Has the Decline of Knowledge Worker Jobs Begun?
The New York Times notes that white-collar workers have faced higher unemployment than other groups in the U.S. over the past few years — along with slower wager growth. Some economists wonder if this trend might be irreversible... and partly attributable to AI: After sitting below 4% for more than two years, the overall unemployment rate has topped that threshold since May... "We're seeing a meaningful transition in the way work is done in the white-collar world," said Carl Tannenbaum, the chief economist of Northern Trust. "I tell people a wave is coming...." Thousands of video game workers lost jobs last year and the year before... Unemployment in finance and related industries, while still low, increased by about a quarter from 2022 to 2024, as rising interest rates slowed demand for mortgages and companies sought to become leaner.... Overall, the latest data from the Federal Reserve Bank of New York show that the unemployment rate for college grads has risen 30% since bottoming out in September 2022 (to 2.6% from 2%), versus about 18% for all workers (to 4% from 3.4%). An analysis by Julia Pollak, chief economist of ZipRecruiter, shows that unemployment has been most elevated among those with bachelor's degrees or some college but no degree, while unemployment has been steady or falling at the very top and bottom of the education ladder — for those with advanced degrees or without a high school diploma. Hiring rates have slowed more for jobs requiring a college degree than for other jobs, according to ADP Research, which studies the labor market.... And artificial intelligence could reduce that need further by increasing the automation of white-collar jobs. A recent academic paper found that software developers who used an AI coding assistant improved a key measure of productivity by more than 25% and that the productivity gains appeared to be largest among the least experienced developers. The result suggested that adopting AI could reduce the wage premium enjoyed by more experienced coders, since it would erode their productivity advantages over novices... [A]t least in the near term, many tech executives and their investors appear to see AI as a way to trim their staffing. A software engineer at a large tech company who declined to be named for fear of harming his job prospects said that his team was about half the size it was last year and that he and his co-workers were expected to do roughly the same amount of work by relying on an AI assistant. Overall, the unemployment rate in tech and related industries jumped by more than half from 2022 to 2024, to 4.4% from 2.9%. "Some economists say these trends may be short term in nature and little cause for concern on their own," the article points out (with one economist noting the unemployment rate is still low compared to historical averages). Harvard labor economist Lawrence Katz even suggested the slower wage growth could reflect the discount that these workers accepted in return for being able to work from home. Thanks to Slashdot reader databasecowgirl for sharing the article. Read more of this story at Slashdot.

Read more of this story at Slashdot.



_Andrew_Angelov_Alamy.jpg?#)
























































![Apple Watch Series 10 Prototype with Mystery Sensor Surfaces [Images]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96892/96892/96892-640.jpg)

![Get Up to 69% Off Anker and Eufy Products on Final Day of Amazon's Big Spring Sale [Deal]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96888/96888/96888-640.jpg)
![Apple Officially Releases macOS Sequoia 15.4 [Download]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96887/96887/96887-640.jpg)





























![watchOS 11.4 was briefly available, and was pulled by Apple [u]](https://photos5.appleinsider.com/gallery/60061-123253-watchOS-11-on-Apple-Watch-Ultra-xl.jpg)






















































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)























































































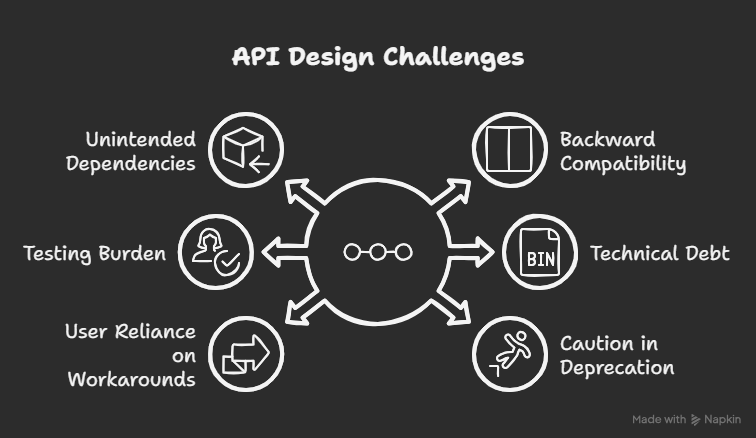



















![Is this a suitable approach to architect a flutter app? [closed]](https://i.sstatic.net/4hMHGb1L.png)
















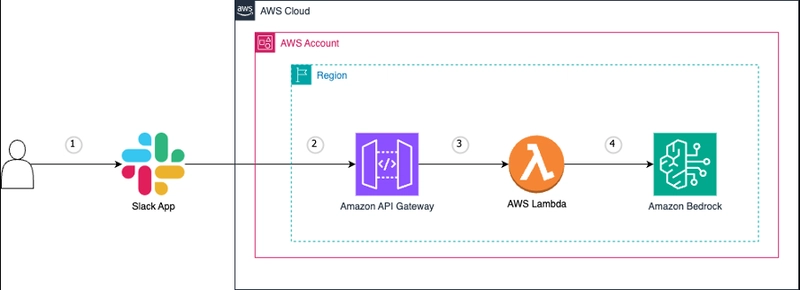
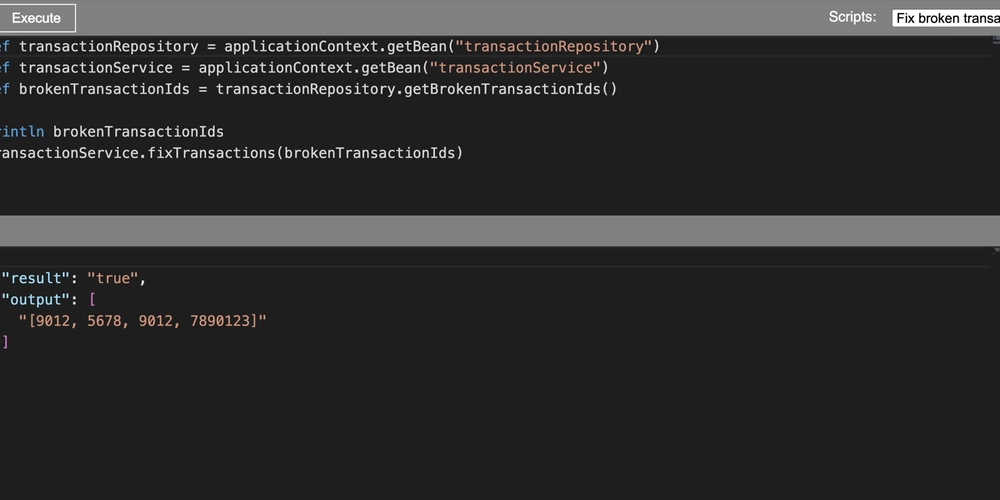

![From broke musician to working dev. How college drop-out Ryan Furrer taught himself to code [Podcast #166]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743189826063/2080cde4-6fc0-46fb-b98d-b3d59841e8c4.png?#)




























-1280x720.jpg?width=1920&height=1920&fit=bounds&quality=80&format=jpg&auto=webp#)





























































