Scientists just uncovered a shocking twist in the story of human evolution
For decades, the dominant theory in human evolution suggested that modern humans descended from a single ancestral lineage in Africa. However, groundbreaking new research from … The post Scientists just uncovered a shocking twist in the story of human evolution appeared first on BGR.
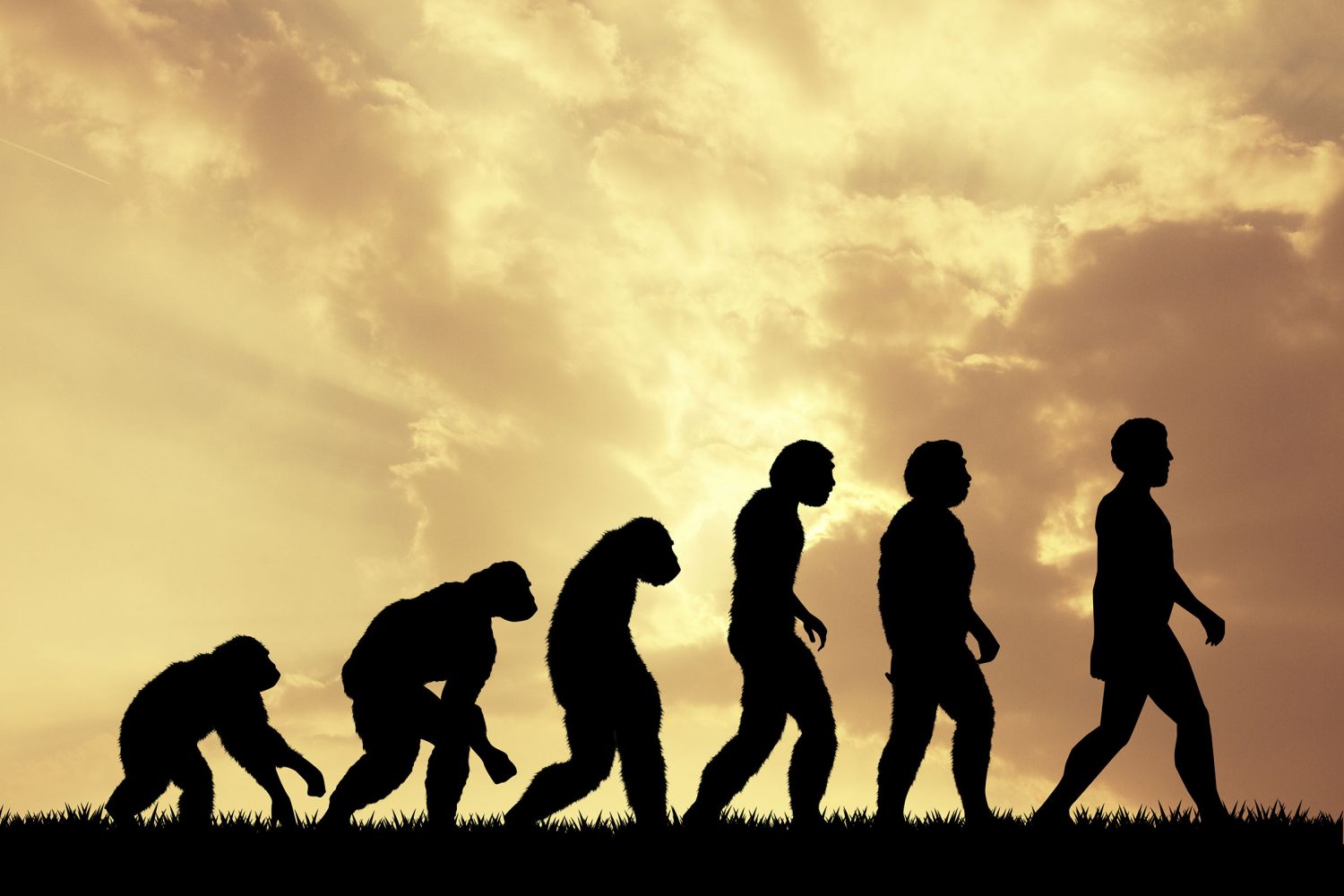


