Testing out Gateway API using Gloo Gateway
Hey folks, been a while, I've been hearing a lot about the Gateway API for the past few months and it seems like the defacto for gateways now. Since we also implemented the Gateway API I thought why not test it out! So today I'll be testing Gloo Gateway which is an opensource API-Gateway based on the extremely performant envoy proxy. Our documentation takes you through this, but I'm going to also do something similar. To begin with we need to make sure we have the Kubernetes Gateway CR's in our cluster. kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/releases/download/v1.2.0/standard-install.yaml You can use the above command to install it in your cluster. I use Talos to setup k8s on my end. You can also create a sample Talos cluster using docker. Moving on we are going to use Helm to test things out. Here we're adding the Gloo Open Source Repository. helm repo add gloo https://storage.googleapis.com/solo-public-helm helm repo update Then we can install the helm chart using helm install -n gloo-system gloo gloo/gloo \ --create-namespace \ --version 1.18.13 \ -f -
Hey folks, been a while, I've been hearing a lot about the Gateway API for the past few months and it seems like the defacto for gateways now.
Since we also implemented the Gateway API I thought why not test it out!
So today I'll be testing Gloo Gateway which is an opensource API-Gateway based on the extremely performant envoy proxy. Our documentation takes you through this, but I'm going to also do something similar.
To begin with we need to make sure we have the Kubernetes Gateway CR's in our cluster.
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/releases/download/v1.2.0/standard-install.yaml
You can use the above command to install it in your cluster. I use Talos to setup k8s on my end. You can also create a sample Talos cluster using docker.
Moving on we are going to use Helm to test things out. Here we're adding the Gloo Open Source Repository.
helm repo add gloo https://storage.googleapis.com/solo-public-helm
helm repo update
Then we can install the helm chart using
helm install -n gloo-system gloo gloo/gloo \
--create-namespace \
--version 1.18.13 \
-f -<You should see something like this
NAME: gloo
LAST DEPLOYED: Mon Mar 31 12:38:09 2025
NAMESPACE: gloo-system
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
Once we have this the GatewayClass should be able to see Gloo Edge
kubectl get gatewayclass gloo-gateway
NAME CONTROLLER ACCEPTED AGE
gloo-gateway solo.io/gloo-gateway True 25m
Now that we have this let's create a Gateway
kubectl apply -n gloo-system -f- <<EOF
kind: Gateway
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: http
spec:
gatewayClassName: gloo-gateway
listeners:
- protocol: HTTP
port: 8080
name: http
allowedRoutes:
namespaces:
from: All
EOF
Once we apply this we can check if the gateway is now created.
I also wanted to see how this looks by default, we have quite a lot of information here.
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2025-03-31T07:21:45Z"
generation: 1
name: http
namespace: gloo-system
resourceVersion: "75078"
uid: 68dfe16f-12ef-4bfc-b20a-0515826721be
spec:
gatewayClassName: gloo-gateway
listeners:
- allowedRoutes:
namespaces:
from: All
name: http
port: 8080
protocol: HTTP
status:
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2025-03-31T07:21:45Z"
message: ""
observedGeneration: 1
reason: Accepted
status: "True"
type: Accepted
- lastTransitionTime: "2025-03-31T07:21:45Z"
message: ""
observedGeneration: 1
reason: Programmed
status: "True"
type: Programmed
listeners:
- attachedRoutes: 0
