Wearable Computing Goes Woven, Wireless, and Washable
Sometimes we come across a wild idea that really tries to re-imagine things, and re-conceiving wearable computing as a distributed system of “fiber computers” embedded into textiles is definitely that. …read more


Sometimes we come across a wild idea that really tries to re-imagine things, and re-conceiving wearable computing as a distributed system of “fiber computers” embedded into textiles is definitely that. The research paper presents fully-functional fiber computers and sensors that are washable, weave-able, wireless, and resist both stretching and bending.
The research paper with all the details is behind a paywall at this time, but we’ll summarize the important parts that are likely to get a hacker’s mind working.
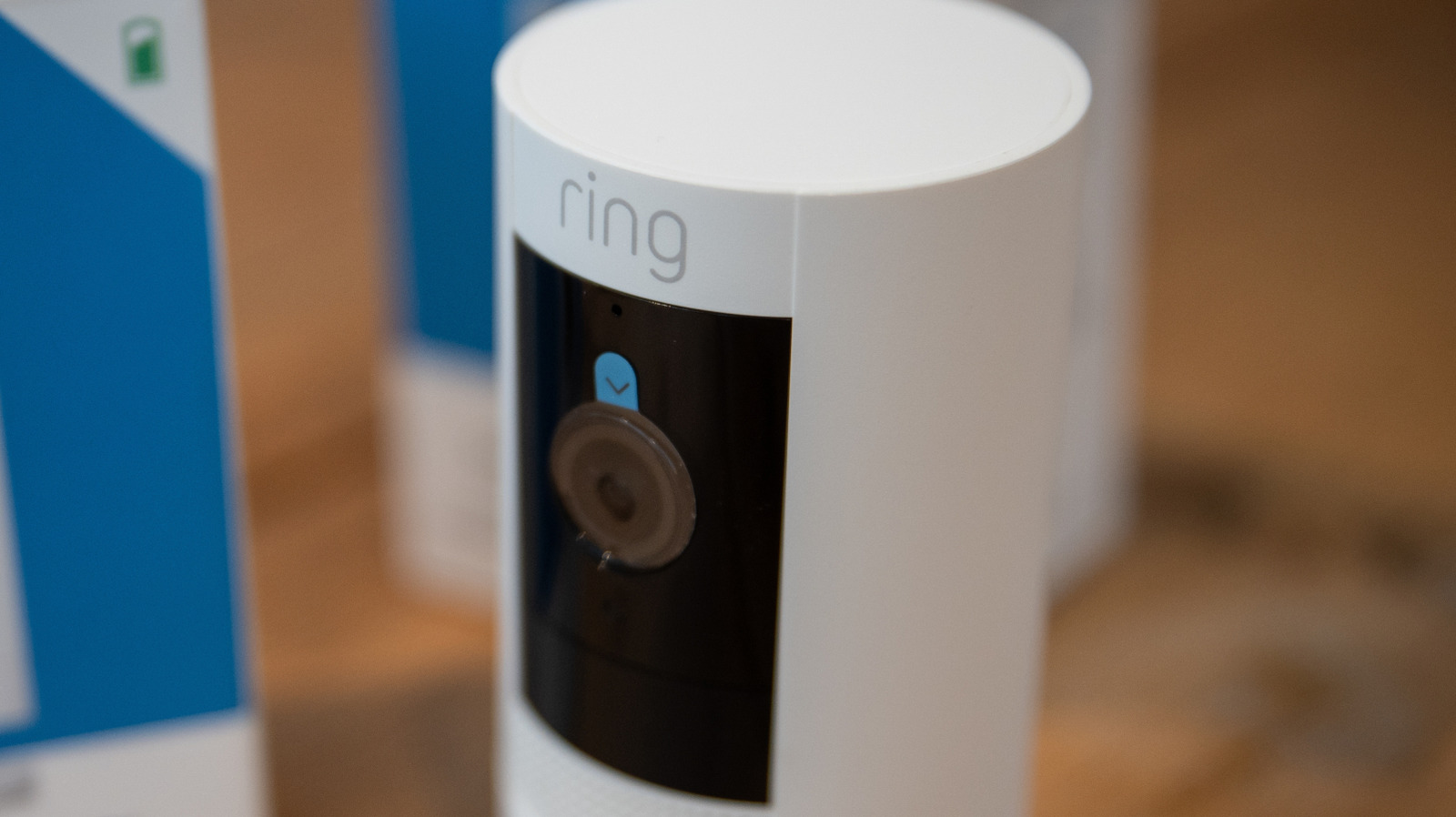
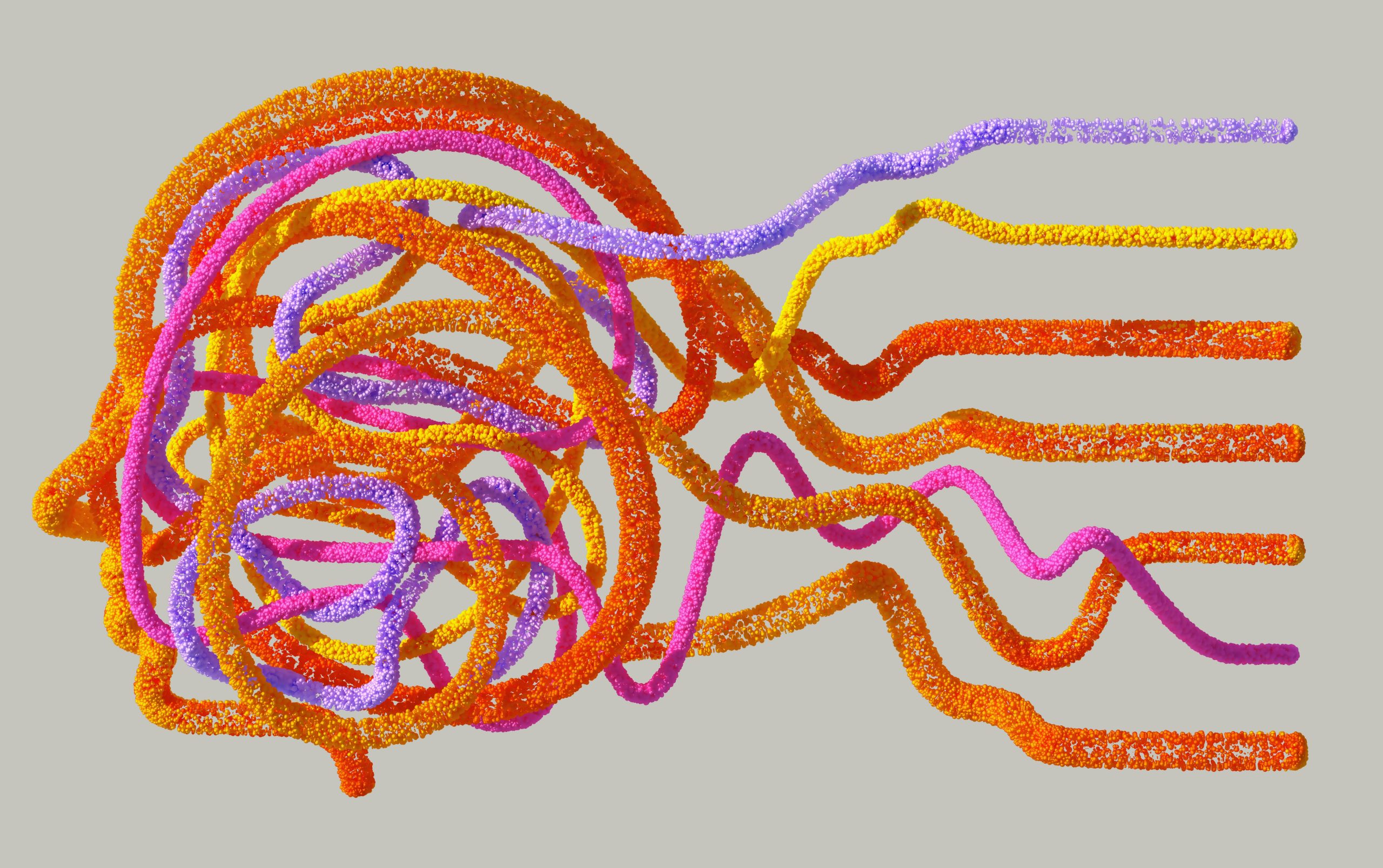
 Each fiber strand (like the one shown here) is a self-contained system. Multiple fibers can communicate with one another wirelessly to create a network that, when integrated into garments, performs tasks like health and activity monitoring while using very little power. And what’s really interesting about these fibers is their profound lack of anything truly exotic when it comes to their worky bits.
Each fiber strand (like the one shown here) is a self-contained system. Multiple fibers can communicate with one another wirelessly to create a network that, when integrated into garments, performs tasks like health and activity monitoring while using very little power. And what’s really interesting about these fibers is their profound lack of anything truly exotic when it comes to their worky bits.
The inner components of a fiber computer are pretty recognizable: each contains a surface-mount microcontroller, LEDs, BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) radio, light sensor, temperature sensor, accelerometer, and photoplethysmography (PPG) sensor for measuring blood volume changes through skin. Power is supplied by a separate segment containing a tiny cylindrical lithium-polymer battery, with a simple plug connector. It’s a tiny battery, but the system is so low-power that it still provides hours of operation.