For decades, the dominant theory in human evolution suggested that modern humans descended from a single ancestral lineage in Africa. However, groundbreaking new research from the University of Cambridge challenges that idea, revealing a far more complex and surprising origin story for early human evolution.
According to this study, modern humans actually evolved from two distinct ancestral populations that split apart 1.5 million years ago, only to reunite around 300,000 years ago, long before Homo sapiens spread across the globe.
This discovery, published in Nature Genetics, comes from an advanced analysis of full genome sequences rather than ancient fossil DNA. The research team used a new computational model called "cobraa," which allowed them to trace ancestral population splits in early human evolution, including genetic reunions over vast timescales.
The results suggest that one of these ancient human populations contributed around 80 percent of modern human DNA, while the other contributed 20 percent—particularly genes linked to brain function and neural development.
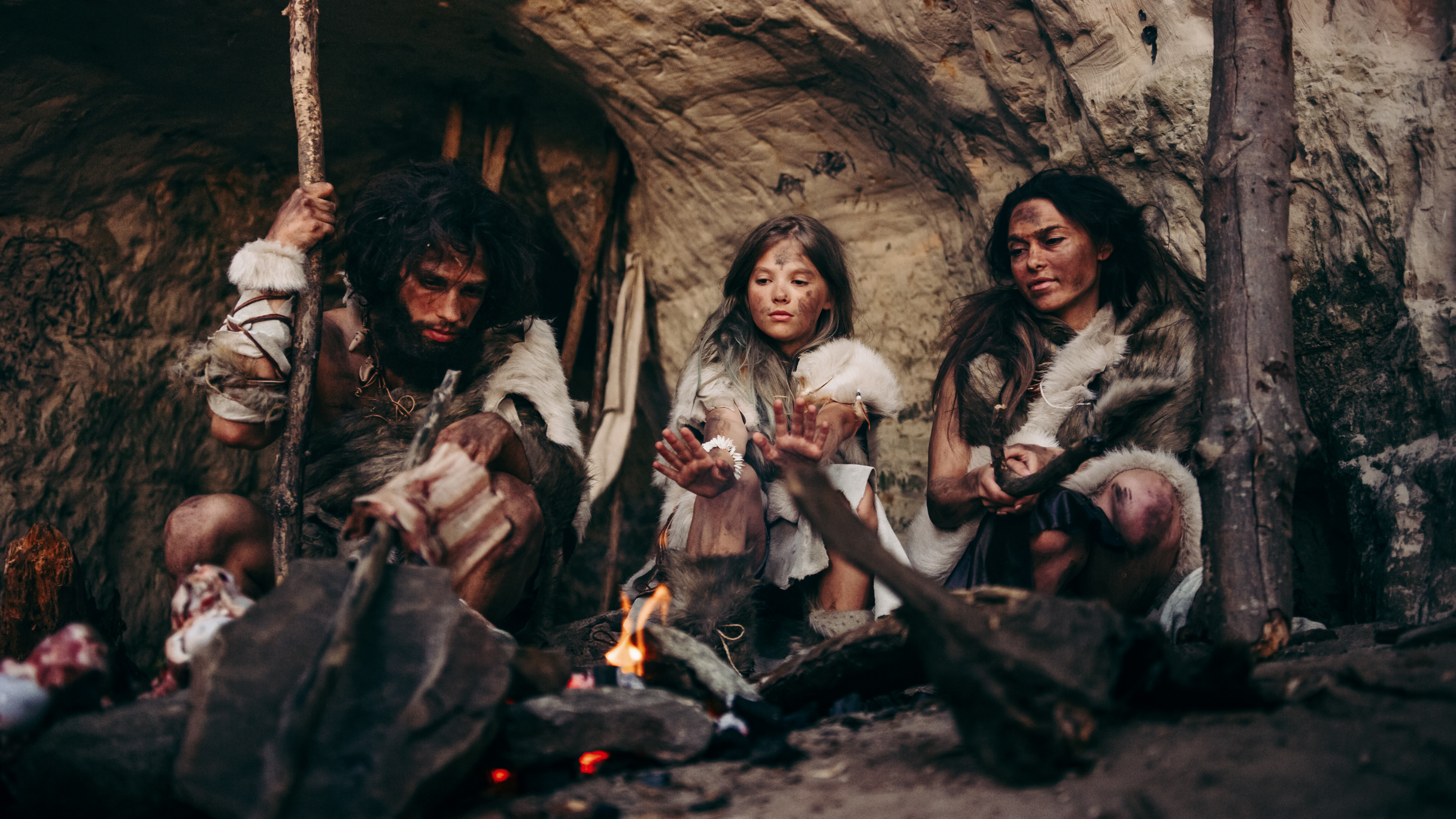

