"Unlocking AI Potential: R1-Zero Training and Knowledge Editing in Language Models"
In a world increasingly driven by artificial intelligence, the quest to unlock its full potential is more pressing than ever. Have you ever wondered how AI language models can be fine-tuned to deliver precise and relevant information? Or how knowledge editing could transform these models into dynamic tools that adapt seamlessly to new data? Welcome to the realm of R1-Zero Training—a groundbreaking approach designed not just for training but for empowering AI with the ability to learn and evolve continuously. In this blog post, we will explore the intricacies of R1-Zero Training and delve into the fascinating concept of knowledge editing, revealing their transformative benefits for both developers and end-users alike. As we navigate through real-world applications, you'll discover how these innovations are reshaping industries—from customer service automation to content creation—while also addressing challenges that come with implementing such advanced techniques. By understanding these concepts, you’ll gain insights that position you at the forefront of AI advancements. Join us on this journey as we uncover future trends in AI language models that promise not only efficiency but also unprecedented adaptability in an ever-changing digital landscape! Introduction to R1-Zero Training R1-Zero-Like Training leverages reinforcement learning (RL) to enhance the reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) without relying on supervised fine-tuning. This innovative approach utilizes models such as Qwen2.5 and DeepSeek-V3-Base, focusing on addressing biases inherent in pretraining and optimization methods like GRPO. The introduction of Dr. GRPO aims for unbiased optimization, crucial for accurate model training. Key Components of R1-Zero Training The minimalist R1-Zero recipe has demonstrated state-of-the-art accuracy on the AIME 2024 dataset, showcasing significant improvements in exploration abilities with base models that utilize templates versus those that do not. Furthermore, it emphasizes domain-specific pretraining's role in enhancing RL performance while exploring self-reflection behaviors during inference stages in models like DeepSeek-V3-Base. By optimizing policy gradients through Monte Carlo techniques and Proximal Policy Optimization objectives, this method addresses critical challenges faced by LLMs in various applications, paving the way for more effective AI-driven solutions across multiple domains. Understanding Knowledge Editing Knowledge editing is a pivotal concept in enhancing the capabilities of Large Multimodal Models (LMMs), particularly within Autonomous Driving Systems (ADS). The ADS-Edit dataset, specifically designed for this purpose, incorporates real-world scenarios and diverse data types to facilitate targeted modifications. By employing knowledge editing techniques, LMMs can adapt and update their understanding in real-time, addressing challenges such as biases and over-attention that may arise during model training. Evaluation Metrics and Methods The evaluation process for knowledge editing involves assessing reliability, generality, and locality metrics. This ensures that the models not only perform well under controlled conditions but also exhibit robustness across various driving scenarios. Manual verification plays a crucial role in maintaining data quality control through calibration processes. Moreover, benchmarks like Nvila highlight the need for ongoing research into effective knowledge updating methods to ensure continuous improvement of language models in dynamic environments like autonomous driving systems.# Benefits of AI Language Models AI language models, particularly those enhanced through R1-Zero-Like Training and reinforcement learning, offer numerous advantages across various domains. These models exhibit improved reasoning capabilities without the need for extensive supervised fine-tuning, allowing for more efficient training processes. For instance, advancements like Qwen2.5 demonstrate significant performance improvements in chatbot development by leveraging self-reflection behaviors that enhance user interactions. Enhanced Performance and Bias Mitigation The introduction of Dr. GRPO optimizes training methods to address biases inherent in traditional optimization algorithms such as GRPO. This ensures fairer model outputs while maintaining high accuracy levels on datasets like AIME 2024. Additionally, domain-specific pretraining enhances the exploration abilities of these models during inference stages, leading to better contextual understanding and response generation. Furthermore, the mathematical frameworks employed in R1-Zero-Like Training optimize policy gradients effectively using techniques such as Monte Carlo policy gradient and Proximal Policy Optimization objectives. As a result, AI language models not only improve their token efficiency but also mitigate bias impacts during reinforcement learning tasks—ultimately contributing to