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2025-03-31T07:21:45Z"
message: ""
observedGeneration: 1
reason: Accepted
status: "True"
type: Accepted
- lastTransitionTime: "2025-03-31T07:21:45Z"
message: ""
observedGeneration: 1
reason: NoConflicts
status: "False"
type: Conflicted
- lastTransitionTime: "2025-03-31T07:21:45Z"
message: ""
observedGeneration: 1
reason: ResolvedRefs
status: "True"
type: ResolvedRefs
- lastTransitionTime: "2025-03-31T07:21:45Z"
message: ""
observedGeneration: 1
reason: Programmed
status: "True"
type: Programmed
name: http
supportedKinds:
- group: gateway.networking.k8s.io
kind: HTTPRoute
Now it's time to run some sample apps and test the gateway.
kubectl create ns httpbin
kubectl -n httpbin apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/solo-io/gloo-mesh-use-cases/main/policy-demo/httpbin.yaml
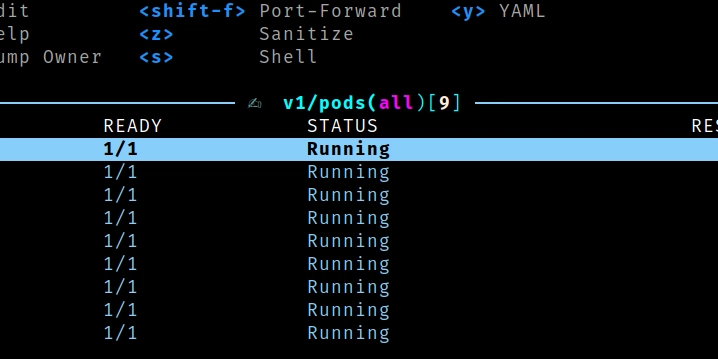
kubectl -n httpbin get pods
Now in order to expose the application, we have to create a HTTPRoute resource.
By definition
HTTPRoute is a Gateway API type for specifying routing behavior of HTTP requests from a Gateway listener to an API object, i.e. Service.
So if we have a service we can route to it using the HTTPRoute
The specification of an HTTPRoute consists of:
ParentRefs- Define which Gateways this Route wants to be attached to.
Hostnames (optional)- Define a list of hostnames to use for matching the Host header of HTTP requests.
Rules- Define a list of rules to perform actions against matching HTTP requests. Each rule consists of matches, filters (optional), backendRefs (optional), timeouts (optional), and name (optional) fields.
(Taken from the official spec)
Back to our setup we can now setup the HTTPRoute
kubectl apply -f- <We can then check how this now looks in the cluster
kubectl get -n httpbin httproute/httpbin -o yaml
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2025-03-31T07:44:46Z"
generation: 1
labels:
example: httpbin-route
name: httpbin
namespace: httpbin
resourceVersion: "76943"
uid: e0f81d5a-7377-4bda-bae1-ce5f36031251
spec:
hostnames:
- www.example.com
parentRefs:
- group: gateway.networking.k8s.io
kind: Gateway
name: http
namespace: gloo-system
rules:
- backendRefs:
- group: ""
kind: Service
name: httpbin
port: 8000
weight: 1
matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /
status:
parents:
- conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2025-03-31T07:44:47Z"
message: ""
observedGeneration: 1
reason: Accepted
status: "True"
type: Accepted
- lastTransitionTime: "2025-03-31T07:44:47Z"
message: ""
observedGeneration: 1
reason: ResolvedRefs
status: "True"
type: ResolvedRefs
controllerName: solo.io/gloo-gateway
parentRef:
group: gateway.networking.k8s.io
kind: Gateway
name: http
namespace: gloo-system
To test the gateway API we are now going to port-forward our setup.
kubectl port-forward deployment/gloo-proxy-http -n gloo-system 8080:8080
Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:8080 -> 8080
Forwarding from [::1]:8080 -> 8080
And this works as expected
curl -i localhost:8080/headers -H "host: www.example.com"
Handling connection for 8080
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
access-control-allow-credentials: true
access-control-allow-origin: *
content-type: application/json; encoding=utf-8
date: Mon, 31 Mar 2025 07:48:28 GMT
content-length: 331
x-envoy-upstream-service-time: 0
server: envoy
{
"headers": {
"Accept": [
"*/*"
],
"Host": [
"www.example.com"
],
"User-Agent": [
"curl/8.12.1"
],
"X-Envoy-Expected-Rq-Timeout-Ms": [
"15000"
],
"X-Forwarded-Proto": [
"http"
],
"X-Request-Id": [
"44449e3f-2442-4899-8238-0c2f70e1ee59"
