Getting Started with Pandas: The Power Tool for Data Analysis in Python
Introduction If you work with data, pandas is your best friend. It lets you manipulate, analyze, and visualize data with just a few lines of code. Installation pip install pandas Basic Objects Series – 1D array with labels DataFrame – 2D table with rows & columns Creating DataFrames import pandas as pd data = { 'Name': ['AF4', 'Shadow', 'Wolf'], 'Score': [90, 85, 95] } df = pd.DataFrame(data) print(df) Reading & Writing Files df = pd.read_csv('file.csv') df.to_csv('output.csv', index=False) DataFrame Operations print(df.describe()) # Stats summary print(df.head()) # First few rows df['Score'] = df['Score'] + 5 Filtering & Selection high_scores = df[df['Score'] > 90] print(high_scores) Grouping and Aggregation df.groupby('Name').mean() Conclusion pandas is the heart of Python data analysis. Once you get comfortable, you'll fly through any dataset like a pro.

Introduction
If you work with data, pandas is your best friend. It lets you manipulate, analyze, and visualize data with just a few lines of code.
Installation
pip install pandas
Basic Objects
- Series – 1D array with labels
- DataFrame – 2D table with rows & columns
Creating DataFrames
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Name': ['AF4', 'Shadow', 'Wolf'],
'Score': [90, 85, 95]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df)
Reading & Writing Files
df = pd.read_csv('file.csv')
df.to_csv('output.csv', index=False)
DataFrame Operations
print(df.describe()) # Stats summary
print(df.head()) # First few rows
df['Score'] = df['Score'] + 5
Filtering & Selection
high_scores = df[df['Score'] > 90]
print(high_scores)
Grouping and Aggregation
df.groupby('Name').mean()
Conclusion
pandas is the heart of Python data analysis. Once you get comfortable, you'll fly through any dataset like a pro.





































































![Rapidus in Talks With Apple as It Accelerates Toward 2nm Chip Production [Report]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96937/96937/96937-640.jpg)










































































































_Christophe_Coat_Alamy.jpg?#)










































































![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)























































