In a world increasingly driven by artificial intelligence, the quest to unlock its full potential is more pressing than ever. Have you ever wondered how AI language models can be fine-tuned to deliver precise and relevant information? Or how knowledge editing could transform these models into dynamic tools that adapt seamlessly to new data? Welcome to the realm of R1-Zero Training—a groundbreaking approach designed not just for training but for empowering AI with the ability to learn and evolve continuously. In this blog post, we will explore the intricacies of R1-Zero Training and delve into the fascinating concept of knowledge editing, revealing their transformative benefits for both developers and end-users alike. As we navigate through real-world applications, you'll discover how these innovations are reshaping industries—from customer service automation to content creation—while also addressing challenges that come with implementing such advanced techniques. By understanding these concepts, you’ll gain insights that position you at the forefront of AI advancements. Join us on this journey as we uncover future trends in AI language models that promise not only efficiency but also unprecedented adaptability in an ever-changing digital landscape!
Introduction to R1-Zero Training
R1-Zero-Like Training leverages reinforcement learning (RL) to enhance the reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) without relying on supervised fine-tuning. This innovative approach utilizes models such as Qwen2.5 and DeepSeek-V3-Base, focusing on addressing biases inherent in pretraining and optimization methods like GRPO. The introduction of Dr. GRPO aims for unbiased optimization, crucial for accurate model training.
Key Components of R1-Zero Training
The minimalist R1-Zero recipe has demonstrated state-of-the-art accuracy on the AIME 2024 dataset, showcasing significant improvements in exploration abilities with base models that utilize templates versus those that do not. Furthermore, it emphasizes domain-specific pretraining's role in enhancing RL performance while exploring self-reflection behaviors during inference stages in models like DeepSeek-V3-Base. By optimizing policy gradients through Monte Carlo techniques and Proximal Policy Optimization objectives, this method addresses critical challenges faced by LLMs in various applications, paving the way for more effective AI-driven solutions across multiple domains.
Understanding Knowledge Editing
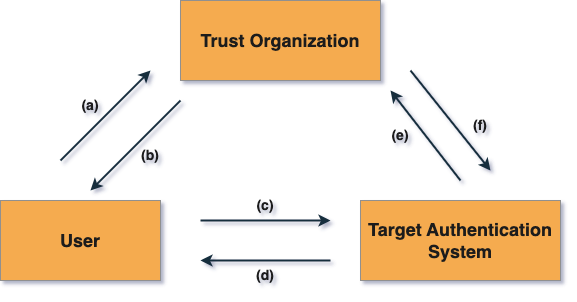
Knowledge editing is a pivotal concept in enhancing the capabilities of Large Multimodal Models (LMMs), particularly within Autonomous Driving Systems (ADS). The ADS-Edit dataset, specifically designed for this purpose, incorporates real-world scenarios and diverse data types to facilitate targeted modifications. By employing knowledge editing techniques, LMMs can adapt and update their understanding in real-time, addressing challenges such as biases and over-attention that may arise during model training.
Evaluation Metrics and Methods
The evaluation process for knowledge editing involves assessing reliability, generality, and locality metrics. This ensures that the models not only perform well under controlled conditions but also exhibit robustness across various driving scenarios. Manual verification plays a crucial role in maintaining data quality control through calibration processes. Moreover, benchmarks like Nvila highlight the need for ongoing research into effective knowledge updating methods to ensure continuous improvement of language models in dynamic environments like autonomous driving systems.# Benefits of AI Language Models
AI language models, particularly those enhanced through R1-Zero-Like Training and reinforcement learning, offer numerous advantages across various domains. These models exhibit improved reasoning capabilities without the need for extensive supervised fine-tuning, allowing for more efficient training processes. For instance, advancements like Qwen2.5 demonstrate significant performance improvements in chatbot development by leveraging self-reflection behaviors that enhance user interactions.
Enhanced Performance and Bias Mitigation
The introduction of Dr. GRPO optimizes training methods to address biases inherent in traditional optimization algorithms such as GRPO. This ensures fairer model outputs while maintaining high accuracy levels on datasets like AIME 2024. Additionally, domain-specific pretraining enhances the exploration abilities of these models during inference stages, leading to better contextual understanding and response generation.
Furthermore, the mathematical frameworks employed in R1-Zero-Like Training optimize policy gradients effectively using techniques such as Monte Carlo policy gradient and Proximal Policy Optimization objectives. As a result, AI language models not only improve their token efficiency but also mitigate bias impacts during reinforcement learning tasks—ultimately contributing to more reliable and trustworthy AI systems capable of performing complex problem-solving tasks with greater precision.
Real-World Applications of R1-Zero Training
R1-Zero training has significant implications across various domains, particularly in enhancing the reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs). By leveraging reinforcement learning without supervised fine-tuning, models like Qwen2.5 and DeepSeek-V3-Base exhibit improved performance in tasks such as chatbot development and mathematical problem-solving. The minimalist R1-Zero recipe achieves state-of-the-art accuracy on datasets like AIME 2024, showcasing its effectiveness. Moreover, the introduction of Dr. GRPO addresses biases inherent in optimization methods, ensuring fairer training processes that enhance model reliability.
Enhancing Chatbot Interactions
In real-world applications, R1-Zero training facilitates more dynamic and context-aware interactions within chatbots. The self-reflection behaviors observed in models trained under this framework allow for adaptive responses based on user input patterns. This capability not only improves user experience but also fosters trust between users and AI systems by providing accurate information tailored to individual needs.
Optimizing Mathematical Problem Solving
The application of Dr. GRPO for online reinforcement tuning significantly boosts token efficiency during math-related tasks. By addressing biases through refined optimization strategies, LLMs can achieve better outcomes when tackling complex problems—demonstrating how R1-Zero methodologies can transform traditional approaches to artificial intelligence challenges into robust solutions with practical utility across diverse fields.