]
}
}
Now that we have the basic setup, let's try something extra with this. I like that using Gloo Gateway means that I can route to traffic that is anywhere
Let's quickly try a static upstream.
To create a Static Upstream we can do the following
kubectl apply -f- <Then let's create a RouteOption, basically you can attach RouteOption to HTTPRoute as a Filter.
kubectl apply -f- <Let's also create a HTTPRoute
kubectl apply -f- <Now let's check our HTTPRoute
kubectl get httproute -A
NAMESPACE NAME HOSTNAMES AGE
default static-upstream ["static.example"] 11s
httpbin httpbin ["www.example.com"] 8m11s
curl -ik localhost:8080/posts -H "host: static.example:8080"
Handling connection for 8080
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
date: Mon, 31 Mar 2025 07:54:29 GMT
content-type: application/json; charset=utf-8
report-to: {"group":"heroku-nel","max_age":3600,"endpoints":[{"url":"https://nel.heroku.com/reports?ts=1743243502&sid=e11707d5-02a7-43ef-b45e-2cf4d2036f7d&s=geYoiMWFeqaCuv2HSvTjAatpMYLmT8EZc0f7Dd%2FnvDw%3D"}]}
reporting-endpoints: heroku-nel=https://nel.heroku.com/reports?ts=1743243502&sid=e11707d5-02a7-43ef-b45e-2cf4d2036f7d&s=geYoiMWFeqaCuv2HSvTjAatpMYLmT8EZc0f7Dd%2FnvDw%3D
nel: {"report_to":"heroku-nel","max_age":3600,"success_fraction":0.005,"failure_fraction":0.05,"response_headers":["Via"]}
x-powered-by: Express
x-ratelimit-limit: 1000
x-ratelimit-remaining: 999
x-ratelimit-reset: 1743243543
vary: Origin, Accept-Encoding
access-control-allow-credentials: true
cache-control: max-age=43200
pragma: no-cache
expires: -1
x-content-type-options: nosniff
etag: W/"6b80-Ybsq/K6GwwqrYkAsFxqDXGC7DoM"
via: 1.1 vegur
cf-cache-status: HIT
age: 17
server: envoy
cf-ray: 928e476ddad0424e-BOM
alt-svc: h3=":443"; ma=86400
server-timing: cfL4;desc="?proto=TCP&rtt=1834&min_rtt=1834&rtt_var=917&sent=1&recv=3&lost=0&retrans=0&sent_bytes=0&recv_bytes=213&delivery_rate=0&cwnd=249&unsent_bytes=0&cid=0000000000000000&ts=0&x=0"
x-envoy-upstream-service-time: 16
transfer-encoding: chunked
[
{
"userId": 1,
"id": 1,
"title": "sunt aut facere repellat provident occaecati excepturi optio reprehenderit",
"body": "quia et suscipit\nsuscipit recusandae consequuntur expedita et cum\nreprehenderit molestiae ut ut quas totam\nnostrum rerum est autem sunt rem eveniet architecto"
},
And with that I would like to end this post, I will be testing this more, so I'll be posting about these.
































































![Nomad Goods Launches 15% Sitewide Sale for 48 Hours Only [Deal]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96899/96899/96899-640.jpg)


![Apple Watch Series 10 Prototype with Mystery Sensor Surfaces [Images]](https://www.iclarified.com/images/news/96892/96892/96892-640.jpg)

















































































































































































![[The AI Show Episode 142]: ChatGPT’s New Image Generator, Studio Ghibli Craze and Backlash, Gemini 2.5, OpenAI Academy, 4o Updates, Vibe Marketing & xAI Acquires X](https://www.marketingaiinstitute.com/hubfs/ep%20142%20cover.png)










































































































![Is this a suitable approach to architect a flutter app? [closed]](https://i.sstatic.net/4hMHGb1L.png)


















![From broke musician to working dev. How college drop-out Ryan Furrer taught himself to code [Podcast #166]](https://cdn.hashnode.com/res/hashnode/image/upload/v1743189826063/2080cde4-6fc0-46fb-b98d-b3d59841e8c4.png?#)