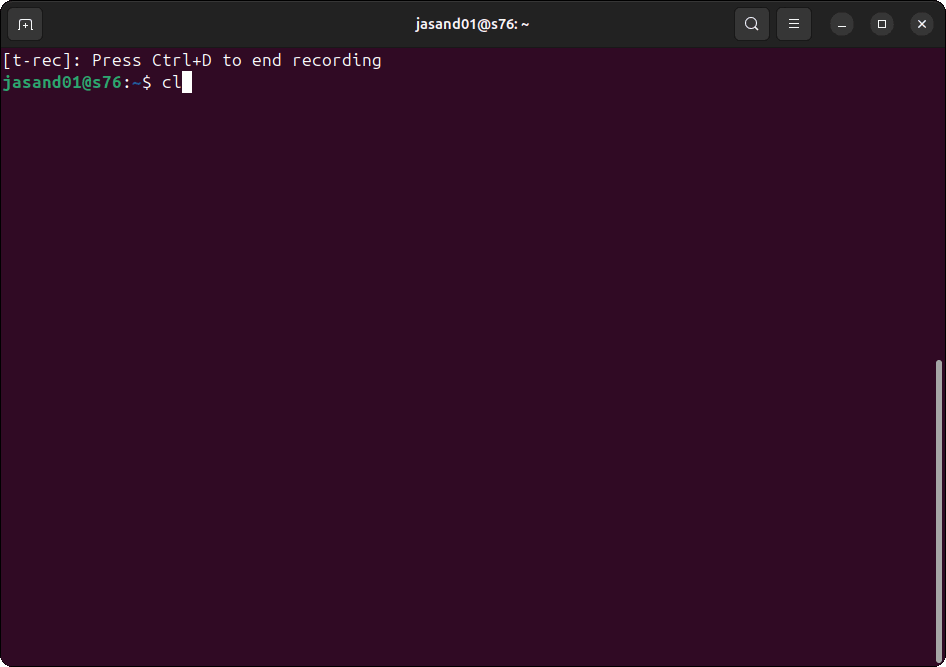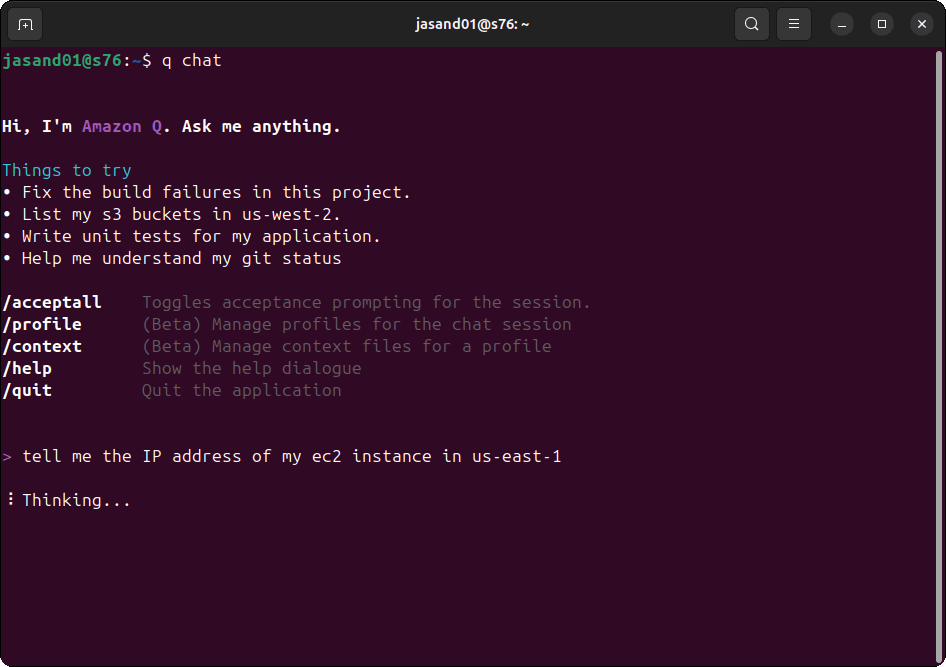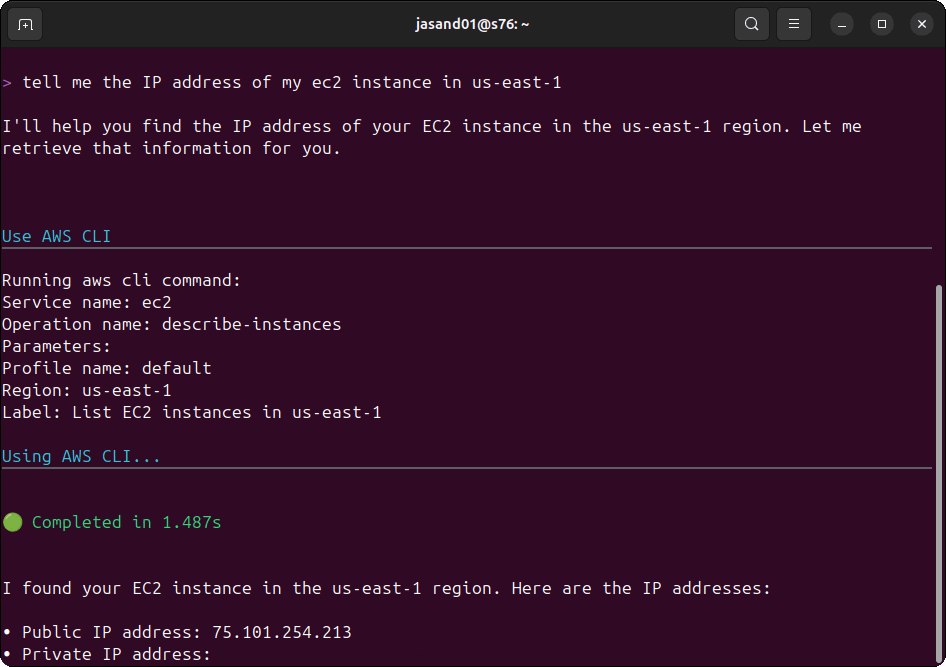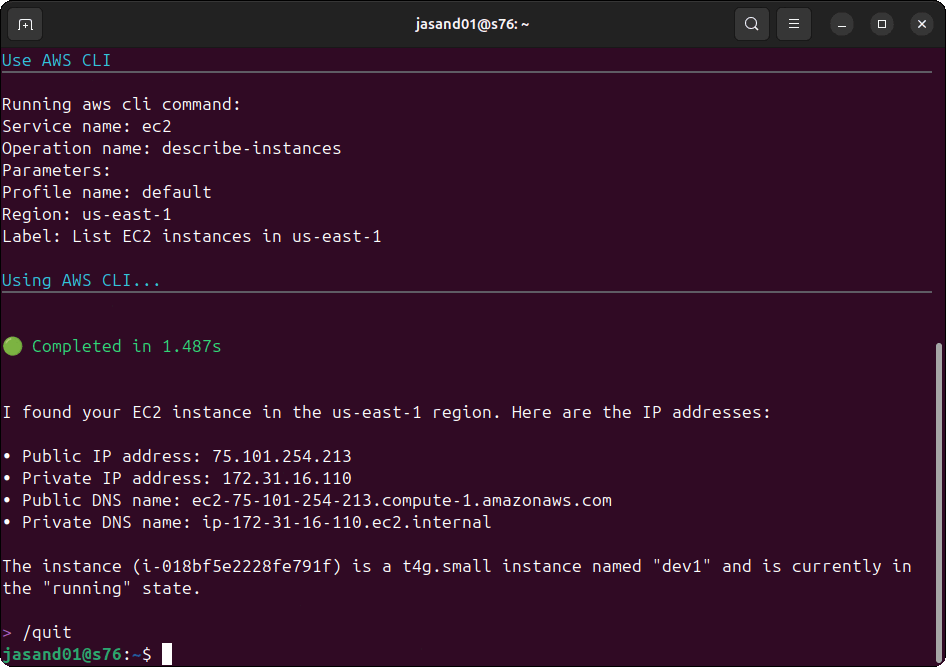







































![From drop-out to software architect with Jason Lengstorf [Podcast #167]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743796461357/f3d19cd7-e6f5-4d7c-8bfc-eb974bc8da68.png?#)



![[FREE EBOOKS] The Kubernetes Bible, The Ultimate Linux Shell Scripting Guide & Four More Best Selling Titles](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)


































.jpg?#)


.png?#)
























