Challenges in Implementing Knowledge Editing
Implementing knowledge editing within Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) presents several challenges that need to be addressed for effective deployment. One significant hurdle is the integration of real-time data updates, which requires a robust framework capable of continuously adapting to new information without compromising model performance. The complexity of managing biases inherent in pretraining and optimization methods further complicates this process; models like GRPO often exhibit skewed learning patterns that can lead to inaccurate outputs. Additionally, ensuring high-quality data through manual verification and calibration processes is essential but resource-intensive. The ADS-Edit dataset aims to mitigate these issues by providing diverse scenarios and evaluation metrics tailored for autonomous driving systems, yet the effectiveness of various editing methods remains variable across different contexts.
Evaluation Metrics and Data Quality Control
The evaluation process for knowledge editing involves assessing reliability, generality, and locality metrics while resolving discrepancies through majority voting mechanisms. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of how well the edited knowledge integrates with existing model frameworks. However, maintaining data quality control poses ongoing challenges due to potential over-attention on specific features or biases introduced during training phases. Continuous research into efficient knowledge updating strategies is crucial as it directly impacts the overall efficacy of LMMs in dynamic environments such as autonomous driving systems or mobile applications where user safety and experience are paramount.
Future Trends in AI and Language Models
The future of AI and language models is poised for significant advancements, particularly with the introduction of R1-Zero-Like Training. This innovative approach leverages reinforcement learning (RL) to enhance reasoning capabilities without relying on supervised fine-tuning. Notable models such as Qwen2.5 and DeepSeek-V3-Base exemplify this trend, showcasing improved performance through self-reflection behaviors during inference stages. The emergence of Dr. GRPO addresses biases inherent in optimization algorithms, promoting fair training processes essential for developing unbiased language models.
Key Innovations
As researchers explore domain-specific pretraining methods, we anticipate a shift towards more efficient RL dynamics that optimize policy gradients using techniques like Monte Carlo policy gradient and Proximal Policy Optimization objectives. These innovations will not only refine model accuracy but also enhance exploration abilities across various applications—from chatbots to complex problem-solving tasks in mathematics—ultimately leading to more intelligent systems capable of adapting to real-world scenarios effectively.
Moreover, continuous knowledge updating mechanisms are expected to become integral components within autonomous driving systems (ADS), further bridging the gap between theoretical advancements and practical implementations in diverse fields such as education, healthcare, and customer service. As these trends unfold, they promise a transformative impact on how we interact with technology daily.
In conclusion, the exploration of R1-Zero training and knowledge editing in language models reveals a transformative potential for artificial intelligence. By understanding R1-Zero training, we can appreciate how it enhances model efficiency while minimizing resource consumption. Knowledge editing offers a promising avenue to refine AI outputs by allowing real-time updates and corrections, ensuring that language models remain relevant and accurate. The benefits of these advancements extend beyond theoretical applications; they are already being harnessed in various sectors such as healthcare, finance, and education to improve decision-making processes and user interactions. However, challenges like ethical considerations and technical limitations must be addressed to fully realize this potential. As we look toward the future trends in AI development, embracing innovative techniques like R1-Zero training will be crucial for creating more adaptable and intelligent systems that align with human needs while fostering responsible use of technology.
FAQs on Unlocking AI Potential: R1-Zero Training and Knowledge Editing in Language Models
1. What is R1-Zero Training?
R1-Zero Training is a novel approach to training language models that focuses on optimizing the learning process by minimizing the amount of data required for effective model performance. This method allows for faster training times and improved efficiency, enabling models to learn from fewer examples while still achieving high accuracy.
2. How does knowledge editing work in AI language models?
Knowledge editing refers to the process of modifying or updating specific information within a trained language model without retraining it entirely. This technique allows developers to correct inaccuracies or add new information seamlessly, enhancing the model's reliability and relevance over time.
3. What are some benefits of using AI language models with R1-Zero Training?
AI language models utilizing R1-Zero Training can benefit from reduced resource consumption, quicker deployment times, and enhanced adaptability to new tasks or domains. These advantages make them more accessible for various applications across industries while maintaining high levels of performance.
4. Can you provide examples of real-world applications for R1-Zero Training in AI?
Real-world applications include customer service chatbots that require rapid adaptation to changing user queries, content generation tools that need quick updates based on current events, and educational platforms where personalized learning experiences can be created efficiently through tailored responses generated by optimized language models.
5. What challenges exist when implementing knowledge editing in AI systems?
Challenges include ensuring consistency after edits are made (to avoid introducing contradictions), managing potential biases that may arise during modifications, and developing robust frameworks for tracking changes effectively without compromising overall model integrity or performance.



































































