: None
1. If v == Null
2. Return
3. If isInternal(v)
4. postorder(v.left)
5. postorder(v.right)
6. Visit v
Inorder Traversal
Input: v (node)
Output: None
1. If v == Null
2. Return
3. If v.left ≠ Null
4. inorder(v.left)
5. Visit v
6. If v.right ≠ Null
7. inorder(v.right)
Euler Tour Traversal
Input: v (node)
Output: None
1. If v == null
2. Return
3. visitBeforeSubtrees(v)
4. If isInternal(v)
5. If v.left ≠ Null
6. eulerTour(v.left)
7. visitBetweenSubtrees(v)
8. If v.right ≠ Null
9. eulerTour(v.right)
10. visitAfterSubtrees(v)
Time Complexity Summary
| Operation | Time Complexity |
|---|---|
| Inorder Walk | O(n) |
| Tree Search | O(h) |
| Tree Insert | O(h) |
| Tree Delete | O(h) |
| Size | O(n) |
| Traversals | O(n) |
Note: h = height of the tree, n = number of nodes
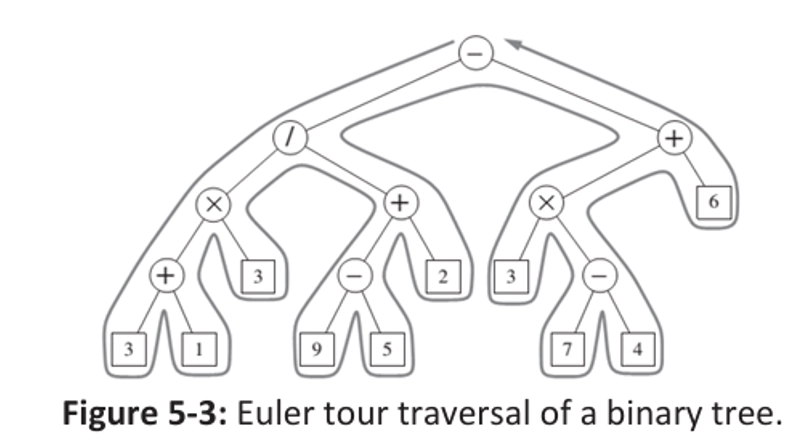
Euler Tour Example
The Euler Tour captures all tree traversal information in a single walk:
- Each node is visited exactly 3 times
- Combines preorder, inorder, and postorder traversals
Example Tree Expression
The Euler Tour can help evaluate complex tree expressions:
((3+1)×(9−5))−(3×(7−4)+6)
This demonstrates how Euler Tour can be used to systematically process and evaluate tree-based mathematical expressions.
Binary Search Tree Operations Complexity Table
| Operation | Time Complexity (Big-O) |
|---|---|
| inorder-tree-walk | O(n) |
| tree-search | O(h) |
| iterative-tree-search | O(h) |
| tree-minimum | O(h) |
| tree-maximum | O(h) |
| tree-insert | O(h) |
| tree-delete | O(h) |
| transplant | O(1) |
| size | O(n) |
| isEmpty | O(1) |
| root | O(1) |
| parent | O(1) |
| children | O(1) |
| leftChild | O(1) |
| rightChild | O(1) |
| sibling | O(1) |
| isInternal | O(1) |
| isExternal | O(1) |
| isRoot | O(1) |
| preorder | O(n) |
| postorder | O(n) |
| inorder | O(n) |
| eulerTour | O(n) |
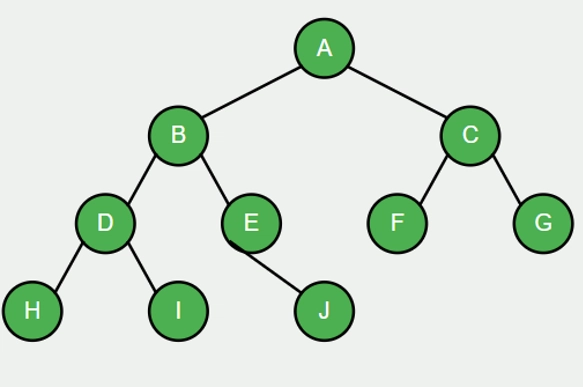
Euler Tour Example with Larger Tree
Euler Tour traversal sequence for a tree with 3 layers:

- A (first visit)
- B (first visit)
- D (first visit)
- H (first visit)
- H (second visit) - no children
- H (third visit)
- D (second visit)
- I (first visit)
- I (second visit) - no children
- I (third visit)
- D (third visit)
- B (second visit)
- E (first visit)
- J (first visit)
- J (second visit) - no children
- J (third visit)
- E (second visit) - E has no right child
- E (third visit)
- B (third visit)
- A (second visit)
- C (first visit)
- F (first visit)
- F (second visit) - no children
- F (third visit)
- C (second visit)
- G (first visit)
- G (second visit) - no children
- G (third visit)
- C (third visit)
- A (third visit)
Note: Each node is visited exactly 3 times, creating a complete "tour" around the tree that captures all the information from preorder, inorder, and postorder traversals in a single walk.
Mathematical Expression Using Euler Tour Algorithm
Q: What is the mathematical expression for this tree when using the Euler Tour algorithm?
Solution:
-
Start with the left subtree of the root (-):
- Left subtree of ×: (3 + 1)
- Right subtree of ×: (9 - 5)
- Combine: (3 + 1) × (9 - 5)
-
Move to the right subtree of the root (-):
- Left subtree of +: 3 × (7 - 4)
- Right subtree of +: 6
- Combine: 3 × (7 - 4) + 6
-
Combine the results from the left and right subtrees of the root:
- Left: (3 + 1) × (9 - 5)
- Right: 3 × (7 - 4) + 6
- Combine: ((3 + 1) × (9 - 5)) - (3 × (7 - 4) + 6)
Final Answer:
The mathematical expression represented by the tree is:
((3+1)×(9−5))−(3×(7−4)+6) => ((4)×(4))−(3×(3)+6) = 16 − (3×3 + 6) = 16 − (9 + 6) = 16 − 15 = 1


































































![New Apple iPad mini 7 On Sale for $399! [Lowest Price Ever]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96096/96096/96096-640.jpg)

![Rapidus in Talks With Apple as It Accelerates Toward 2nm Chip Production [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96937/96937/96937-640.jpg)










































































































_Christophe_Coat_Alamy.jpg?#)










































































![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)































































































































![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)



![[FREE EBOOKS] The Kubernetes Bible, The Ultimate Linux Shell Scripting Guide & Four More Best Selling Titles](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)


































.jpg?#)



.png?#)