Apache Tomcat Vulnerability (CVE-2025-24813) Exploited to Execute Code on Servers
A critical vulnerability in Apache Tomcat has been actively exploited by attackers to achieve remote code execution (RCE) on vulnerable servers. This vulnerability affects versions 9.0.0-M1 to 9.0.98, 10.1.0-M1 to 10.1.34, and 11.0.0-M1 to 11.0.2 and has been resolved in versions 9.0.99, 10.1.35, and 11.0.3. The flaw exploits Apache Tomcat’s handling of partial PUT requests […] The post Apache Tomcat Vulnerability (CVE-2025-24813) Exploited to Execute Code on Servers appeared first on Cyber Security News.

A critical vulnerability in Apache Tomcat has been actively exploited by attackers to achieve remote code execution (RCE) on vulnerable servers.
This vulnerability affects versions 9.0.0-M1 to 9.0.98, 10.1.0-M1 to 10.1.34, and 11.0.0-M1 to 11.0.2 and has been resolved in versions 9.0.99, 10.1.35, and 11.0.3.
The flaw exploits Apache Tomcat’s handling of partial PUT requests and path equivalence, allowing attackers to bypass security constraints and execute arbitrary code without authentication under specific conditions.

Exploitation Techniques and Impact
According to Insikt Group, the exploitation involves a two-step process. First, attackers send a PUT request with a maliciously crafted, serialized Java payload to a writable directory.
This payload is designed to trigger RCE upon deserialization. Then, a GET request is sent with a specially crafted “JSESSIONID” cookie, causing the server to deserialize the payload and execute arbitrary code.
Successful exploitation requires specific conditions, including write permissions for the default servlet, partial PUT support, and the use of file-based session persistence with a deserialization-vulnerable library.
These conditions are not typically met by default, limiting the scope of exploitation. Active exploitation attempts have been observed globally, with attackers targeting systems primarily in the United States, Japan, India, South Korea, and Mexico.
The rapid availability of proof-of-concept (PoC) exploits has lowered the barrier for exploitation, allowing even less sophisticated attackers to attempt to exploit this vulnerability.
Despite these attempts, successful exploitation is challenging due to the specific prerequisites required.
Mitigations
To mitigate the risks associated with CVE-2025-24813, organizations should upgrade to the patched versions of Apache Tomcat (9.0.99, 10.1.35, or 11.0.3) as soon as possible.
For instances where upgrading is not immediately feasible, implementing network-level controls to restrict access to the Tomcat server can provide temporary protection.
Additionally, disabling unnecessary HTTP methods and enforcing strict access controls can further reduce the risk of exploitation.
To detect and block malicious traffic, continuous monitoring for threat indicators and the use of web application firewalls (WAFs) are also recommended.
The post Apache Tomcat Vulnerability (CVE-2025-24813) Exploited to Execute Code on Servers appeared first on Cyber Security News.



_Andrew_Angelov_Alamy.jpg?#)
























































![Apple Watch Series 10 Prototype with Mystery Sensor Surfaces [Images]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96892/96892/96892-640.jpg)

![Get Up to 69% Off Anker and Eufy Products on Final Day of Amazon's Big Spring Sale [Deal]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96888/96888/96888-640.jpg)
![Apple Officially Releases macOS Sequoia 15.4 [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96887/96887/96887-640.jpg)





























![watchOS 11.4 was briefly available, and was pulled by Apple [u]](https://photos5.appleinsider.com/gallery/60061-123253-watchOS-11-on-Apple-Watch-Ultra-xl.jpg)























































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)










































































































![Is this a suitable approach to architect a flutter app? [closed]](https://i.sstatic.net/4hMHGb1L.png)
