![Apple's M5 iPad Pro Enters Advanced Testing for 2025 Launch [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96865/96865/96865-640.jpg)
![M5 MacBook Pro Set for Late 2025, Major Redesign Waits Until 2026 [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96868/96868/96868-640.jpg)
![Apple to Revamp Health App with AI-Powered Doctor [Gurman]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96870/96870/96870-640.jpg)
![Lowest Prices Ever: Apple Pencil Pro Just $79.99, USB-C Pencil Only $49.99 [Deal]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96863/96863/96863-640.jpg)














![What Google Messages features are rolling out [March 2025]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2023/12/google-messages-name-cover.png?resize=1200%2C628&quality=82&strip=all&ssl=1)






































![Chip Glitching 101 with [Hash]](https://hackaday.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/glitching.jpeg?#)























































































































![[The AI Show Episode 141]: Road to AGI (and Beyond) #1 — The AI Timeline is Accelerating](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20141.1.png)
![[The AI Show Episode 140]: New AGI Warnings, OpenAI Suggests Government Policy, Sam Altman Teases Creative Writing Model, Claude Web Search & Apple’s AI Woes](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20140%20cover.png)
![[The AI Show Episode 139]: The Government Knows AGI Is Coming, Superintelligence Strategy, OpenAI’s $20,000 Per Month Agents & Top 100 Gen AI Apps](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20139%20cover-2.png)
























































































































![From broke musician to working dev. How college drop-out Ryan Furrer taught himself to code [Podcast #166]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743189826063/2080cde4-6fc0-46fb-b98d-b3d59841e8c4.png?#)


![[FREE EBOOKS] The Ultimate Linux Shell Scripting Guide, Artificial Intelligence for Cybersecurity & Four More Best Selling Titles](https://www.javacodegeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/12/jcg-logo.jpg)





































.png?#)