Unlike Neanderthal and Denisovan DNA, which makes up only about two percent of the genome in non-African populations, this earlier genetic mixing event had a much larger influence on all modern humans.
These findings challenge the traditional view that human evolution was a clean, linear process, instead painting a picture of populations drifting apart, evolving separately, and then coming back together to form the species we now recognize as Homo sapiens.
The researchers also discovered that one of the ancestral groups experienced a major population bottleneck, shrinking to a tiny size before slowly recovering over the course of a million years. This group eventually became the main genetic source of modern humans and also gave rise to Neanderthals and Denisovans.
Meanwhile, the minor genetic contributor appears to have introduced beneficial traits, though some of its genes were later filtered out through natural selection. Beyond rewriting the story of human origins, this research highlights a broader trend in evolutionary science—the realization that species rarely evolve in isolated, distinct lineages.
By applying their methods to chimps, gorillas, dolphins, and bats, the researchers found similar patterns of genetic exchange and reintegration. This suggests that interbreeding has played a key role in shaping many species, not just humans.
This discovery opens the door for further investigation into early human diversity, especially as scientists try to match these genetic ancestors with known fossil groups like Homo erectus and Homo heidelbergensis. As the field of genetics advances, we may be forced to rethink everything we thought we knew about where we came from.
The post Scientists just uncovered a shocking twist in the story of human evolution appeared first on BGR.
Today's Top Deals
- Today’s deals: $50 off new M4 MacBook Air, $57 Insignia smart TV, $199 DJI Osmo action camera, more
- Today’s deals: $269 iPad 10, $90 Ninja blender, 20% off Coop pillows, $400 Samsung M8 monitor, more
- Best deals: Tech, laptops, TVs, and more sales
- Amazon gift card deals, offers & coupons 2025: Get $2,000+ free
Scientists just uncovered a shocking twist in the story of human evolution originally appeared on BGR.com on Fri, 21 Mar 2025 at 16:34:00 EDT. Please see our terms for use of feeds.





























































![Apple to Craft Key Foldable iPhone Components From Liquid Metal [Kuo]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96784/96784/96784-640.jpg)

![Apple to Focus on Battery Life and Power Efficiency in Future Premium Devices [Rumor]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96781/96781/96781-640.jpg)







































































































_Federico_Caputo_Alamy.jpg?#)



































































![[The AI Show Episode 139]: The Government Knows AGI Is Coming, Superintelligence Strategy, OpenAI’s $20,000 Per Month Agents & Top 100 Gen AI Apps](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20139%20cover-2.png)


![[The AI Show Episode 138]: Introducing GPT-4.5, Claude 3.7 Sonnet, Alexa+, Deep Research Now in ChatGPT Plus & How AI Is Disrupting Writing](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20138%20cover.png)








































































































![From hating coding to programming satellites at age 37 with Francesco Ciulla [Podcast #165]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1742585568977/09b25b8e-8c92-4f4b-853f-64b7f7915980.png?#)































.jpg?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=80&format=jpg&auto=webp#)





.png?#)