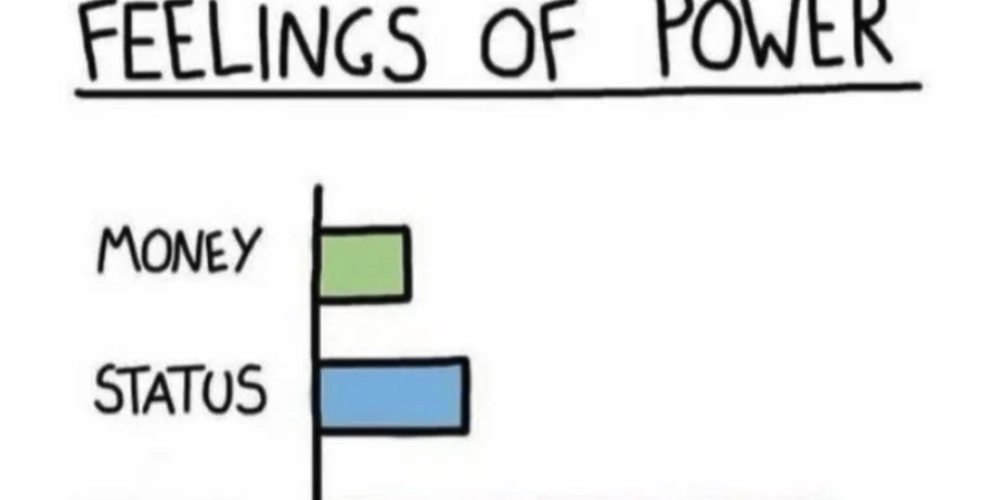
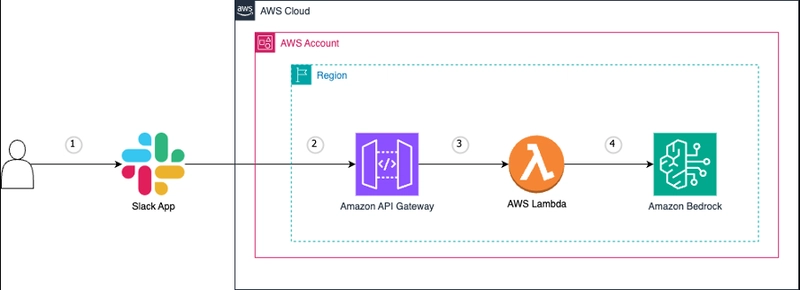
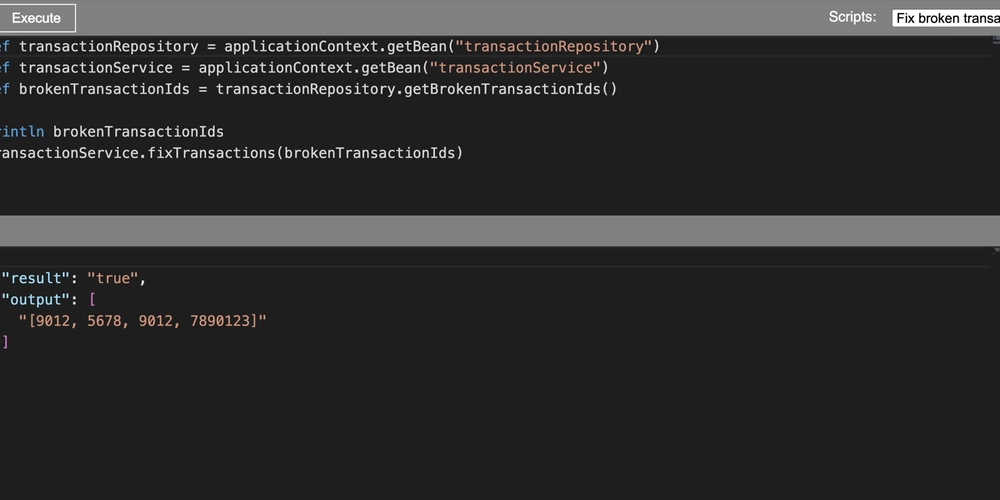

![From broke musician to working dev. How college drop-out Ryan Furrer taught himself to code [Podcast #166]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743189826063/2080cde4-6fc0-46fb-b98d-b3d59841e8c4.png?#)




























-1280x720.jpg?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=80&format=jpg&auto=webp#)





























