If there’s a secret sauce, it’s in the fabrication. The first step is stretching a system into a long, thin circuit. Each component is nested onto a small piece of flex PCB that acts a little like a breakout board, and that flex PCB gets rolled around each component to make as tiny a package as possible. These little payloads are connected to one another by thin wires, evenly spaced to form a long circuit. That circuit gets (carefully!) sealed into a thermoformed soft polymer and given an overbraid, creating a fiber that has a few lumps here and there but is nevertheless remarkably thin and durable. The result can be woven into fabrics, worn, washed, bent, and in general treated like a piece of clothing.

Multiple fibers are well-suited to being woven into clothing in a distributed way, such as one for each limb. Each fiber is self-contained but communicates with its neighbors using a BLE mesh, or transmitting data optically via embedded LEDs and light sensors. Right now, such a distributed system has been shown to be able to perform health monitoring and accurately classify different physical activities.
We’ve seen sensors directly on skin and transmitting power over skin, but this is a clever fusion of conventional parts and unconventional design — wearable computing that’s not just actually wearable and unobtrusive, but durable and even washable.


































































![iOS 19 Leak: First Look at Alleged VisionOS Inspired Redesign [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96824/96824/96824-640.jpg)

![OpenAI Announces 4o Image Generation [Video]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96821/96821/96821-640.jpg)






























































































.webp?#)
.webp?#)




































































![[The AI Show Episode 140]: New AGI Warnings, OpenAI Suggests Government Policy, Sam Altman Teases Creative Writing Model, Claude Web Search & Apple’s AI Woes](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20140%20cover.png)
![[The AI Show Episode 139]: The Government Knows AGI Is Coming, Superintelligence Strategy, OpenAI’s $20,000 Per Month Agents & Top 100 Gen AI Apps](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20139%20cover-2.png)











































































































































.jpg?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=80&format=jpg&auto=webp#)